如何合理管控Java语言的异常
作者:找不到、了
异常是程序运行过程中出现的错误。而异常的处理框架,是Java语言健壮性的一个重要体现。
1、介绍
Java把异常当作对象来处理,并定义一个基类java.lang.Throwable作为所有异常的超类。
异常类分为两大类,错误Error和异常Exception。Java异常体系结构呈树状,其层次结构图如图所示:
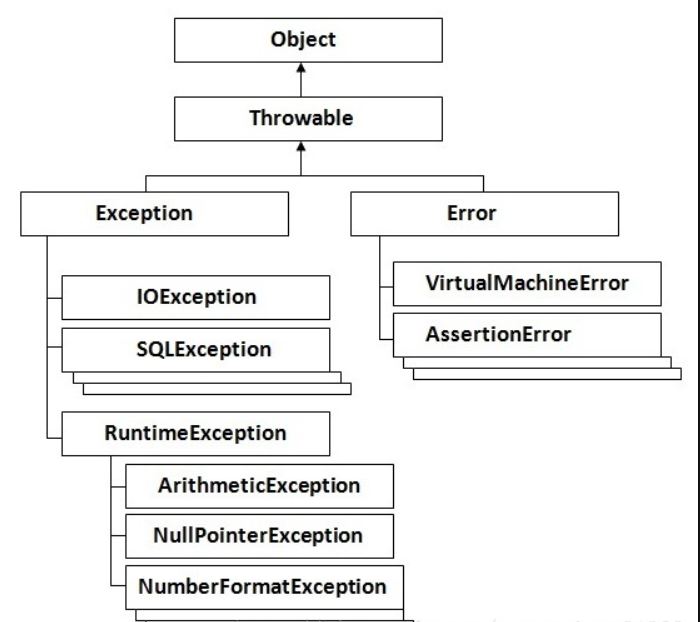
2、Thorwable类
Thorwable类所有异常和错误的超类,有两个子类Error和Exception,分别表示错误和异常。
3、Error
系统错误(system error) 是由 Java 虚拟机抛出的,用 Error 类表示。
Error 类描述的是内部系统错误,这样的错误很少发生。如果发生,除了通知用户以及尽量稳妥地终止程序外,几乎什么也不能做。

- OutOfMemoryError :内存耗尽 ;
- NoClassDefFoundError :无法加载某个Class ;
- StackOverflowError :栈溢出。
4、Exception类
异常类Exception又分为运行时异常(RuntimeException)和非运行时异常,这两种异常有很大的区别,也称之为不检查异常(Unchecked Exception)和检查异常(Checked Exception)。
4.1、检查异常
这类异常在编译时就会被编译器检查,程序必须对其进行处理(捕获或声明抛出),否则无法通过编译。常见的受检查异常有:
IOException:输入输出操作时可能出现的异常,如文件读取失败。SQLException:执行 SQL 语句时可能出现的异常。
4.2、运行时异常
这类异常在编译时不会被编译器检查,程序可以选择处理也可以不处理。常见的不受检查异常有:
NullPointerException:当尝试访问一个空对象的方法或属性时抛出。ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:当访问数组时使用的索引超出数组范围时抛出。
5、处理方式
5.1. 捕获异常
使用 try-catch 块可以捕获并处理异常。try 块中包含可能会抛出异常的代码,catch 块用于捕获并处理特定类型的异常。
public class TryCatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
// 这里会抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(numbers[3]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到数组越界异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5.2. 多重捕获
可以在一个 try 块后面跟随多个 catch 块,用于捕获不同类型的异常。
public class MultipleCatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] numbers = null;
// 这里会抛出 NullPointerException
System.out.println(numbers[0]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到数组越界异常: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到空指针异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5.3. thorws
如果一个方法可能会抛出受检查异常,但不想在该方法内部处理,可以使用 throws 关键字在方法声明中声明抛出该异常,将异常处理的责任交给调用者。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ThrowsExample {
public static void readFile() throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("nonexistent.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
readFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到文件未找到异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5.4. throw 关键字
可以使用 throw 关键字在代码中手动抛出一个异常对象。
public class ThrowExample {
public static void checkAge(int age) {
if (age < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("年龄不能为负数");
}
System.out.println("年龄合法: " + age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
checkAge(-5);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到非法参数异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5.5. finally 块
finally 块通常和 try-catch 块一起使用,无论 try 块中是否抛出异常,finally 块中的代码都会被执行。
public class FinallyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
// 这里会抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(numbers[3]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到数组越界异常: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally 块中的代码一定会执行");
}
}
}6、执行顺序
举个简单的例子,
1、在return的配合下,finally的return就是必须要执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int test = test();
System.out.println("test==="+test);
}
private static int test() {
int x = 1;
try {
x= x/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常了:x="+x);
return 2;
} finally {
return 3;
}
}
输出:
出现异常了:x=1
test===32、finally如果没有return,则判断try代码块里面是否有异常,
- 如果有,则返回catch里面return;
- 如果没有,则返回catch块里面的return;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int test = test();
System.out.println("test==="+test);
}
private static int test() {
int x = 1;
try {
x= x/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常了:x="+x);
return 2;
} finally {
// return 3;
}
}
输出:
出现异常了:x=1
test===27、常见异常
1、java.lang.NullPointerException
空指针异常;出现原因:调用了未经初始化的对象或者是不存在的对象。
public class NullArrayIterationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = null;
// 这里会抛出 NullPointerException,因为 numbers 为 null
for (int num : numbers) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}2、java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
指定的类找不到;出现原因:类的名称和路径加载错误;通常都是程序试图通过字符串来加载某个类时可能引发异常。
public class ClassNotFoundForNameExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 尝试加载一个不存在的类
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.NonExistentClass");
System.out.println("类加载成功:" + clazz.getName());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到 ClassNotFoundException: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}3、java.lang.NumberFormatException
字符串转换为数字异常;出现原因:字符型数据中包含非数字型字符。
public class StringToIntExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abc";
try {
// 尝试将非数字字符串转换为整数
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("转换后的整数: " + num);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到 NumberFormatException: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}4、java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException
数组角标越界异常,常见于操作数组对象时发生。
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
try {
// 尝试访问数组中不存在的索引位置
int element = array[10];
System.out.println("访问到的元素是: " + element);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}5、java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
方法传递参数错误。
public class CustomMethodExample {
public static void calculateArea(int length, int width) {
if (length <= 0 || width <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("长度和宽度必须为正数");
}
int area = length * width;
System.out.println("矩形的面积是: " + area);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 传入不合法的参数
calculateArea(-5, 10);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到 IllegalArgumentException: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}6、java.lang.ClassCastException
当试图将对象强制转换为它并不是的类型时会抛出该异常。
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating.");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void bark() {
System.out.println("Dog is barking.");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void meow() {
System.out.println("Cat is meowing.");
}
}
public class BasicClassCastExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Cat();
try {
// 尝试将 Cat 对象强制转换为 Dog 类型,会抛出异常
Dog dog = (Dog) animal;
dog.bark();
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
System.out.println("捕获到 ClassCastException: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}7、文件已结束异常:EOFException
当输入过程中意外到达文件末尾(EOF)或者流结束时,就会抛出这个异常。通常在使用输入流读取数据时,如果尝试读取超出流末尾的数据,就会触发该异常。
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class EOFExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.ser"))) {
while (true) {
// 尝试从文件中读取对象
Object obj = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
// 当到达文件末尾时,捕获 EOFException
System.out.println("已到达文件末尾,读取结束。");
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}8、文件未找到异常:FileNotFoundException
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class FileNotFoundExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 尝试打开一个不存在的文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("nonexistentfile.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("文件未找到: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}9、实例化异常:java.lang.InstantiationException
class AbstractClassExample {
// 这是一个抽象类
public abstract static class MyAbstractClass {
public abstract void doSomething();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 尝试实例化抽象类
MyAbstractClass obj = MyAbstractClass.class.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
System.out.println("实例化异常: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}10、UnsupportedOperationException - 不支持的操作异常
import java.util.AbstractList;
import java.util.List;
public class ImmutableListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> immutableList = new AbstractList<String>() {
@Override
public String get(int index) {
return "Element " + index;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return 10;
}
@Override
public boolean add(String s) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("此列表为不可变列表,不支持添加操作");
}
};
try {
immutableList.add("New Element");
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}总结
通过掌握 Java 的异常处理机制,可以编写出更健壮、可靠的程序,有效应对各种异常情况。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
