Python替换字符串replace()函数使用方法详解
作者:士别三日wyx
replace() 可以「替换」字符串中的内容
语法
string.replace( old, new, count )
参数
- old :(必选,字符串类型)被替换的字符串
- new :(必选,字符串类型)替换后的字符串
- count :(可选,整型)替换的次数
返回值
- 返回替换后的新字符串
实例:将字符串中的 “hello” 替换成 “world”
str1 = 'hello hello hello hello world'
str2 = str1.replace('hello', 'world')
print(str2)输出:
world world world world world
1、不改变原字符串
因为Python中的字符串是「不可变」的,所以 replace() 不会改变原字符串的内容,而是返回一个新的字符串。
我们分别打印替换前、后的两个字符串「内容」和「内存地址」。
str1 = 'hello hello hello hello world'
print(id(str1))
str2 = str1.replace('hello', 'world')
print(str1, id(str1))
print(str2, id(str2))输出:
2834751121168
hello hello hello hello world 2834751121168
world world world world world 2834751121568
可以看到,原字符串的内容和内存地址没有发生变化。
2、指定替换次数
「不指定」次数,默认替换「所有」匹配到的字符串
str1 = 'hello_1 hello_2 hello_3 hello_4'
print(str1.replace('hello', 'world'))输出:
world_1 world_2 world_3 world_4
替换次数为「正数」时,按照从左到右的顺序替换,设置几次就替换几次
str1 = 'hello_1 hello_2 hello_3 hello_4'
print(str1.replace('hello', 'world', 1))
print(str1.replace('hello', 'world', 3))输出:
world_1 hello_2 hello_3 hello_4
world_1 world_2 world_3 hello_4
替换次数为「负数」时,无论负几,都会替换所有匹配到的内容
str1 = 'hello_1 hello_2 hello_3 hello_4'
print(str1.replace('hello', 'world', -1))
print(str1.replace('hello', 'world', -3))输出:
world_1 world_2 world_3 world_4
world_1 world_2 world_3 world_4
指定的次数必须是「整型」,否则会报错 TypeError: ‘str’ object cannot be interpreted as an integer
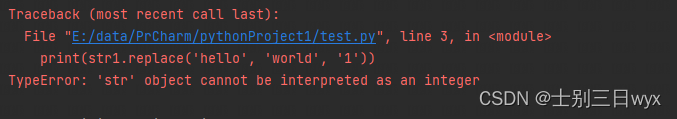
或者 TypeError: integer argument expected,

3、转义符
字符串中的转义符不会打印出来,但 replace() 可以替换这些转义符,比如替换换行符\n
str1 = 'hello world\n'
print(str1)
print(str1.replace('\n', ' new'))输出:
hello world
hello world new
从结果可以看到,替换前会换行,替换后不会换行,因为转义符被替换掉了。
4、替换列表、元组、字典的元素
对「列表」中的元素使用 replace() ,可以使用下面这种方式
arr = ['hello', 'hello', 'hello']
print([string.replace('hello', 'world') for string in arr])输出:
['world', 'world', 'world']
这种方式本质上是生成了一个「新数组」,我们可以看一下内存地址
arr = ['hello', 'hello', 'hello']
print(id(arr))
print(id([string.replace('hello', 'world') for string in arr]))输出:
1658941612416
1658941612544
或者使用「循环」的方式替换列表中的元素,这种方式不会生成新数组,替换前、后的内存地址是一样的。
arr1 = ['hello', 'hello', 'hello']
print(arr1, id(arr1))
for a in range(len(arr1)):
arr1[a] = arr1[a].replace('hello', 'world')
print(arr1, id(arr1))输出:
['hello', 'hello', 'hello'] 1672076599552
['world', 'world', 'world'] 1672076599552
替换「元祖」中的元素,需要先转成列表,再循环替换,替换完成再转回元组,这种方式同样会改变内存地址。
tu = ('hello', 'hello', 'hello')
print(id(tu))
arr1 = list(tu)
for a in range(len(arr1)):
arr1[a] = arr1[a].replace('hello', 'world')
tu = tuple(arr1)
print(tu, id(tu))输出:
2255689005696
('world', 'world', 'world') 2255689005824
替换「字典」的值,直接循环替换
dic = {'key1': 'zhangsan', 'key2': 'lisi'}
for a in dic:
dic[a] = dic[a].replace('zhangsan', 'new')
print(dic)输出:
{'key1': 'new', 'key2': 'lisi'}
5、连续替换
因为 replace() 返回的是一个字符串,所以我们可以对返回的结果再次replace(),比如下面这样:
str1 = 'zhangsan lisi wangwu'
print(str1.replace('zhangsan', 'new').replace('lisi', 'new'))输出:
new new wangwu
有多个内容需要替换时,可以使用这种简化的方式。
到此这篇关于Python替换字符串replace()函数使用方法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python replace()函数内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
