Python中字符串的常用方法总结
作者:Mrwhite86
1、strip()、lstrip()、rstrip()
作用:去除两边空格、左边空格、右边空格
s = " abcd "
print("|"+s.strip()+"|")
print("|"+s.lstrip()+"|")
print("|"+s.rstrip()+"|")查看运行结果:

2、removeprefix()、removesuffix()
作用:移除前缀、移除后缀
s = "hello:world"
print(s.removeprefix("hello"))
print(s.removesuffix("world"))查看运行结果:

3、replace()
作用:替换字符串中的内容替换成指定的内容
s = "hello:world"
s = s.replace(":", "-")
print(s)查看运行结果:

4、split()、rsplit()
作用:从左边起根据对用的内容分割字符串、从右边起根据对用的内容分割字符串(当指定字符串的分隔次数时存在区别)
s = "hello:world:ok"
print(s.split(":"))
print(s.rsplit(":"))
print(s.split(":", maxsplit=1))
print(s.rsplit(":", maxsplit=1))查看运行结果:

5、join()
作用:将括号内的元素(均需要满足字符串格式)合并成一个新的字符串,已join前的字符作为分隔符
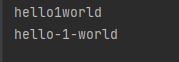
l = ["hello", "1", "world"]
print("".join(l))
print("-".join(l))查看运行结果:
6、upper()、lower()、capitalize()
作用:将所有字母转为大写、将所有字母转为小写、将首字母转为大写
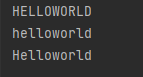
s = "helloWORLD" print(s.upper()) print(s.lower()) print(s.capitalize())
查看运行结果:
7、islower()、isupper()、isalpha()、isnumeric()、isalnum()
作用:检查字符串中字母是否都为小写、检查字符串中字母是否都为大写、检查字符串中字符是否都是字母、检查字符串中字符是否都是数字、检查所有的字符串是否都是数字或字母
s1 = "helloworld" s2 = "OK" s3 = "hello OK" s4 = "567" s5 = "hello123" print(s1.islower()) print(s2.isupper()) print(s3.islower(), s3.isupper()) print(s1.isalpha()) print(s4.isnumeric()) print(s5.isalpha(), s5.isnumeric()) print(s5.isalnum()) print(s3.isalnum())
查看运行结果:

8、count()
作用:返回指定内容在字符串中出现的次数
s = "hello world"
print(s.count("o"))查看运行结果:

9、find()、rfind()
作用:返回字符串中是否包含指定内容的索引信息(从左边开始第一个出现的),不包含时返回-1、返回字符串中是否包含指定内容的索引信息(从右边开始第一个出现的),不包含时返回-1
s = "hello world"
print(s.find("x"))
print(s.find("o"))
print(s.rfind("o"))查看运行结果:

10、startswith()、endswith()
作用:检查字符串是否是以指定内容开头、检查字符串是否是以指定内容结束
s = "hello world"
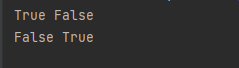
print(s.startswith("h"), s.endswith("h"))
print(s.startswith("d"), s.endswith("d"))查看运行结果:
11、partition()
作用:有点像find()和split()的结合体。将字符串根据指定的内容拆分为三个元素的元祖,其中第二个元素为指定的内容,如果不包含指定的内容的话,返回的第一个元素为原字符串
s = "hello world"
print(s.partition(" "))
print(s.partition("hello"))
print(s.partition("123"))查看运行

12、center()、ljust()、rjust()
作用:
返回一个原字符串居中,并使用指定内容(默认为空格)填充至长度width的新字符串
返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用指定内容(默认为空格)填充至长度width的新字符串
返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用指定内容(默认为空格)填充至长度width的新字符串。
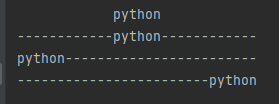
s = "python" print(s.center(30)) print(s.center(30, "-")) print(s.ljust(30, "-")) print(s.rjust(30, "-"))
查看运行结果:
13、字符串专用f表达式
作用:是格式化字符串的新语法,更易读,更简洁,不易出错,而且速度更快!需要python3.6+的版本支持
name = "bk"
age = 15
print(f"my name is {name},and i am {age} years old!")查看运行结果:

14、swapcase()
作用:翻转字符串中的字母大小写
name = "My Name is Mr.white" print(name.swapcase())
查看运行结果:

15、zfill()
作用:返回长度为width的字符串,原字符串string右对齐,前面填充0
print("100".zfill(5))
print("+100".zfill(5))
print("-100".zfill(5))
print("+0010".zfill(5))查看运行结果:

到此这篇关于Python中字符串的常用方法总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python字符串方法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
