Linux下实时获取WiFi与热点状态的方法详解
作者:极地星光
在智能设备开发中,网络状态感知是基础而关键的功能,本文将手把手教你用Qt在Linux环境下实现热点和无线网络状态的检测,需要的朋友可以参考下
一、引言:为什么需要网络状态检测?
1.1 典型应用场景
在物联网和智能设备开发中,网络状态检测是基础而关键的功能。想象以下场景:
- 智能家居:当家庭WiFi断开时,智能音箱自动开启热点模式,让用户通过手机直连配置
- 工业设备:生产线设备在检测到网络异常时,自动记录状态并开启维护通道
- 移动终端:平板电脑在不同网络环境下自动调整同步策略,节省电量
1.2 技术实现目标
实现以下核心功能:
| 功能 | 描述 | 技术指标 |
|---|---|---|
| WiFi连接检测 | 判断设备是否连接到无线网络 | 响应时间<1s |
| WiFi名称获取 | 获取当前连接的无线网络SSID | 支持特殊字符 |
| 热点状态检测 | 判断设备是否处于热点模式 | 准确率100% |
| 热点名称获取 | 获取设备热点的SSID | 多编码支持 |
1.3 技术原理概述
Linux系统通过NetworkManager服务管理网络连接,提供了丰富的命令行工具:
- iwgetid:查询无线接口连接状态
- nmcli:NetworkManager的命令行接口
- hostapd:热点管理服务
Qt的QProcess类可以无缝调用这些系统命令,并通过解析输出来获取网络状态信息。
二、核心思路:结合Qt与Linux命令
2.1 技术架构设计
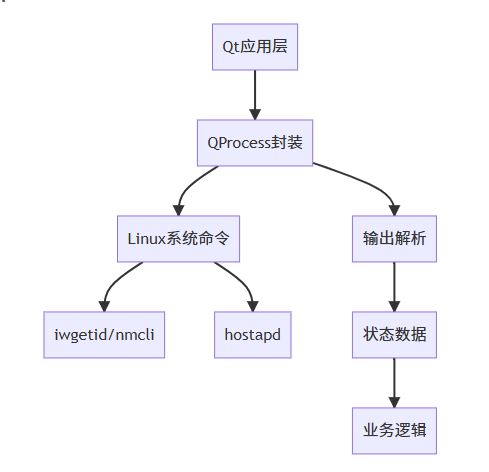
2.2 关键命令分析
检测WiFi连接状态
# 返回当前连接的SSID(无连接则返回空) iwgetid -r # 示例输出: # MyHomeWiFi
检测热点状态
# 查看活动连接中的热点 nmcli connection show --active | grep wifi | grep ap # 查看hostapd进程 pgrep hostapd
获取热点名称
# 通过nmcli获取 nmcli device wifi show | grep SSID # 通过hostapd配置获取 grep ssid= /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
2.3 性能考量
- 命令执行时间:各命令在树莓派4上的平均执行时间
iwgetid:50-100msnmcli:200-300mspgrep:10-20ms
- 优化策略:
- 缓存结果,减少命令调用
- 异步执行,避免阻塞UI
- 合理设置检测间隔(建议1-5秒)
三、详细实现:
3.1 核心类实现
NetworkTool.h
#ifndef NETWORKTOOL_H
#define NETWORKTOOL_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QProcess>
#include <QTimer>
class NetworkTool : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit NetworkTool(QObject *parent = nullptr);
// 基础检测功能
Q_INVOKABLE bool isWifiConnected();
Q_INVOKABLE QString wifiName();
Q_INVOKABLE bool isHotspotActive();
Q_INVOKABLE QString hotspotName();
// 高级功能
Q_INVOKABLE void startAutoRefresh(int interval = 3000);
Q_INVOKABLE void stopAutoRefresh();
signals:
void wifiStatusChanged(bool connected, const QString &name);
void hotspotStatusChanged(bool active, const QString &name);
private slots:
void refreshStatus();
private:
QString executeCommand(const QString &cmd, const QStringList &args = {});
QString parseWifiName(const QString &output);
QString parseHotspotName(const QString &output);
QTimer m_refreshTimer;
bool m_lastWifiState = false;
QString m_lastWifiName;
bool m_lastHotspotState = false;
QString m_lastHotspotName;
};
#endif // NETWORKTOOL_H
NetworkTool.cpp
#include "NetworkTool.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QFile>
NetworkTool::NetworkTool(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
m_refreshTimer.setSingleShot(false);
connect(&m_refreshTimer, &QTimer::timeout, this, &NetworkTool::refreshStatus);
}
bool NetworkTool::isWifiConnected()
{
return !wifiName().isEmpty();
}
QString NetworkTool::wifiName()
{
QString output = executeCommand("iwgetid", {"-r"});
return parseWifiName(output);
}
bool NetworkTool::isHotspotActive()
{
// 方法1:使用nmcli检测
QString output = executeCommand("nmcli", {"connection", "show", "--active"});
if (output.contains("wifi") && output.contains("ap")) {
return true;
}
// 方法2:检测hostapd进程
output = executeCommand("pgrep", {"hostapd"});
return !output.isEmpty();
}
QString NetworkTool::hotspotName()
{
// 尝试通过nmcli获取
QString output = executeCommand("nmcli", {"device", "wifi", "show"});
QString name = parseHotspotName(output);
if (!name.isEmpty()) return name;
// 回退到读取hostapd配置
QFile config("/etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf");
if (config.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly)) {
while (!config.atEnd()) {
QByteArray line = config.readLine().trimmed();
if (line.startsWith("ssid=")) {
return QString::fromUtf8(line.mid(5));
}
}
}
return "Unknown";
}
void NetworkTool::startAutoRefresh(int interval)
{
m_refreshTimer.start(interval);
}
void NetworkTool::stopAutoRefresh()
{
m_refreshTimer.stop();
}
void NetworkTool::refreshStatus()
{
// 获取当前状态
bool wifiConnected = isWifiConnected();
QString currentWifiName = wifiName();
bool hotspotActive = isHotspotActive();
QString currentHotspotName = hotspotName();
// 检查状态变化
if (wifiConnected != m_lastWifiState || currentWifiName != m_lastWifiName) {
m_lastWifiState = wifiConnected;
m_lastWifiName = currentWifiName;
emit wifiStatusChanged(wifiConnected, currentWifiName);
}
if (hotspotActive != m_lastHotspotState || currentHotspotName != m_lastHotspotName) {
m_lastHotspotState = hotspotActive;
m_lastHotspotName = currentHotspotName;
emit hotspotStatusChanged(hotspotActive, currentHotspotName);
}
}
QString NetworkTool::executeCommand(const QString &cmd, const QStringList &args)
{
QProcess process;
process.start(cmd, args);
if (!process.waitForFinished(1000)) {
qWarning() << "Command timeout:" << cmd << args;
return "";
}
return QString::fromUtf8(process.readAllStandardOutput()).trimmed();
}
QString NetworkTool::parseWifiName(const QString &output)
{
// iwgetid -r 直接返回SSID或空
return output;
}
QString NetworkTool::parseHotspotName(const QString &output)
{
// 解析nmcli输出中的SSID
QStringList lines = output.split('\n');
for (const QString &line : lines) {
if (line.trimmed().startsWith("SSID:")) {
return line.mid(5).trimmed();
}
}
return "";
}
3.2 UI集成示例
Qt Widgets版本
// MainWindow.h
#include <QMainWindow>
#include "NetworkTool.h"
namespace Ui { class MainWindow; }
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~MainWindow();
private slots:
void onWifiStatusChanged(bool connected, const QString &name);
void onHotspotStatusChanged(bool active, const QString &name);
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
NetworkTool m_networkTool;
};
// MainWindow.cpp
#include "MainWindow.h"
#include "ui_MainWindow.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
// 连接信号
connect(&m_networkTool, &NetworkTool::wifiStatusChanged,
this, &MainWindow::onWifiStatusChanged);
connect(&m_networkTool, &NetworkTool::hotspotStatusChanged,
this, &MainWindow::onHotspotStatusChanged);
// 启动自动刷新
m_networkTool.startAutoRefresh();
// 初始化状态
onWifiStatusChanged(m_networkTool.isWifiConnected(),
m_networkTool.wifiName());
onHotspotStatusChanged(m_networkTool.isHotspotActive(),
m_networkTool.hotspotName());
}
void MainWindow::onWifiStatusChanged(bool connected, const QString &name)
{
ui->wifiStatusLabel->setText(connected ? "已连接" : "未连接");
ui->wifiNameLabel->setText(connected ? name : "N/A");
ui->wifiIcon->setPixmap(QPixmap(connected ? ":/icons/wifi-on.png"
: ":/icons/wifi-off.png"));
}
void MainWindow::onHotspotStatusChanged(bool active, const QString &name)
{
ui->hotspotStatusLabel->setText(active ? "已开启" : "未开启");
ui->hotspotNameLabel->setText(active ? name : "N/A");
ui->hotspotIcon->setPixmap(QPixmap(active ? ":/icons/hotspot-on.png"
: ":/icons/hotspot-off.png"));
}
QML版本
// main.qml
import QtQuick 2.15
import QtQuick.Controls 2.15
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.15
ApplicationWindow {
id: window
width: 400
height: 300
visible: true
title: "网络状态监测"
NetworkTool {
id: networkTool
onWifiStatusChanged: {
wifiStatusText.text = connected ? "已连接" : "未连接"
wifiNameText.text = name || "N/A"
}
onHotspotStatusChanged: {
hotspotStatusText.text = active ? "已开启" : "未开启"
hotspotNameText.text = name || "N/A"
}
Component.onCompleted: startAutoRefresh()
}
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 20
spacing: 15
GroupBox {
title: "WiFi状态"
Layout.fillWidth: true
GridLayout {
columns: 2
width: parent.width
Label { text: "状态:" }
Label { id: wifiStatusText }
Label { text: "名称:" }
Label { id: wifiNameText }
}
}
GroupBox {
title: "热点状态"
Layout.fillWidth: true
GridLayout {
columns: 2
width: parent.width
Label { text: "状态:" }
Label { id: hotspotStatusText }
Label { text: "名称:" }
Label { id: hotspotNameText }
}
}
Button {
text: "手动刷新"
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignHCenter
onClicked: networkTool.refreshStatus()
}
}
}
四、注意事项:避坑指南
4.1 权限问题解决
常见权限错误:
nmcli报错:“权限不足”iwgetid无法获取信息
解决方案:
Polkit规则配置(推荐):
sudo nano /etc/polkit-1/rules.d/10-network-info.rules
添加内容:
polkit.addRule(function(action, subject) {
if (action.id.indexOf("org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.") == 0 &&
subject.isInGroup("users")) {
return polkit.Result.YES;
}
});
用户组配置:
sudo usermod -aG netdev,network $USER
sudo免密码(开发测试用):
echo "$USER ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/nmcli, /usr/bin/iwgetid" | sudo tee /etc/sudoers.d/network
4.2 系统兼容性处理
不同发行版适配:
| 发行版 | 检测命令 | 配置文件路径 |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu/Debian | nmcli/iwgetid | /etc/NetworkManager/ |
| CentOS/RHEL | nmcli/iw | /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ |
| Arch Linux | iw/wpa_cli | /etc/netctl/ |
兼容性代码改进:
QString NetworkTool::wifiName()
{
// 尝试iwgetid
QString output = executeCommand("iwgetid", {"-r"});
if (!output.isEmpty()) return output;
// 回退到iw命令
output = executeCommand("iw", {"dev", "wlan0", "link"});
QRegularExpression regex("SSID: (.+)");
QRegularExpressionMatch match = regex.match(output);
if (match.hasMatch()) {
return match.captured(1);
}
return "";
}
4.3 性能优化进阶
优化策略:
- 命令执行优化:
// 异步执行命令
void NetworkTool::executeCommandAsync(
const QString &cmd,
const QStringList &args,
std::function<void(QString)> callback)
{
QProcess *process = new QProcess(this);
connect(process, QOverload<int, QProcess::ExitStatus>::of(&QProcess::finished),
[=](int exitCode, QProcess::ExitStatus exitStatus){
if (exitStatus == QProcess::NormalExit) {
callback(QString::fromUtf8(process->readAllStandardOutput()));
}
process->deleteLater();
});
process->start(cmd, args);
}
- 智能刷新机制:
void NetworkTool::refreshStatus()
{
// 仅当界面可见时刷新
if (!m_windowVisible) return;
// 根据网络状态动态调整间隔
if (m_lastWifiState) {
m_refreshTimer.setInterval(5000); // 连接状态稳定时降低频率
} else {
m_refreshTimer.setInterval(1000); // 未连接时提高检测频率
}
// ...原有刷新逻辑...
}
- 结果缓存:
struct NetworkCache {
bool wifiConnected;
QString wifiName;
bool hotspotActive;
QString hotspotName;
QDateTime lastUpdated;
};
NetworkCache m_cache;
void NetworkTool::refreshCache()
{
if (m_cache.lastUpdated.secsTo(QDateTime::currentDateTime()) < 2) {
return; // 2秒内不重复更新
}
// ...更新缓存...
}
五、扩展
智能网络切换:
void autoSwitchNetwork()
{
if (!m_networkTool.isWifiConnected() &&
!m_networkTool.isHotspotActive()) {
// WiFi断开且热点未开启时,自动开启热点
QProcess::startDetached("nmcli", {
"device", "wifi", "hotspot",
"ssid", "RescueHotspot",
"password", "12345678"
});
}
}
网络质量监测:
int getWifiSignalStrength()
{
QString output = executeCommand("iwconfig", {"wlan0"});
QRegularExpression regex("Signal level=(-?\\d+) dBm");
QRegularExpressionMatch match = regex.match(output);
if (match.hasMatch()) {
return match.captured(1).toInt();
}
return 0;
}
历史状态记录:
void logNetworkStatus()
{
QFile logFile("network_status.log");
if (logFile.open(QIODevice::Append)) {
QString log = QString("%1|%2|%3|%4\n")
.arg(QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString())
.arg(m_lastWifiState)
.arg(m_lastWifiName)
.arg(m_lastHotspotState);
logFile.write(log.toUtf8());
}
}
以上就是Linux下实时获取WiFi与热点状态的方法详解的详细内容,更多关于Linux获取WiFi与热点状态的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
