Spring Bean三级缓存机制的技术指南
作者:拾荒的小海螺
1、简述
在 Spring 框架中,Bean 的创建和管理是容器的核心功能之一。为了提高性能,Spring 采用了多级缓存机制来减少不必要的对象创建和配置。特别是在 Spring 的单例 Bean 的管理中,三级缓存机制是一个非常重要的优化手段。它的目的是减少对 Bean 的多次初始化,确保线程安全,并提高应用程序的启动性能。
本文将详细介绍 Spring 中 Bean 三级缓存的实现原理,并通过代码示例帮助你理解这个机制的工作方式。
2、什么是 Spring Bean 三级缓存?
Spring 的三级缓存是 Spring 容器在创建和管理单例 Bean 时使用的一种缓存机制。它主要用于解决多线程环境下对同一个 Bean 实例化的并发问题。Spring 三级缓存分为以下三类:
- 一级缓存:存储已经完全初始化的单例 Bean。
- 二级缓存:存储已经实例化但尚未完全初始化的 Bean 实例。
- 三级缓存:存储待初始化的 Bean 代理对象,通常用于解决 Bean 循环依赖。
通过三级缓存,Spring 能够在不同阶段缓存 Bean 实例,确保 Bean 在多线程环境中的安全性,并避免重复的初始化工作。
3、Spring 三级缓存的实现机制
Spring 通过 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry 类实现了 Bean 的三级缓存。下面是三级缓存机制的具体实现流程。
- 一级缓存(singletonObjects):存放已完全初始化的单例 Bean。在 Bean 初始化完成后,会被加入一级缓存中,供后续的调用使用。
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
- 二级缓存(
earlySingletonObjects):存放已经实例化但未完全初始化的 Bean。当 Spring 处理 Bean 的依赖注入和初始化时,这些 Bean 实例会放入二级缓存。
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);
- 三级缓存(
singletonFactories):存放待初始化 Bean 的代理工厂。当遇到循环依赖时,Spring 会创建一个代理对象(通常是 CGLIB 或 JDK 动态代理)并放入三级缓存中,防止在 Bean 初始化过程中多次创建相同的对象。
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
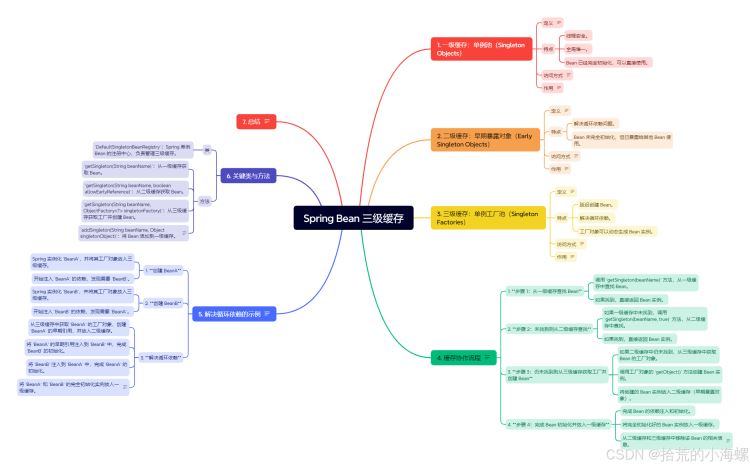
4、Spring 三级缓存的工作流程
实例化 Bean
当 Spring 容器启动时,它会根据 Bean 的配置来决定是否需要实例化该 Bean。实例化的过程是通过createBean方法来完成的。依赖注入与初始化
在实例化 Bean 后,Spring 会将 Bean 的依赖项注入到 Bean 中(即调用 Bean 的 setter 方法或构造器注入)。随后,Spring 会执行 Bean 的初始化方法。循环依赖的解决
如果 Spring 在初始化 Bean 时发现该 Bean 存在循环依赖问题(例如 A 依赖 B,B 又依赖 A),Spring 会通过三级缓存来避免重复的创建过程。具体而言,Spring 会创建一个代理 Bean,并将其放入三级缓存中,确保在循环依赖的情况下仍能顺利完成 Bean 的创建和注入。Bean 完成初始化
在 Bean 完成初始化后,它会被加入到一级缓存中,表示该 Bean 已经是一个完全初始化的对象。
以下是 Spring 中 Bean 三级缓存的实现代码示例,演示了 Spring 如何使用三级缓存来解决循环依赖问题。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SingletonBeanRegistry;
public class CustomSingletonBeanRegistry extends DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry {
@Override
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 获取 Bean 时,先尝试从一级缓存中获取
Object singleton = super.getSingleton(beanName);
if (singleton != null) {
return singleton;
}
// 若一级缓存中没有,则检查是否需要从二级缓存中获取
if (allowEarlyReference) {
singleton = earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singleton != null) {
return singleton;
}
}
// 若二级缓存中也没有,则从三级缓存(即singletonFactories)中获取
singleton = singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singleton != null) {
return singleton;
}
// 如果三级缓存中也没有,就执行标准的实例化过程
return createBean(beanName);
}
}
public class BeanLifecycleExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingletonBeanRegistry beanRegistry = new CustomSingletonBeanRegistry();
// 模拟一个循环依赖的情况:A依赖B,B依赖A
beanRegistry.registerSingleton("A", new A(beanRegistry));
beanRegistry.registerSingleton("B", new B(beanRegistry));
A aBean = (A) beanRegistry.getSingleton("A", true);
System.out.println(aBean);
}
}
class A {
private final SingletonBeanRegistry registry;
public A(SingletonBeanRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
System.out.println("A bean instantiated");
}
public void setB(B b) {
System.out.println("B injected into A");
}
}
class B {
private final SingletonBeanRegistry registry;
public B(SingletonBeanRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
System.out.println("B bean instantiated");
}
public void setA(A a) {
System.out.println("A injected into B");
}
}
在这个例子中,我们创建了 A 和 B 两个类,它们互相依赖。通过自定义 SingletonBeanRegistry 类,我们可以模拟 Spring 通过三级缓存来解决循环依赖问题。
5、三级缓存的作用与优势
减少实例化开销
Spring 通过缓存已实例化的 Bean 和未完全初始化的 Bean,避免了每次需要获取 Bean 时都重新实例化。这样可以减少大量的性能开销。解决循环依赖
通过三级缓存,Spring 能够在遇到循环依赖时,不会无限递归地创建 Bean,从而避免了死循环。三级缓存存储了 Bean 的代理对象,可以在循环依赖中起到替代作用。提高性能
通过缓存机制,Spring 能够提高 Bean 的创建效率,尤其是在高并发环境下,减少了不必要的对象创建和初始化,提高了应用程序的启动速度。
6、总结
Spring 的 Bean 三级缓存是一个关键的优化机制,旨在解决 Bean 实例化过程中的循环依赖问题,提升性能。它通过将单例 Bean 分为三级缓存(一级缓存、二级缓存、三级缓存)来减少多线程环境下的实例化开销,并确保线程安全。理解并掌握 Spring 三级缓存的实现原理,能够帮助我们更高效地使用 Spring 框架,特别是在处理复杂的依赖关系时。
以上就是Spring Bean三级缓存机制的技术指南的详细内容,更多关于Spring Bean三级缓存机制的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
