pytorch K折交叉验证过程说明及实现方式
作者:Foneone
这篇文章主要介绍了pytorch K折交叉验证过程说明及实现方式,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教
K折交叉交叉验证的过程如下
以200条数据,十折交叉验证为例子,十折也就是将数据分成10组,进行10组训练,每组用于测试的数据为:数据总条数/组数,即每组20条用于valid,180条用于train,每次valid的都是不同的。
(1)将200条数据,分成按照 数据总条数/组数(折数),进行切分。然后取出第i份作为第i次的valid,剩下的作为train
(2)将每组中的train数据利用DataLoader和Dataset,进行封装。
(3)将train数据用于训练,epoch可以自己定义,然后利用valid做验证。得到一次的train_loss和 valid_loss。
(4)重复(2)(3)步骤,得到最终的 averge_train_loss和averge_valid_loss
上述过程如下图所示:

上述的代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader,Dataset
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
#####构造的训练集####
x = torch.rand(100,28,28)
y = torch.randn(100,28,28)
x = torch.cat((x,y),dim=0)
label =[1] *100 + [0]*100
label = torch.tensor(label,dtype=torch.long)
######网络结构##########
class Net(nn.Module):
#定义Net
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:]
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
##########定义dataset##########
class TraindataSet(Dataset):
def __init__(self,train_features,train_labels):
self.x_data = train_features
self.y_data = train_labels
self.len = len(train_labels)
def __getitem__(self,index):
return self.x_data[index],self.y_data[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
########k折划分############
def get_k_fold_data(k, i, X, y): ###此过程主要是步骤(1)
# 返回第i折交叉验证时所需要的训练和验证数据,分开放,X_train为训练数据,X_valid为验证数据
assert k > 1
fold_size = X.shape[0] // k # 每份的个数:数据总条数/折数(组数)
X_train, y_train = None, None
for j in range(k):
idx = slice(j * fold_size, (j + 1) * fold_size) #slice(start,end,step)切片函数
##idx 为每组 valid
X_part, y_part = X[idx, :], y[idx]
if j == i: ###第i折作valid
X_valid, y_valid = X_part, y_part
elif X_train is None:
X_train, y_train = X_part, y_part
else:
X_train = torch.cat((X_train, X_part), dim=0) #dim=0增加行数,竖着连接
y_train = torch.cat((y_train, y_part), dim=0)
#print(X_train.size(),X_valid.size())
return X_train, y_train, X_valid,y_valid
def k_fold(k, X_train, y_train, num_epochs=3,learning_rate=0.001, weight_decay=0.1, batch_size=5):
train_loss_sum, valid_loss_sum = 0, 0
train_acc_sum ,valid_acc_sum = 0,0
for i in range(k):
data = get_k_fold_data(k, i, X_train, y_train) # 获取k折交叉验证的训练和验证数据
net = Net() ### 实例化模型
### 每份数据进行训练,体现步骤三####
train_ls, valid_ls = train(net, *data, num_epochs, learning_rate,\
weight_decay, batch_size)
print('*'*25,'第',i+1,'折','*'*25)
print('train_loss:%.6f'%train_ls[-1][0],'train_acc:%.4f\n'%valid_ls[-1][1],\
'valid loss:%.6f'%valid_ls[-1][0],'valid_acc:%.4f'%valid_ls[-1][1])
train_loss_sum += train_ls[-1][0]
valid_loss_sum += valid_ls[-1][0]
train_acc_sum += train_ls[-1][1]
valid_acc_sum += valid_ls[-1][1]
print('#'*10,'最终k折交叉验证结果','#'*10)
####体现步骤四#####
print('train_loss_sum:%.4f'%(train_loss_sum/k),'train_acc_sum:%.4f\n'%(train_acc_sum/k),\
'valid_loss_sum:%.4f'%(valid_loss_sum/k),'valid_acc_sum:%.4f'%(valid_acc_sum/k))
#########训练函数##########
def train(net, train_features, train_labels, test_features, test_labels, num_epochs, learning_rate,weight_decay, batch_size):
train_ls, test_ls = [], [] ##存储train_loss,test_loss
dataset = TraindataSet(train_features, train_labels)
train_iter = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True)
### 将数据封装成 Dataloder 对应步骤(2)
#这里使用了Adam优化算法
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=net.parameters(), lr= learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter: ###分批训练
output = net(X)
loss = loss_func(output,y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
### 得到每个epoch的 loss 和 accuracy
train_ls.append(log_rmse(0,net, train_features, train_labels))
if test_labels is not None:
test_ls.append(log_rmse(1,net, test_features, test_labels))
#print(train_ls,test_ls)
return train_ls, test_ls
def log_rmse(flag,net,x,y):
if flag == 1: ### valid 数据集
net.eval()
output = net(x)
result = torch.max(output,1)[1].view(y.size())
corrects = (result.data == y.data).sum().item()
accuracy = corrects*100.0/len(y) #### 5 是 batch_size
loss = loss_func(output,y)
net.train()
return (loss.data.item(),accuracy)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() ###申明loss函
k_fold(10,x,label) ### k=10,十折交叉验证上述代码中,直接按照顺序从x中每次截取20条作为valid,也可以先打乱然后在截取,这样效果应该会更好。
如下所示:
import random import torch x = torch.rand(100,28,28) y = torch.randn(100,28,28) x = torch.cat((x,y),dim=0) label =[1] *100 + [0]*100 label = torch.tensor(label,dtype=torch.long) index = [i for i in range(len(x))] random.shuffle(index) x = x[index] label = label[index]
交叉验证区分k折代码分析
from sklearn.model_selection import GroupKFold
x = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10])
y = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10])
z = np.array(['hello1','hello2','hello3','hello4','hello5','hello6','hello7','hello8','hello9','hello10'])
gkf = GroupKFold(n_splits = 5)
for i,(train_idx,valid_idx) in enumerate(list(gkf.split(x,y,z))):
#groups:object,Always ignored,exists for compatibility.
print('train_idx = ')
print(train_idx)
print('valid_idx = ')
print(valid_idx)
可以看出来首先train_idx以及valid_idx的相应值都是从中乱序提取的,其次每个相应值只提取一次,不会重复提取。
注意交叉验证的流程:这里首先放一个对应的交叉验证的图片:
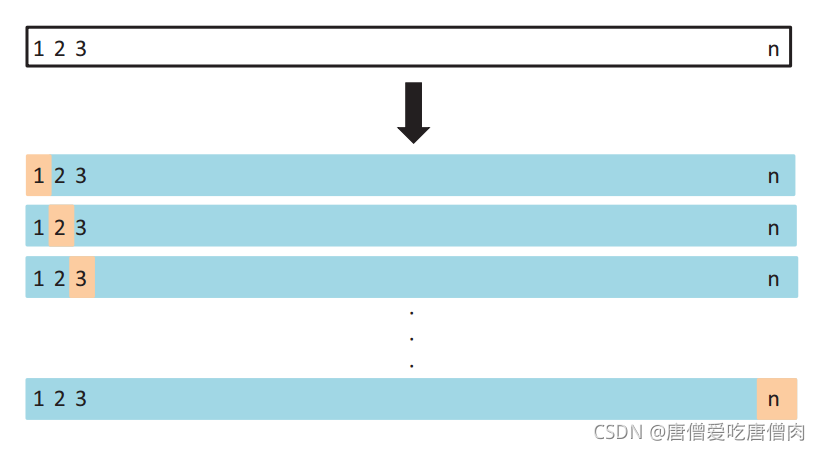
注意这里的训练方式是每个初始化的模型分别训练n折的数值,然后算出对应的权重内容
也就是说这里每一次计算对应的权重内容(1~n)的时候,需要将模型的权重初始化,然后再进行训练,训练最终结束之后,模型的权重为训练完成之后的平均值,多模类似于模型融合
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
