JAVA十大排序算法之计数排序详解
作者:阿粤Ayue
计数排序
一种非比较排序。计数排序对一定范围内的整数排序时候的速度非常快,一般快于其他排序算法。但计数排序局限性比较大,只限于对整数进行排序,而且待排序元素值分布较连续、跨度小的情况。
如果一个数组里所有元素都是整数,而且都在0-k以内。对于数组里每个元素来说,如果能知道数组里有多少项小于或等于该元素,就能准确地给出该元素在排序后的数组的位置。
如给定一个0~5范围内的数组[2,5,3,0,2,3,0,3],对于元素5为其中最大的元素,创建一个大小为(5-0+1 = 6)的计数数组,如果原数组中的值对应计数数组的下标,则下标对应计数数组的值加1。
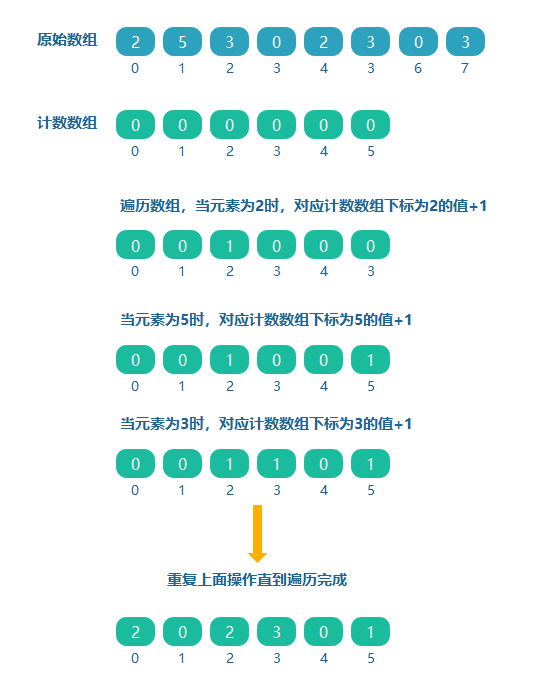
问题
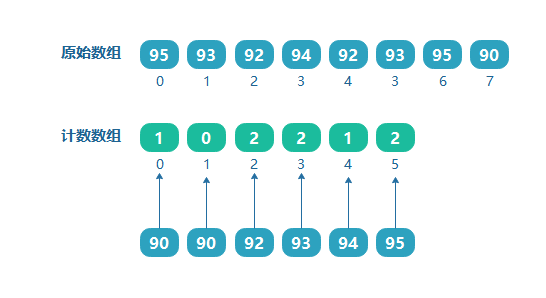
上面是通过数组的最大值来确定计数数组的长度的,但如果需要对学生的成绩进行排序,如学生成绩为:[95,93,92,94,92,93,95,90],如果按照上面的方法来处理,则需要一个大小为100的数组,但是可以看到其中的最小值为90,那也就是说前面 0~89 的位置都没有数据存放,造成了资源浪费。
如果我们知道了数组的最大值和最小值,则计数数组的大小为(最大值 - 最小值 + 1),如上面数组的最大值为99,最小值为90,则定义计数数组的大小为(95 - 90 + 1 = 6)。并且索引分别对应原数组9095的值。我们把090的范围用一个偏移量来表示,即最小值90就是这个偏移量。
代码实现
public class CountSort {
public static final int[] ARRAY = {2, 5, 3, 0, 2, 3, 0, 3};
public static final int[] ARRAY2 = {95,93,92,94,92,93,95,90};
//优化前
private static int[] sort(int[] array) {
if (array.length < 2) return array;
//找出数组的最大值
int max = array[0];
for (int i : array) {
if (i > max) {
max = i;
}
}
//初始化一个计数数组且值为0
int[] countArray = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < countArray.length; i++) {
countArray[i] = 0;
}
//填充计数数组
for (int temp : array) {
countArray[temp]++;
}
int o_index = 0;//原数组下标
int n_index = 0;//计数数组下标
while (o_index < array.length) {
//只要计数数组的下标不为0,就将计数数组的值从新写回原数组
if (countArray[n_index] != 0) {
array[o_index] = n_index;//计数数组下标对应元素组的值
countArray[n_index]--;//计数数组的值要-1
o_index++;
} else {
n_index++;//上一个索引的值为0后开始下一个
}
}
return array;
}
//优化后
private static int[] sort2(int[] array) {
if (array.length < 2) return array;
//找出数组中的最大值和最小值
int min = array[0], max = array[0];
for (int i : array) {
if (i > max) {
max = i;
}
if (i < min) {
min = i;
}
}
//定义一个偏移量,即最小值前面0~min的范围,这里直接用一个负数来表示
int bias = 0 - min;
//初始化一个计数数组且值为0
int[] countArray = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < countArray.length; i++) {
countArray[i] = 0;
}
for (int temp : array) {
countArray[temp + bias]++;
}
//填充计数数组
int o_index = 0;//原数组下标
int n_index = 0;//计数数组下标
while (o_index < array.length) {
if (countArray[n_index] != 0) {
array[o_index] = n_index - bias;
countArray[n_index]--;
o_index++;
} else {
n_index++;
}
}
return array;
}
public static void print(int[] array) {
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
print(ARRAY);
System.out.println("============================================");
print(sort(ARRAY));
System.out.println("=================优化排序====================");
print(ARRAY2);
System.out.println("============================================");
print(sort2(ARRAY2));
}
}
时间复杂度
很明显,在排序过程中,我们至少遍历了三次原始数组,一次计数数组,所以它的复杂度为Ο(n+m)。因此,计数排序比任何排序都要块,这是一种牺牲空间换取时间的做法,因为排序过程中需要用一个计数数组来存元素组的出现次数。
算法稳定性
在新建的计数数组中记录原始数组中每个元素的数量,如果原始数组有相同的元素,则在输出时,无法保证元素原来的排序,是一种不稳定的排序算法。
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注脚本之家的更多内容!
