pytorch中torch.cat和torch.stack的区别小结
作者:coderxiaohan
本文主要介绍pytorch中的stack和cat的区别,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
torch.cat 和 torch.stack 是 PyTorch 中用于组合张量的两个常用函数,它们的核心区别在于输入张量的维度和输出张量的维度变化。以下是详细对比:
1.torch.cat (Concatenate)
作用:沿现有维度拼接多个张量,不创建新维度
输入要求:所有张量的形状必须除拼接维度外完全相同。
语法:
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0) # dim 指定拼接的维度
示例:
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) # shape (2, 2) b = torch.tensor([[5, 6]]) # shape (1, 2) # 沿 dim=0 拼接(行方向) c = torch.cat([a, b], dim=0) print(c) # tensor([[1, 2], # [3, 4], # [5, 6]]) # shape (3, 2)
特点:
- 拼接后的张量在指定维度上的大小是输入张量该维度大小的总和。
- 其他维度必须完全一致。
2. torch.stack
作用:沿新维度堆叠多个张量,创建新维度。
输入要求:所有张量的形状必须完全相同。
语法:
torch.stack(tensors, dim=0) # dim 指定新维度的位置
示例:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2]) # shape (2,) b = torch.tensor([3, 4]) # shape (2,) # 沿新维度 dim=0 堆叠 c = torch.stack([a, b], dim=0) print(c) # tensor([[1, 2], # [3, 4]]) # shape (2, 2) # 沿新维度 dim=1 堆叠 d = torch.stack([a, b], dim=1) print(d) # tensor([[1, 3], # [2, 4]]) # shape (2, 2)
特点:
- 输出张量比输入张量多一个维度。
- 适用于将多个相同形状的张量合并为批次(如
batch_size维度)。
3. 关键区别总结
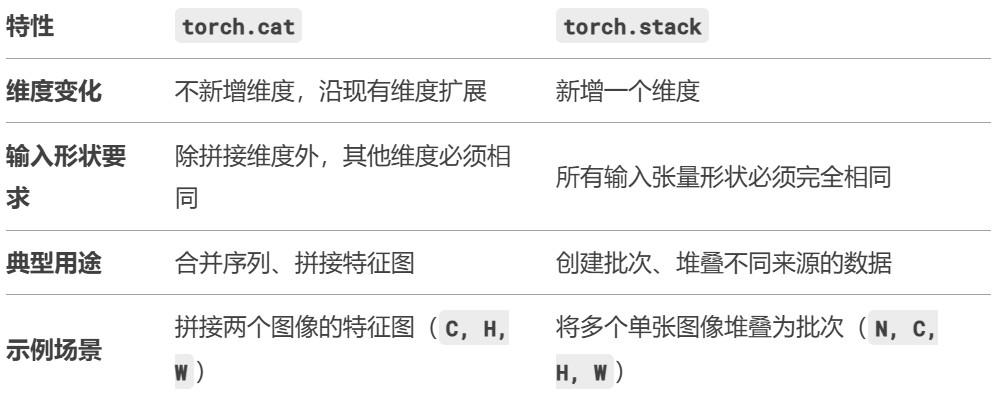
4. 直观对比示例
假设有两个张量:
x = torch.tensor([1, 2]) # shape (2,) y = torch.tensor([3, 4]) # shape (2,)
torch.cat 结果:
torch.cat([x, y], dim=0) # tensor([1, 2, 3, 4]), shape (4,)
torch.stack 结果:
torch.stack([x, y], dim=0) # tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), shape (2, 2)
5. 如何选择?
- 用
torch.cat当需要扩展现有维度(如拼接多个特征图)。 - 用
torch.stack当需要创建新维度(如构建批次数据或堆叠不同模型的输出)
通过理解两者的维度变化逻辑,可以避免常见的形状错误(如 size mismatch)。
到此这篇关于pytorch中torch.cat和torch.stack的区别小结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pytorch torch.cat和torch.stack内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
