在android中如何用Java加载解析so
作者:小道安全
理论基础
so的加载是一种解析式装载,这与dex有一定区别,dex是先加载进行优化验证生成odex,再去解析odex文件,而so更像边解析边装载,在加载过程中主要解析是load段。
下面主要是以java层的so加载进行从源码上进行解析加载流程。
java层的so加载流程分析
System.loadLibrary入口点
在java层我们知道加载so文件是通过System.loadLibrary函数其实现的,下面就以其作为入口点进行分析它的调用关系和实现。
System.loadLibrary在的函数定义系统source\libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\lang\system.java的文件中。
下面是其函数定义实现。
//参数就是要加载的so文件名称
public static void loadLibrary(String libName) {
//通过调用Runtime下面的loadLibrary函数实现
//函数有两个参数,参数1是加载的so文件名,参数2 类加载器。
Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary(libName, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader());
}
Runtime的loadLibray解析
通过上面的System.java的loadLibrary函数我们需要继续分析Runtime.java文件中的loadLibray函数的定义实现。
Runtime的loadLibrary函数在android系统中的位置是
source\libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\lang\Runtime.java文件。
下面是Runtime的 loadLibrary函数的定义实现源码。
/*
* Searches for and loads the given shared library using the given ClassLoader.
*/
void loadLibrary(String libraryName, ClassLoader loader) {
if (loader != null) {
//通过加载器去查找要加载的so文件名
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
//查找失败
if (filename == null) {
// It's not necessarily true that the ClassLoader used
// System.mapLibraryName, but the default setup does, and it's
// misleading to say we didn't find "libMyLibrary.so" when we
// actually searched for "liblibMyLibrary.so.so".
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(loader + " couldn't find \"" +
System.mapLibraryName(libraryName) + "\"");
}
//加载so文件名
String error = doLoad(filename, loader);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
}
String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
List<String> candidates = new ArrayList<String>();
String lastError = null;
//循环遍历文件路径
for (String directory : mLibPaths) {
//文件路径和文件名进行拼接
String candidate = directory + filename;
candidates.add(candidate);
if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(candidate)) {
String error = doLoad(candidate, loader);
if (error == null) {
return; // We successfully loaded the library. Job done.
}
lastError = error;
}
}
if (lastError != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(lastError);
}
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Library " + libraryName + " not found; tried " + candidates);
}
Runtime的doLoad解析
通过上面的Runtime的loadLibrary函数,我们看到加载so的函数是走到doLoad函数,那么我们就需要继续分析Runtime下的doload函数的定义实现。
Rutime下的doload函数在系统中的
source\libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\lang\Runtime.java文件中。
下面的代码是Runtime的doload函数的定义实现。
private String doLoad(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
// Android apps are forked from the zygote, so they can't have a custom LD_LIBRARY_PATH,
// which means that by default an app's shared library directory isn't on LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
// The PathClassLoader set up by frameworks/base knows the appropriate path, so we can load
// libraries with no dependencies just fine, but an app that has multiple libraries that
// depend on each other needed to load them in most-dependent-first order.
// We added API to Android's dynamic linker so we can update the library path used for
// the currently-running process. We pull the desired path out of the ClassLoader here
// and pass it to nativeLoad so that it can call the private dynamic linker API.
// We didn't just change frameworks/base to update the LD_LIBRARY_PATH once at the
// beginning because multiple apks can run in the same process and third party code can
// use its own BaseDexClassLoader.
// We didn't just add a dlopen_with_custom_LD_LIBRARY_PATH call because we wanted any
// dlopen(3) calls made from a .so's JNI_OnLoad to work too.
// So, find out what the native library search path is for the ClassLoader in question...
String ldLibraryPath = null;
if (loader != null && loader instanceof BaseDexClassLoader) {
ldLibraryPath = ((BaseDexClassLoader) loader).getLdLibraryPath();
}
// nativeLoad should be synchronized so there's only one LD_LIBRARY_PATH in use regardless
// of how many ClassLoaders are in the system, but dalvik doesn't support synchronized
// internal natives.
synchronized (this) {
return nativeLoad(name, loader, ldLibraryPath);
}
}
总结
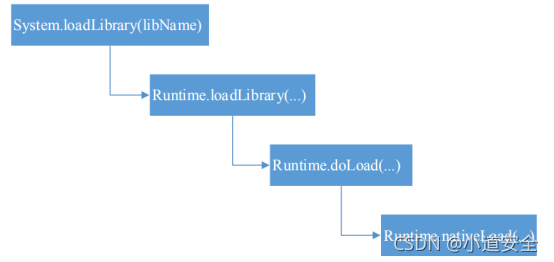
从以上的源码实现流程分析,我们可以看出Android在java层加载so的接口是System.loadLibrary(),通过层层递进关系从而实现java层的加载so。
下图是详细的java层加载so函数的调用关系。
到此这篇关于在android中如何用Java加载解析so的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android 加载so内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
