Python TensorFlow 2.6获取MNIST数据的示例代码
作者:深色風信子
这篇文章主要介绍了Python TensorFlow 2.6获取MNIST数据的的相关示例,文中有详细的代码示例供大家参考,对大家的学习或工作有一定的帮助,需要的朋友可以参考下
1 Python TensorFlow 2.6 获取 MNIST 数据
1.1 获取 MNIST 数据
获取 MNIST 数据
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets
print(tf.__version__)
(train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
np.savez('D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\mnist.npz', train_data = train_data, train_label = train_label, test_data = test_data,
test_label = test_label)
C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\python.exe E:/SourceCode/PyCharm/Test/study/exam.py 2.6.0 Process finished with exit code 0
1.2 检查 MNIST 数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
data = np.load('D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\mnist.npz')
print(data.files)
image = data['train_data'][0:100]
label = data['train_label'].reshape(-1, )
print(label)
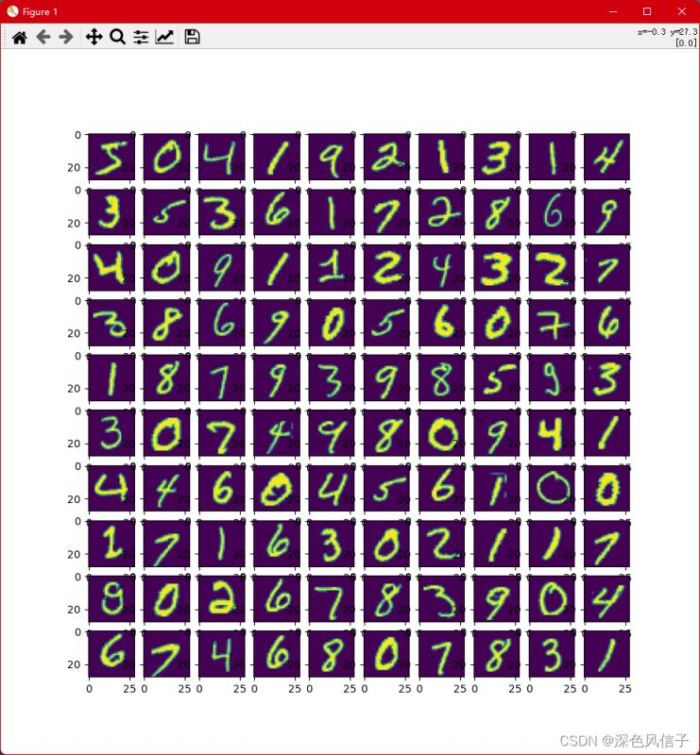
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 10))
for i in range(100):
print('%f, %f' % (i, label[i]))
plt.subplot(10, 10, i + 1)
plt.imshow(image[i])
plt.show()
2 Python 将npz数据保存为txt
import numpy as np
# 加载mnist数据
data = np.load('D:\\学习\\mnist.npz')
# 获取 训练数据
train_image = data['x_test']
train_label = data['y_test']
train_image = train_image.reshape(train_image.shape[0], -1)
train_image = train_image.astype(np.int32)
train_label = train_label.astype(np.int32)
train_label = train_label.reshape(-1, 1)
index = 0
file = open('D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\predict.txt', 'w+')
for arr in train_image:
file.write('{0}->{1}\n'.format(train_label[index][0], ','.join(str(i) for i in arr)))
index = index + 1
file.close()
3 Java 获取数据并使用SVM训练
package com.xu.opencv;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.opencv.core.Core;
import org.opencv.core.CvType;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import org.opencv.core.TermCriteria;
import org.opencv.ml.Ml;
import org.opencv.ml.SVM;
/**
* @author Administrator
*/
public class Train {
static {
System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
predict();
}
public static void predict() throws Exception {
SVM svm = SVM.load("D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\ai.xml");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\predict.txt"));
Mat train = new Mat(6, 28 * 28, CvType.CV_32FC1);
Mat label = new Mat(1, 6, CvType.CV_32SC1);
Map<String, Mat> map = new HashMap<>(2);
int index = 0;
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
int[] data = Arrays.asList(line.split("->")[1].split(",")).stream().mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 28 * 28; i++) {
train.put(index, i, data[i]);
}
label.put(index, 0, Integer.parseInt(line.split("->")[0]));
index++;
if (index >= 6) {
break;
}
}
Mat response = new Mat();
svm.predict(train, response);
for (int i = 0; i < response.height(); i++) {
System.out.println(response.get(i, 0)[0]);
}
}
public static void train() throws Exception {
SVM svm = SVM.create();
svm.setC(1);
svm.setP(0);
svm.setNu(0);
svm.setCoef0(0);
svm.setGamma(1);
svm.setDegree(0);
svm.setType(SVM.C_SVC);
svm.setKernel(SVM.LINEAR);
svm.setTermCriteria(new TermCriteria(TermCriteria.EPS + TermCriteria.MAX_ITER, 1000, 0));
Map<String, Mat> map = read("D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\data.txt");
svm.train(map.get("train"), Ml.ROW_SAMPLE, map.get("label"));
svm.save("D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\ai.xml");
}
public static Map<String, Mat> read(String path) throws Exception {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line = null;
Mat train = new Mat(60000, 28 * 28, CvType.CV_32FC1);
Mat label = new Mat(1, 60000, CvType.CV_32SC1);
Map<String, Mat> map = new HashMap<>(2);
int index = 0;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
int[] data = Arrays.asList(line.split("->")[1].split(",")).stream().mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 28 * 28; i++) {
train.put(index, i, data[i]);
}
label.put(index, 0, Integer.parseInt(line.split("->")[0]));
index++;
}
map.put("train", train);
map.put("label", label);
reader.close();
return map;
}
}
4 Python 测试SVM准确度
9.8% 求帮助
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
# 加载预测数据
data = np.load('D:\\学习\\mnist.npz')
print(data.files)
# 预测数据 处理
test_image = data['x_test']
test_label = data['y_test']
test_image = test_image.reshape(test_image.shape[0], -1)
test_image = test_image.astype(np.float32)
test_label = test_label.astype(np.float32)
test_label = test_label.reshape(-1, 1)
svm = cv.ml.SVM_load('D:\\OneDrive\\桌面\\ai.xml')
predict = svm.predict(test_image)
predict = predict[1].reshape(-1, 1).astype(np.int32)
result = (predict == test_label.astype(np.int32))
print('{0}%'.format(str(result.mean() * 100)))
C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\envs\opencv\python.exe E:/SourceCode/PyCharm/OpenCV/svm/predict.py ['x_train', 'y_train', 'x_test', 'y_test'] 9.8% Process finished with exit code 0
以上就是Python TensorFlow 2.6获取MNIST数据的示例代码的详细内容,更多关于Python TensorFlow获取MNIST的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
