基于AOP+Redis的简易滑动窗口限流
作者:TCChzp
在分布式系统设计中,限流是保障服务稳定性的核心技术之一。滑动窗口限流算法以其精确性和平滑性优势,成为解决传统固定窗口限流临界突变问题的理想方案。本文将深入解析滑动窗口算法原理,并通过AOP+Redis滑动窗口限流。
固定窗口与滑动窗口对比
固定窗口限流及其缺陷
固定窗口限流将时间划分为固定区间(如每分钟),统计每个区间内的请求数量。这种方法虽然简单,但存在严重缺陷:
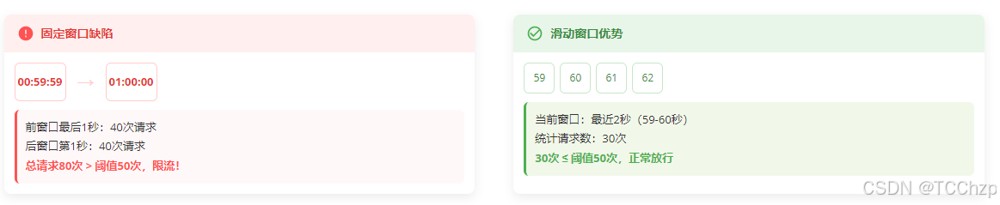
当大量请求集中在两个窗口的交界处时(如00:59:59和01:00:00),系统会在极短时间内接收双倍于阈值的请求,导致服务过载。滑动窗口限流通过动态时间区间解决了这个问题。
核心原理:为每个请求动态定义一个以当前时间为终点、向前回溯固定时长T的时间区间(滑动窗口),统计该区间内的请求数:
- 动态窗口:每个请求到达时计算
[当前时间 - T, 当前时间]区间 - 实时统计:计算该区间内的请求数量
- 决策执行:请求数 < 阈值 → 允许;否则拒绝
- 窗口滑动:过期请求自动移出统计范围
Redis实现方案
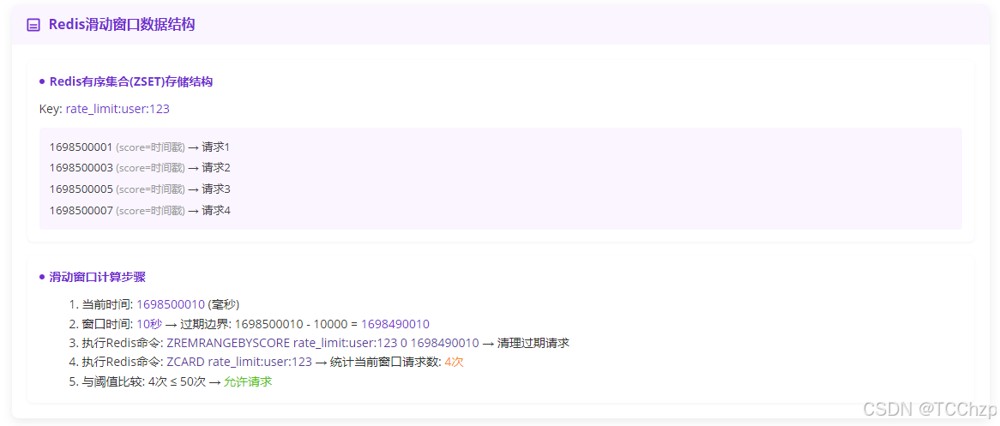
Redis的有序集合(ZSET)是实现滑动窗口限流的理想数据结构:
ZSET结合了集合(Set)和哈希(Hash)的特性:
- 唯一成员:每个成员(member)在集合中唯一
- 分数排序:每个成员关联一个分数(score),用于排序
- 自动排序:成员按分数值从小到大排序
之所以是滑动窗口限流的理想选择,关键在于它完美解决了滑动窗口算法的三个核心需求:
- 时间序列的天然支持:ZSET的分数(score)机制为时间戳提供了原生支持。当我们将请求时间戳作为score存储时,所有请求按时间顺序自动排序,形成精确的时间序列。这使得界定时间窗口边界变得简单——只需计算
当前时间 - 窗口大小就能得到窗口起始点,无需额外维护时间索引。这种设计让滑动窗口的"滑动"机制得以自然实现。 - 高效的范围操作能力:滑动窗口的核心操作是清理过期请求,ZSET的
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE命令正是为此而生。它能以O(log(N)+M)的复杂度高效删除指定时间范围外的历史请求。这种高效的范围删除能力确保了窗口滑动时的实时性能。 - 精确的实时统计特性:通过
ZCARD和ZCOUNT命令,ZSET提供原子级的精确计数能力。在滑动窗口算法中,我们需要实时统计当前窗口内的请求数并与阈值比较,这些命令能以O(1)和O(log(N))复杂度瞬间完成统计。这种即时反馈机制对高并发场景至关重要,确保限流决策的及时性和准确性。
| 命令 | 统计范围 | 时间复杂度 | 典型使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZCARD key | 整个 ZSET 的总成员数 | O(1) | 清理过期数据后快速获取当前窗口请求总数 |
| ZCOUNT key min max | 指定 score 范围内的成员数 | O(log(N)) | 动态统计子窗口/特定时间段的请求量 |
代码
自定义注解
首先自定义注解,定义限流维度、窗口大小、时间单位、窗口内最大请求数量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SlidingWindowLimit {
/**
* 限流维度的 SpEL 表达式
* 示例:
* - 按邮箱: "#email"
* - 按 IP: "#request.remoteAddr"
* - 按用户 ID + 邮箱: "#user.id + ':' + #user.email"
*/
String keySpEL() default "#email";
/**
* 窗口大小
*/
int windowSize() default 60;
/**
* 时间单位
*/
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.SECONDS;
/**
* 窗口内最大请求数
*/
int maxRequests() default 10;
}
切面类
1. 切面配置与基础结构
首先创建切面类
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20)
public class SlidingWindowLimitAspect {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SlidingWindowLimitAspect.class);
private static final String RATE_LIMIT_PREFIX = "rate_limit";
}
@Aspect:声明该类为AOP切面@Order:设置切面执行优先级(数字越小优先级越高)redissonClient:Redis客户端操作接口RATE_LIMIT_PREFIX:Redis键名前缀,用于区分限流数据
2. 切面入口方法 - around()
@Around("@annotation(slidingWindowLimit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, SlidingWindowLimit slidingWindowLimit) throws Throwable {
//获取方法签名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
String methodName = method.getName();
//判断是否为Http请求
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if(attributes == null){
log.warn("方法 {} 不在 Web 请求上下文中,跳过限流检查。", methodName);
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
try {
Object parseSpEL = parseSpEL(joinPoint, signature, slidingWindowLimit.keySpEL());
String rateLimitKey = buildRateLimitKey(parseSpEL, slidingWindowLimit);
if(isRateLimited(rateLimitKey, slidingWindowLimit.windowSize(), slidingWindowLimit.timeUnit(), slidingWindowLimit.maxRequests())){
throw new RateLimitExceededException("Rate limit exceeded");
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}catch (RateLimitExceededException e){
log.warn("方法 {} 触发了限流,已拒绝访问。", methodName);
throw e;
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("方法 {} 触发了异常,已拒绝访问。", methodName, e);
throw e;
}
}
执行过程:
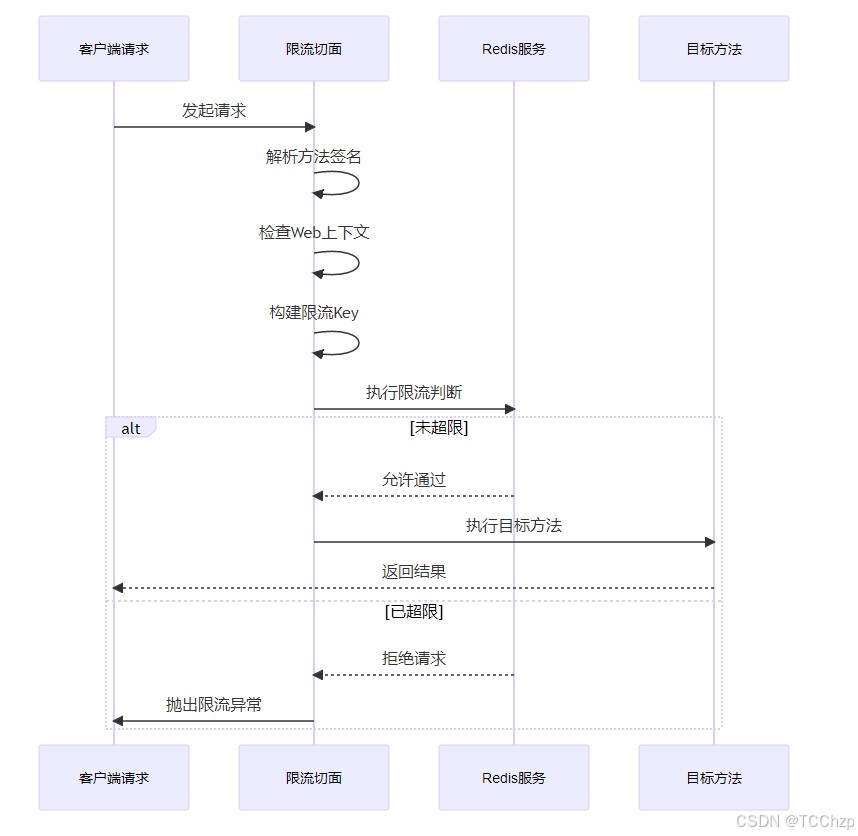
3. SpEL解析方法 - parseSpEL()
private Object parseSpEL(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,MethodSignature signature, String keySpEL){
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String[] parameterNames = signature.getParameterNames();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
if(parameterNames!=null && i< parameterNames.length){
context.setVariable(parameterNames[i], args[i]);
}else {
context.setVariable("arg" + i, args[i]);
}
}
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
return parser.parseExpression(keySpEL).getValue(context);
}
功能说明:
- 动态解析注解中的SpEL表达式(如
#email) - 将方法参数注入表达式上下文
- 支持灵活的限流键生成策略
4.限流键构建方法 - buildRateLimitKey()
private String buildRateLimitKey(Object keyValue, SlidingWindowLimit slidingWindowLimit){
if(keyValue == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("限流参数不能为空");
}
return String.format("%s:%s:%s",RATE_LIMIT_PREFIX,slidingWindowLimit.keySpEL(), keyValue);
}
键格式说明:
rate_limit:SpEL表达式:参数值 ↓ ↓ ↓ rate_limit:#email:user@example.com
5. 限流核心逻辑 - isRateLimited()
private boolean isRateLimited(String key, int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit, int maxRequests){
//获取当前时间数
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long windowStartTime = currentTime - convertToMillis(windowSize, timeUnit);
// 获取 Redisson 的 ZSet 操作对象
RScoredSortedSet<Long> scoredSortedSet = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet(key);
// 1. 删除窗口外的过期请求
scoredSortedSet.removeRangeByScore(0, true, windowStartTime, true); // [0, windowStartTime]
// 2. 添加当前请求的时间戳到 ZSet
scoredSortedSet.add(currentTime, currentTime); // score 和 value 均为时间戳
// 3. 统计窗口内请求数量
int count = scoredSortedSet.size();
return count > maxRequests;
}
Redis操作序列:
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key 0 windowStart:删除过期请求ZADD key currentTime currentTime:添加当前请求ZCARD key:获取当前请求数
6. 时间单位转换 - convertToMillis()
private long convertToMillis(int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
return switch (timeUnit) {
case SECONDS -> timeUnit.toMillis(windowSize);
case MINUTES -> timeUnit.toMillis(windowSize);
case HOURS -> timeUnit.toMillis(windowSize);
case DAYS -> timeUnit.toMillis(windowSize);
case MILLISECONDS -> windowSize;
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException("不支持的时间单位: " + timeUnit);
};
}
完整代码
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20)
public class SlidingWindowLimitAspect {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SlidingWindowLimitAspect.class);
private static final String RATE_LIMIT_PREFIX = "rate_limit";
@Around("@annotation(slidingWindowLimit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, SlidingWindowLimit slidingWindowLimit) throws Throwable {
//获取方法签名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
String methodName = method.getName();
//判断是否为Http请求
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if(attributes == null){
log.warn("方法 {} 不在 Web 请求上下文中,跳过限流检查。", methodName);
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
try {
Object parseSpEL = parseSpEL(joinPoint, signature, slidingWindowLimit.keySpEL());
String rateLimitKey = buildRateLimitKey(parseSpEL, slidingWindowLimit);
if(isRateLimited(rateLimitKey, slidingWindowLimit.windowSize(), slidingWindowLimit.timeUnit(), slidingWindowLimit.maxRequests())){
throw new RateLimitExceededException("Rate limit exceeded");
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}catch (RateLimitExceededException e){
log.warn("方法 {} 触发了限流,已拒绝访问。", methodName);
throw e;
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("方法 {} 触发了异常,已拒绝访问。", methodName, e);
throw e;
}
}
private Object parseSpEL(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,MethodSignature signature, String keySpEL){
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String[] parameterNames = signature.getParameterNames();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
if(parameterNames!=null && i< parameterNames.length){
context.setVariable(parameterNames[i], args[i]);
}else {
context.setVariable("arg" + i, args[i]);
}
}
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
return parser.parseExpression(keySpEL).getValue(context);
}
private String buildRateLimitKey(Object keyValue, SlidingWindowLimit slidingWindowLimit){
if(keyValue == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("限流参数不能为空");
}
return String.format("%s:%s:%s",RATE_LIMIT_PREFIX,slidingWindowLimit.keySpEL(), keyValue);
}
private boolean isRateLimited(String key, int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit, int maxRequests){
//获取当前时间数
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long windowStartTime = currentTime - convertToMillis(windowSize, timeUnit);
// 获取 Redisson 的 ZSet 操作对象
RScoredSortedSet<Long> scoredSortedSet = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet(key);
// 1. 删除窗口外的过期请求
scoredSortedSet.removeRangeByScore(0, true, windowStartTime, true); // [0, windowStartTime]
// 2. 添加当前请求的时间戳到 ZSet
scoredSortedSet.add(currentTime, currentTime); // score 和 value 均为时间戳
// 3. 统计窗口内请求数量
int count = scoredSortedSet.size();
return count > maxRequests;
}
/**
* 时间单位转换,将时间单位转换为毫秒数
* @param windowSize 窗口大小
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
* @return
*/
private long convertToMillis(int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit){
return switch (timeUnit){
case NANOSECONDS, SECONDS, MICROSECONDS, MINUTES, HOURS, DAYS -> timeUnit.toMillis(windowSize);
case MILLISECONDS -> windowSize;
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException("不支持的时间单位: " + timeUnit);
};
}
}
注解使用
比如说我们现在定义发送验证码的方法60秒内只能发送三次
@PostMapping("/send/code")
@SlidingWindowLimit(keySpEL = "#email.email",windowSize = 60, maxRequests = 3)
public Result sendVerificationCode(@RequestBody EmailSendDTO email) {
userService.sendVerificationCode(email.getEmail());
return Result.success();
}
每一次访问时,Redis都会记录下时间戳,如果第四次访问时的时间戳与第一次访问的时间戳之间少于60秒,则返回
{
"code": 429,
"message": "请求过于频繁,请稍后再试",
"data": null
}
优化
private boolean isRateLimited(String key, int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit, int maxRequests){
//获取当前时间数
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long windowStartTime = currentTime - convertToMillis(windowSize, timeUnit);
// 获取 Redisson 的 ZSet 操作对象
RScoredSortedSet<Long> scoredSortedSet = redissonClient.getScoredSortedSet(key);
// 1. 删除窗口外的过期请求
scoredSortedSet.removeRangeByScore(0, true, windowStartTime, true); // [0, windowStartTime]
// 2. 添加当前请求的时间戳到 ZSet
scoredSortedSet.add(currentTime, currentTime); // score 和 value 均为时间戳
// 3. 统计窗口内请求数量
int count = scoredSortedSet.size();
return count > maxRequests;
}
在这个方法中,存在几个问题:
代码中直接将时间戳作为ZSET的成员(member)和分数(score),当同一毫秒内有多个请求时,后写入的请求会覆盖先前的请求(ZSET成员唯一),导致计数不准确。
当前操作序列:
在并发场景下,多个请求可能同时通过计数检查,导致实际请求量超过阈值
- 删除过期请求
- 添加当前请求
- 获取当前计数
当某个限流键长时间无请求时,对应的空ZSET会永久占用内存
那么优化时,可以利用UUID作为member 这样不会出现覆盖的情况,使用Lua脚本进行执行避免多个请求同时通过计数检查的情况,针对问题三可以通过设置过期时间来解决,优化后的代码如下:
private boolean isRateLimited(String key, int windowSize, TimeUnit timeUnit, int maxRequests) {
// 1. 计算窗口大小(毫秒)
long windowMillis = convertToMillis(windowSize, timeUnit);
// 2. 获取当前时间和窗口起始时间
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long windowStartTime = currentTime - windowMillis;
// 3. 生成唯一请求ID
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 4. 计算过期时间(秒)
long expireSeconds = calculateExpireSeconds(windowMillis);
// 5. Lua脚本(使用分数范围精确统计)
String luaScript =
"redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', KEYS[1], '-inf', ARGV[2])\n" + // 清理过期数据
"local count = redis.call('ZCOUNT', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], ARGV[1])\n" + // 精确统计窗口内请求
"if count >= tonumber(ARGV[4]) then\n" +
" return 1\n" + // 触发限流
"end\n" +
"redis.call('ZADD', KEYS[1], ARGV[1], ARGV[3])\n" + // 添加当前请求
"redis.call('EXPIRE', KEYS[1], ARGV[5])\n" + // 设置过期时间
"return 0"; // 允许通过
try {
RScript script = redissonClient.getScript();
Long result = script.eval(
RScript.Mode.READ_WRITE,
luaScript,
RScript.ReturnType.INTEGER,
Collections.singletonList(key),
currentTime, windowStartTime, requestId, maxRequests, expireSeconds
);
return result != null && result == 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("限流服务异常,降级放行", e);
return false; // Redis故障时允许请求
}
}
private long calculateExpireSeconds(long windowMillis) {
// 过期时间 = 2 * 窗口大小(秒),向上取整
double expireSec = (windowMillis * 2.0) / 1000;
long result = (long) Math.ceil(expireSec);
return Math.max(1, result); // 至少1秒
}
Lua 脚本执行逻辑:
redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', KEYS[1], '-inf', ARGV[2]):清理过期数据,将 ZSET 中分数小于等于窗口起始时间的成员删除。local count = redis.call('ZCOUNT', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], ARGV[1]):精确统计窗口内请求数量,即分数在窗口起始时间和当前时间之间的成员数量。if count >= tonumber(ARGV[4]) then return 1 end:如果统计的请求数量大于等于阈值,则返回 1,表示触发限流。redis.call('ZADD', KEYS[1], ARGV[1], ARGV[3]):添加当前请求,将当前请求的唯一 ID 作为成员,当前时间作为分数添加到 ZSET 中。redis.call('EXPIRE', KEYS[1], ARGV[5]):设置 ZSET 的过期时间,避免长时间无请求时空 ZSET 占用内存。return 0:如果未触发限流,则返回 0,表示允许请求通过。
我们从命令行可以看到,每一次请求后,都会在ZSET中多一条记录,并且每次都会重置过期时间,当触发限流后,不再允许访问。
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com 0 -1 1) "fbd525dd-0e1e-4abf-a578-8c1207e8f6f0" 127.0.0.1:6379> TTL rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com (integer) 355 127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com 0 -1 1) "fbd525dd-0e1e-4abf-a578-8c1207e8f6f0" 2) "a7c8d5c2-f4da-46ce-9f98-472ad702e1ad" 127.0.0.1:6379> TTL rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com (integer) 355 127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com 0 -1 1) "fbd525dd-0e1e-4abf-a578-8c1207e8f6f0" 2) "a7c8d5c2-f4da-46ce-9f98-472ad702e1ad" 3) "12ed502c-6225-45bd-b85e-1d3ed9e46ef6" 127.0.0.1:6379> TTL rate_limit:#email.email:6888@example.com (integer) 355

到此这篇关于基于AOP+Redis的简易滑动窗口限流的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关AOP+Redis滑动窗口限流内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
