SpringBoot读取配置文件的6种实现方式
作者:蓝眸少年CY
SpringBoot读取配置文件的6种方式
在SpringBoot中,可以使用以下6种方式读取 yml、properties配置:
- 使用@Value注解:读取springboot全局配置文件单个配置。
- 使用Environment接口:通过Environment接口动态获取配置。(将yml全部数据封装到Environment对象)
- 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解:在配置类上使用@ConfigurationProperties注解并指定加载配置项的前缀,就可以批量读取配置注入自定义类的成员变量中。(自定义类需要提供setter方法)
- 使用PropertySource注解:加载properties文件配置,然后在字段上使用@Value获取配置。
- 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean加载自定义yml文件,然后在字段上使用@Value获取配置。
- Java原生方式获取配置。(IO流)
1. 使用@Value注解读取单个配置
(1)编写application.yml文件配置:
student: name: 张三 age: 20
(2)使用@Value读取配置:
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class ValueTest {
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${student.age}")
private Integer age;
@Test
public void test() {
log.info("@Value 配置获取 name:{},age:{}",name,age);
}
}@Value注意事项:
@Value 注解只能读取单个配置进行赋值,无法读取整个配置文件批量赋值。当使用@Value注解读取配置时,确保配置在yml中存在,否则启动程序时就会报错。
注解中属性名引用方式如下:
@Value("${一级属性名.二级属性名...}")当使用 @Value 注解引用属性时,可以在属性名称后面使用冒号(: default-value )的形式添加默认值。
这样,如果在配置文件中找不到对应的属性,就会使用默认值。如果在配置文件中找到了属性,其值将会覆盖默认值。
//可以使用各种类型的默认值,包括字符串、数字、布尔值等
@Value("${student.name:aopmin}")
private String name;
@Value("${student.age:18}")
private Integer age;//表示一个空字符串作为默认值
@Value("${student.name:}")
private String name;@Value注解只能用于被Spring管理的Bean中使用,如使用@Component、@Service、@Controller等注解修饰的类,或者使用Java配置编写的@Configuration类中。@Value注解可以用于字段、构造函数参数、方法参数和方法上。当将它放在方法上时,Spring容器初始化时会调用该方法,并将配置属性的值作为方法的参数传递进去。
/*
@Value注解被用于构造函数参数、setter方法和普通方法上。容器初始化时,会将配置属性的值作为参数传递到构造函数、setter方法和普通方法中。
*/
@Component
public class MyBean {
private String myProperty;
@Autowired
public MyBean(@Value("${my.property}") String myProperty) {
this.myProperty = myProperty;
}
@Value("${another.property}")
public void setAnotherProperty(String anotherProperty) {
// do something with anotherProperty...
}
@Value("${yet.another.property}")
public void processValue(String value) {
// do something with value...
}
}@Value 注解不能在 static 修饰的字段上使用。因为@Value注解是通过访问Spring容器中的上下文来解析属性值并注入到目标字段中的。
由于static字段不属于对象实例,无法通过实例访问容器,所以在静态字段上使用@Value注解是无效的。
2. 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解批量绑定
(1)编写application.yml文件配置:
student: name: zhangsan age: 18
(2)使用@ConfigurationProperties批量绑定:
package cn.hk.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 参数配置类 (需要提供setter方法)
*/
//将这个类与配置文件前缀为student的配置绑定,然后把yml、properties中关于student的配置信息注入到当前类的成员变量中
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
public class StudentProperties {
private String name;
}(3)测试
@SpringBootTest
public class ConfigurationPropertiesTest {
@Autowired
private StudentProperties studentProperties;
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("读取配置: name==="+studentProperties.getName());
}
}@ConfigurationProperties注意事项:
- 确保添加了@EnableConfigurationProperties注解:为了使@ConfigurationProperties生效,需要在主配置类上添加@EnableConfigurationProperties(value=xxxxProperties.class)注解,开启@ConfigurationProperties注解自动装配功能。
- 配置文件中的属性名与类字段名的映射规则:默认情况下,@ConfigurationProperties会将配置文件中的属性名与类字段名进行映射。例如,配置文件中的属性student.name会自动映射到类字段name上。如果配置文件中的属性名与类字段名不一致,可以使用@Value注解或通过setter方法来指定映射关系。
- 类必须是Spring管理的Bean:被@ConfigurationProperties注解标记的类必须是由Spring容器管理的Bean,因此需要确保该类被@Component或其他相关注解标记,以便Spring能够扫描并创建该类的实例。
- 支持类型转换:@ConfigurationProperties支持自动类型转换,将配置文件中的字符串值转换为目标字段的类型。例如,将字符串转换为整数、布尔值等。如果无法进行类型转换,会抛出异常。
- 默认值和可选属性:可以为@ConfigurationProperties注解的字段设置默认值,以防止配置文件中缺少对应的属性。可以使用":“符号指定默认值,例如@Value(”${my.property:default-value}")。另外,可以使用required属性来指定某个属性是否为必需的。
- 配置项的验证和校验:可以使用JSR-303/349规范的注解对@ConfigurationProperties注解的字段进行验证和校验。例如,使用@NotBlank、@Min、@Max等注解来限制属性值的有效性。
3. 使用Environment动态获取配置
(1)编写application.yml文件配置:
student: name: zhangsan age: 18
(2)使用Environment动态获取配置:(将Environment对象自动装配,然后调用getProperty()方法获取指定属性值)
package cn.hk.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Environment是springboot核心的环境配置接口,它提供了一些方法用于访问应用程序配置属性。
* 包括系统属性、操作系统环境变量、命令行参数、以及配置文件中定义的属性等等
*/
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvironmentTest {
@Resource
private Environment env;
@Test
public void test() {
String name = env.getProperty("student.name");
// 逻辑处理...(也可以控制某一个bean是否生效)
log.info("Environment配置读取: name:{}", name);
}
}除了自动装配方式,也可以从spring容器中获取bean:
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvironmentTest2 implements EnvironmentAware {
private Environment env;
@Test
public void test() {
String name = env.getProperty("student.name");
log.info("Environment配置读取: name:{}", name);
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
// 逻辑处理...(也可以控制某一个bean是否生效)
this.env = environment;
}
}Aware是Spring框架提供的一组特殊接口,可以让Bean从Spring容器中拿到一些资源信息。
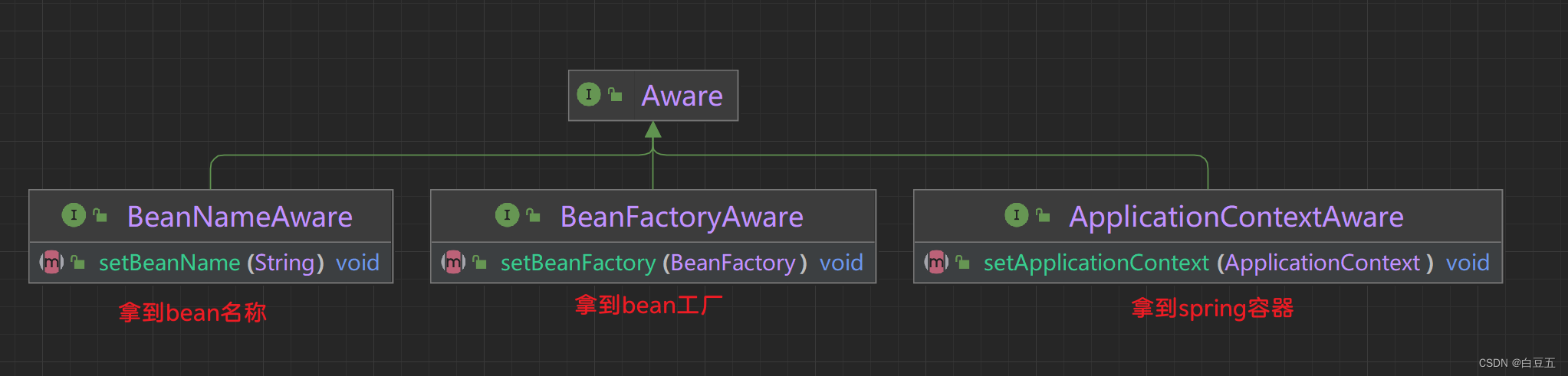
Aware接口是一种回调机制,当Bean被实例化并注册到Spring容器中时,容器会自动调用Bean中实现了特定Aware接口的方法,将相应的资源或信息传递给Bean。
以下是几个常用的Aware接口:
- ApplicationContextAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问ApplicationContext对象,从而获取Spring容器的相关信息。
- BeanFactoryAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问BeanFactory对象,从而获取Bean在容器中的相关信息。
- EnvironmentAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问Environment对象,从而获取环境相关的配置属性,比如系统属性、环境变量等。
- ResourceLoaderAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问ResourceLoader对象,从而获取资源加载器,用于加载类路径下的资源文件。
- MessageSourceAware:通过实现该接口,Bean可以访问MessageSource对象,从而获取国际化消息。
4.使用@PropertySources注解获取外部配置
前3种都是从springboot全局配置文件中获取配置,如果获取外部自定义文件就不可以啦,我们可以通过@PropertySources注解获取==.properties==文件配置。
1、在resources目录下创建student.properties文件:
student.id=1001 student.name=hello
2、在配置类中使用@PropertySources注解绑定配置:
package cn.hk.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
/**
* 绑定自定义properties配置
*/
@Data
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:student.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
public class PropertySourcesConf {
@Value("${student.id}")
private Integer id;
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
}3、测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class PropertySourcesTest {
@Resource
private PropertySourcesConf propertySourcesConf;
@Test
public void test() {
log.info("PropertySources配置读取 id: {}", propertySourcesConf.getId());
log.info("name: {}", propertySourcesConf.getName());
}
}5. 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean获取外部配置
1、编写student.yml配置:
file: type: text
2、 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer获取自定义yml文件配置:
package cn.hk.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 配置PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer读取yml配置
*/
@Configuration
public class MyYamlConfig {
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer yamlConfigurer() {
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yaml = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
yaml.setResources(new ClassPathResource("student.yml"));//自定义yml文件
//Objects.requireNonNull()方法的作用是如果对象为空,则抛出空指针异常,否则返回对象本身。
configurer.setProperties(Objects.requireNonNull(yaml.getObject()));
return configurer;
}
}3、测试
@SpringBootTest
public class LoadYamlTest {
@Value("${file.type}")
private String fileType;
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("读取yaml配置:"+fileType);
}
}6. Java原生方式获取配置
通过IO流读取配置,然后放入propertis配置对象中。
package cn.hk.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Properties;
@SpringBootTest
public class CustomTest {
@Test
public void test() {
// 配置对象
Properties props = new Properties();
InputStreamReader input = null;
try {
// 输入流 (字节流转字符流)
input = new InputStreamReader(
//通过类加载器来获取指定路径下的资源文件,并返回一个InputStream对象
this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("student.properties"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); //指定编码格式
// 加载配置
props.load(input);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (input!=null)
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取配置
System.out.println("id:" + props.getProperty("student.id") + ", name:" + props.getProperty("student.name"));
}
}总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
