python授权加密的几种常见方案
作者:三块钱0794
文章介绍了几种提高软件授权码安全性的方法,包括使用非对称加密、硬件绑定、时间限制、HMAC或对称加密以及使用在线授权服务器,建议企业级产品采用服务器+本地加密结合的方式,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧
要让软件授权码(License Key)更安全,并能限定服务器和使用时间,通常可以结合加密、硬件绑定和时间限制等方式来增强安全性。以下是几种常见的方案:
1. 采用非对称加密(RSA、ECC)
使用非对称加密(如 RSA、ECC)来生成和验证授权码,避免私钥泄露:
- 生成授权码时:服务器用私钥加密生成带有使用时间和设备信息的授权码;
- 客户端验证:客户端软件用公钥解密并校验授权码的有效性。
示例
- 授权码内容:
- 用 RSA 私钥加密并生成授权码
- 客户端用 RSA 公钥解密并验证有效性
2. 绑定服务器(机器)信息
防止授权码在多个设备上使用,可以绑定 硬件 ID(如 CPU ID、MAC 地址、硬盘序列号等)。
- 生成授权码时,记录服务器的唯一硬件标识
- 客户端运行时校验当前设备信息是否匹配授权码
实现方法
- 获取设备唯一 ID,例如:
- Windows:
wmic cpu get ProcessorId - Linux:
cat /etc/machine-id
- Windows:
- 生成授权码时,把硬件 ID加入授权信息
- 在客户端解密授权码后比对当前设备 ID
3. 设置时间限制(防止永久使用)
授权码应包含有效期,并防止用户篡改系统时间:
- 在授权码中嵌入到期时间,如
expire: "2025-12-31" - 服务器定期验证授权码,或者客户端检查到期时间
- 防止修改系统时间:
- 可使用 NTP 服务器获取时间
- 记录本地第一次使用的时间戳,并在下次启动时对比是否倒退
4. 使用 HMAC 或对称加密(AES)防篡改
为了防止授权码被篡改,可以使用 HMAC(哈希消息认证码) 或 AES 加密:
- HMAC 方式(SHA256):服务器用密钥签名授权码,客户端验证签名
- AES 方式:用对称密钥加密整个授权码,客户端解密后校验
验证授权码时,客户端用相同的 secret_key 计算签名并校验。
5. 结合在线授权服务器
为了更安全,可以使用在线授权服务器,客户端每次启动时需向服务器验证:
- 授权服务器存储授权码和绑定的设备信息
- 客户端每次启动时请求服务器验证授权码
- 服务器返回结果,是否授权、是否过期、是否被盗用
额外措施:
- 允许离线模式(如本地缓存授权信息)
- 服务器可吊销授权码(如检测到异常使用)
最佳方案推荐
- 本地校验:使用RSA(公私钥加密)+ HMAC(防篡改)
- 绑定设备:获取 CPU ID 或 MAC 地址,存入授权码
- 限制时间:内嵌到期时间,并校验系统时间防修改
- 服务器验证(可选):定期检查授权码状态,支持远程吊销
如果是企业级产品,建议采用服务器+本地加密结合的方式,避免破解和滥用。
上代码
管理员:
1.生成公钥私钥
import rsa
# 生成 2048 位密钥
(public_key, private_key) = rsa.newkeys(2048)
# 保存私钥(供授权中心使用)
with open("private.pem", "wb") as priv_file:
priv_file.write(private_key.save_pkcs1())
# 保存公钥(供客户端使用)
with open("public.pem", "wb") as pub_file:
pub_file.write(public_key.save_pkcs1())
print("RSA 密钥对已生成:private.pem(私钥) 和 public.pem(公钥)")2.生成授权文件
import rsa
import json
import base64
import os
from datetime import datetime
# 读取私钥
with open("private.pem", "rb") as priv_file:
private_key = rsa.PrivateKey.load_pkcs1(priv_file.read())
# 获取目标设备的 CPU ID
# def get_machine_id():
# try:
# if os.name == 'nt':
# machine_id = os.popen("wmic cpu get ProcessorId").read().split()[1]
# print('授权设备的唯一标识:'+machine_id)
# else:
# return os.popen("cat /etc/machine-id").read().strip()
# except:
# return "UNKNOWN"
# 生成授权文件
def generate_license(user, expire_date, machine_id):
license_data = {
"user": user,
"expire": expire_date,
"machine_id": machine_id
}
print(license_data)
# 签名授权数据
data_str = f"{user}|{expire_date}|{machine_id}".encode()
signature = rsa.sign(data_str, private_key, 'SHA-256')
# 添加签名并保存 JSON
license_data["signature"] = base64.b64encode(signature).decode()
with open("license.json", "w") as license_file:
json.dump(license_data, license_file, indent=4)
print("✅ 授权文件 license.json 生成成功!")
# 示例:为某个客户生成授权
generate_license(user="client1", expire_date="2025-12-31", machine_id="机器码")3.授权文件格式
{
"user": "client1",
"expire": "2025-12-31",
"machine_id": "BFE***ED",
"signature": "R62******8/w=="
}4.要被授权控制的软件
import os
import time
import threading
import json
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox, ttk
from datetime import datetime
import boto3
import configparser
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
from urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
import warnings
import base64
import logging # 添加 logging 模块
import rsa
import hashlib
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError, EndpointConnectionError
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=InsecureRequestWarning)
# ==================== 配置日志 ====================
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
filename=f'logs/file_search_{datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")}.log',
filemode='w'
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# ==================== 授权管理 ====================
LICENSE_FILE = "license.json"
PUBLIC_KEY_FILE = "public.pem"
def get_machine_id():
""" 获取当前设备的唯一标识(CPU ID)"""
try:
if os.name == 'nt':
machine_id = os.popen("wmic cpu get ProcessorId").read().split()[1]
print('获取当前设备的唯一标识:'+machine_id)
return machine_id
else:
return os.popen("cat /etc/machine-id").read().strip()
except:
return "UNKNOWN"
def load_rsa_public_key():
""" 加载 RSA 公钥 """
try:
with open(PUBLIC_KEY_FILE, "rb") as f:
return rsa.PublicKey.load_pkcs1(f.read())
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"无法加载公钥: {e}")
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "授权系统异常,无法加载公钥")
exit(1)
def verify_license():
""" 验证授权码 """
if not os.path.exists(LICENSE_FILE):
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "未找到授权文件,请联系管理员")
exit(1)
try:
with open(LICENSE_FILE, "r") as f:
license_data = json.load(f)
user = license_data.get("user")
expire = license_data.get("expire")
machine_id = license_data.get("machine_id")
signature = base64.b64decode(license_data.get("signature"))
if not all([user, expire, machine_id, signature]):
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "授权文件损坏")
exit(1)
# 校验过期时间
if datetime.strptime(expire, "%Y-%m-%d") < datetime.now():
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "授权已过期,请联系管理员续费")
exit(1)
# 校验机器码
if machine_id != get_machine_id():
print(machine_id)
print(get_machine_id())
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "设备不匹配,授权无效")
exit(1)
# 验证签名
public_key = load_rsa_public_key()
data_str = f"{user}|{expire}|{machine_id}".encode()
try:
rsa.verify(data_str, signature, public_key)
except rsa.VerificationError:
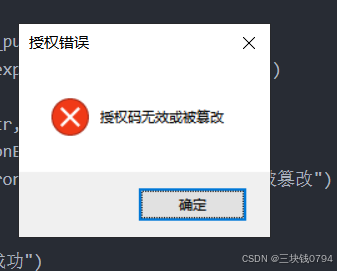
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "授权码无效或被篡改")
exit(1)
logger.info("授权验证成功")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"授权验证失败: {e}")
messagebox.showerror("授权错误", "授权文件无效")
exit(1)5.将公钥和授权json文件放在要授权的程序下

6.运行效果
python main.py
获取当前设备的唯一标识:178B****F10
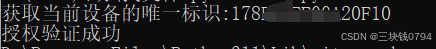
7.修改授权文件任性信息授权报错

到此这篇关于python授权加密的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python授权加密内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
