Java根据IP地址实现归属地获取
作者:秃了也弱了。
一、使用Ip2region离线获取
1、Ip2region简介
目前支持其他语言的查询客户端,项目地址:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region
Java版本的文档:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region/blob/master/binding/java/ReadMe.md
Ip2region是一个离线IP地址定位库和IP定位数据管理框架,10微秒级别的查询效率,提供了众多主流编程语言的 xdb 数据生成和查询客户端实现。
2、导包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.lionsoul</groupId>
<artifactId>ip2region</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
3、下载xdb文件
下载地址:https://github.com/lionsoul2014/ip2region/blob/master/data/ip2region.xdb
4、Java获取IP地址归属地
(1)完全基于文件的查询
基于文件的查询性能较差,并且Searcher类是线程不安全的。并发使用,每个线程需要创建一个独立的 searcher 对象单独使用。
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.Searcher;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SearcherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1、创建 searcher 对象,需要指定 xdb文件的位置
String dbPath = "E:\\javacodes\\ip2region.xdb";
Searcher searcher = null;
try {
searcher = Searcher.newWithFileOnly(dbPath);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("failed to create searcher with `%s`: %s\n", dbPath, e);
return;
}
// 2、查询
try {
String ip = "27.219.61.123";
long sTime = System.nanoTime();
String region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMicros((long) (System.nanoTime() - sTime));
System.out.printf("{region: %s, ioCount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getIOCount(), cost);
// {region: 中国|0|山东省|青岛市|联通, ioCount: 2, took: 408 μs}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to search", e);
}
// 3、关闭资源
searcher.close();
// 备注:并发使用,每个线程需要创建一个独立的 searcher 对象单独使用。
}
}
(2)缓存 VectorIndex 索引
我们可以提前从 xdb 文件中加载出来 VectorIndex 数据,然后全局缓存,每次创建 Searcher 对象的时候使用全局的 VectorIndex 缓存可以减少一次固定的 IO 操作,从而加速查询,减少 IO 压力。
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.Searcher;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SearcherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String dbPath = "E:\\javacodes\\SpringbootDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\ip2region.xdb";
// 1、从 dbPath 中预先加载 VectorIndex 缓存,并且把这个得到的数据作为全局变量,后续反复使用。
byte[] vIndex;
try {
vIndex = Searcher.loadVectorIndexFromFile(dbPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to load vector index from `%s`: %s\n", dbPath, e);
return;
}
// 2、使用全局的 vIndex 创建带 VectorIndex 缓存的查询对象。
Searcher searcher;
try {
searcher = Searcher.newWithVectorIndex(dbPath, vIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to create vectorIndex cached searcher with `%s`: %s\n", dbPath, e);
return;
}
// 3、查询
try {
String ip = "27.219.61.123";
long sTime = System.nanoTime();
String region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMicros((long) (System.nanoTime() - sTime));
System.out.printf("{region: %s, ioCount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getIOCount(), cost);
// {region: 中国|0|山东省|青岛市|联通, ioCount: 2, took: 408 μs}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to search", e);
}
// 4、关闭资源
searcher.close();
// 备注:每个线程需要单独创建一个独立的 Searcher 对象,但是都共享全局的制度 vIndex 缓存。
}
}
(3)缓存整个 xdb 数据
我们也可以预先加载整个 ip2region.xdb 的数据到内存,然后基于这个数据创建查询对象来实现完全基于文件的查询,类似之前的 memory search。
并发使用,用整个 xdb 数据缓存创建的查询对象可以安全的用于并发,也就是你可以把这个 searcher 对象做成全局对象去跨线程访问。
import org.lionsoul.ip2region.xdb.Searcher;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SearcherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String dbPath = "E:\\javacodes\\SpringbootDemo\\src\\main\\resources\\ip2region.xdb";
// 1、从 dbPath 加载整个 xdb 到内存。
byte[] cBuff;
try {
cBuff = Searcher.loadContentFromFile(dbPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to load content from `%s`: %s\n", dbPath, e);
return;
}
// 2、使用上述的 cBuff 创建一个完全基于内存的查询对象。
Searcher searcher;
try {
searcher = Searcher.newWithBuffer(cBuff);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to create content cached searcher: %s\n", e);
return;
}
// 3、查询
try {
String ip = "27.219.61.123";
long sTime = System.nanoTime();
String region = searcher.search(ip);
long cost = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMicros((long) (System.nanoTime() - sTime));
System.out.printf("{region: %s, ioCount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getIOCount(), cost);
// {region: 中国|0|山东省|青岛市|联通, ioCount: 0, took: 1044 μs}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("failed to search", e);
}
// 4、关闭资源 - 该 searcher 对象可以安全用于并发,等整个服务关闭的时候再关闭 searcher
// searcher.close();
// 备注:并发使用,用整个 xdb 数据缓存创建的查询对象可以安全的用于并发,也就是你可以把这个 searcher 对象做成全局对象去跨线程访问。
}
}
二、使用第三方网站在线查询
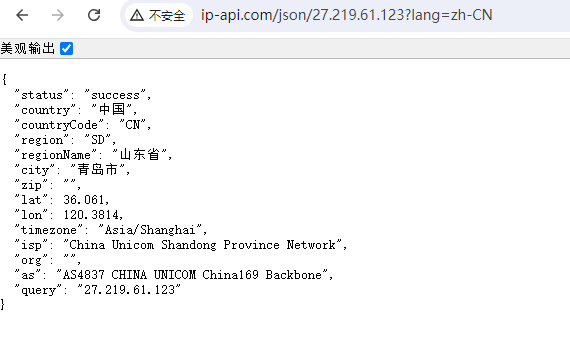
在这里推荐两个查询网站,需要手动调取API
http://ip-api.com/json/27.219.61.123?lang=zh-CN
http://whois.pconline.com.cn/ipJson.jsp?ip=27.219.61.123&json=true

以上就是Java根据IP地址实现归属地获取的详细内容,更多关于Java IP地址获取归属地的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
