Java通过Caffeine和自定义注解实现本地防抖接口限流
作者:不掉头发的阿水
一、背景与需求
在实际项目开发中,经常遇到接口被前端高频触发、按钮被多次点击或者接口重复提交的问题,导致服务压力变大、数据冗余、甚至引发幂等性/安全风险。
常规做法是前端节流/防抖、后端用Redis全局限流、或者API网关限流。但在很多场景下:
- 接口只要求单机(本地)防抖,不需要全局一致性;
- 只想让同一个业务对象(同一手机号、同一业务ID、唯一标识)在自定义设置秒内只处理一次;
- 想要注解式配置,让代码更优雅、好维护。
这个时候,Caffeine+自定义注解+AOP的本地限流(防抖)方案非常合适。
二、方案设计
1. Caffeine介绍
Caffeine 是目前Java领域最热门、性能最高的本地内存缓存库,QPS可达百万级,适用于低延迟、高并发、短TTL缓存场景。
在本地限流、防抖、接口去重等方面天然有优势。
2. 自定义注解+AOP
用自定义注解(如@DebounceLimit)标记要防抖的接口,AOP切面拦截后判断是否需要限流,核心思路是:
- 以唯一标识作为key;
- 每次访问接口,先查询本地Caffeine缓存;
- 如果key在2秒内已被处理过,则直接拦截;
- 否则执行业务逻辑,并记录处理时间。
这种方式无侵入、代码简洁、可扩展性强,适合绝大多数本地场景。
效果图如下:
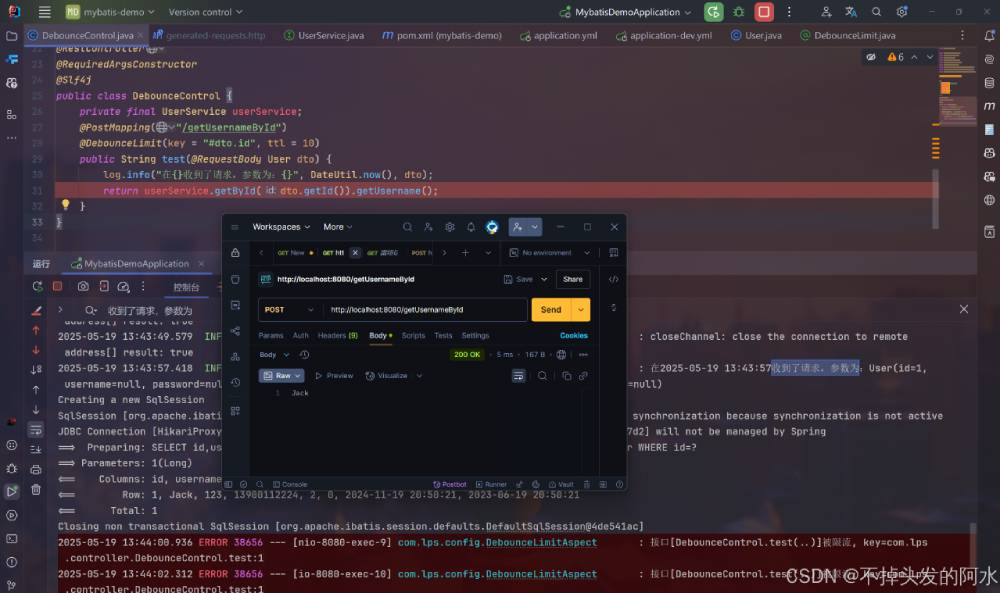
三、完整实现步骤
1.Pom依赖如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>2.9.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>2. 定义自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DebounceLimit {
/**
* 唯一key(支持SpEL表达式,如 #dto.id)
*/
String key();
/**
* 防抖时间,单位秒
*/
int ttl() default 2;
/**
* 是否返回上次缓存的返回值
*/
boolean returnLastResult() default true;
}3. 配置Caffeine缓存Bean
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Configuration
public class DebounceCacheConfig {
@Bean
public Cache<String, Object> debounceCache() {
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.maximumSize(100_000)
.build();
}
}4. 编写AOP切面
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import com.lps.anno.DebounceLimit;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class DebounceLimitAspect {
@Autowired
private Cache<String, Object> debounceCache;
private final ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
@Around("@annotation(debounceLimit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, DebounceLimit debounceLimit) throws Throwable {
// 1. 获取方法、参数
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
String[] paramNames = methodSignature.getParameterNames();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
context.setVariable(paramNames[i], args[i]);
}
// 2. 解析SpEL表达式得到唯一key
String key = parser.parseExpression(debounceLimit.key()).getValue(context, String.class);
String cacheKey = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName() + ":" + key;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
DebounceResult<Object> debounceResult = (DebounceResult<Object>) debounceCache.getIfPresent(cacheKey);
if (debounceResult != null && (now - debounceResult.getTimestamp() < debounceLimit.ttl() * 1000L)) {
String methodName = pjp.getSignature().toShortString();
log.error("接口[{}]被限流, key={}", methodName, cacheKey);
// 是否返回上次结果
if (debounceLimit.returnLastResult() && debounceResult.getResult() != null) {
return debounceResult.getResult();
}
// 统一失败响应,可自定义异常或返回结构
return new RuntimeException("操作过于频繁,请稍后再试!");
}
Object result = pjp.proceed();
debounceCache.put(cacheKey, new DebounceResult<>(result, now));
return result;
}
@Getter
static class DebounceResult<T> {
private final T result;
private final long timestamp;
public DebounceResult(T result, long timestamp) {
this.result = result;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
}
}5. 控制器里直接用注解实现防抖
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class DebounceControl {
private final UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/getUsernameById")
@DebounceLimit(key = "#dto.id", ttl = 10)
public String test(@RequestBody User dto) {
log.info("在{}收到了请求,参数为:{}", DateUtil.now(), dto);
return userService.getById(dto.getId()).getUsername();
}
}只要加了这个注解,同一个id的请求在自定义设置的秒内只处理一次,其他直接被拦截并打印日志。
四、扩展与注意事项
1.SpEL表达式灵活
可以用 #dto.id、#dto.mobile、#paramName等,非常适合多参数、复杂唯一性业务场景。
2.returnLastResult适合有“缓存返回结果”的场景
比如查询接口、表单重复提交直接复用上次的返回值。
3.本地限流仅适用于单机环境
多节点部署建议用Redis分布式限流,原理一样。
4.缓存key建议加上方法签名
避免不同接口之间key冲突。
5.Caffeine最大缓存、过期时间应根据业务并发和内存合理设置
绝大多数接口几千到几万key都没压力。
五、适用与不适用场景
适用:
- 单机接口防抖/限流
- 短时间重复提交防控
- 按业务唯一标识维度防刷
- 秒杀、报名、投票等接口本地保护
不适用:
- 分布式场景(建议用Redis或API网关限流)
- 需要全局一致性的业务
- 内存非常敏感/极端高并发下,需结合Redis做混合限流
六、总结
Caffeine + 注解 + AOP的本地限流防抖方案,实现简单、代码优雅、性能极高、扩展灵活
到此这篇关于Java通过Caffeine和自定义注解实现本地防抖接口限流的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java本地防抖接口限流内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
