Springboot SseEmitter流式输出的实现代码
作者:专注写bug
Springboot SseEmitter流式输出
前言
最近做AI类的开发,看到各大AI模型的输出方式都是采取的一种EventStream的方式实现。
不是通常的等接口处理完成后,一次性返回。
而是片段式的处理完成一个分片,就立马告知前端做出处理;后续处理出新的片段则再次发送给客户端。
在Spring框架中就有一个类似的方式实现。SseEmitter。
SseEmitter 简介
SseEmitter 是在Spring 4.2开始引入的,使用的话需要注意版本,不过Springboot 2.X 是可以玩的。
测试demo
编写一段代码,循环返回给客户端。如下所示:
package cn.xj.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/sse/mitter")
public class SseMitterController {
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = "text/event-stream")
public SseEmitter stream() {
// 设置默认超时时间 0L 表示无限
// 注意:这里的单位是 ms
SseEmitter sseEmitter = new SseEmitter(30000L);
// 最好不要阻塞主线程
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sseEmitter.send("这只是一个流式输出案例:" + i);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
// 通知客户端消息发送完毕
sseEmitter.complete();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sseEmitter.completeWithError(e);
}
});
return sseEmitter;
}
}浏览器请求,打开控制台查看数据格式,如下所示:
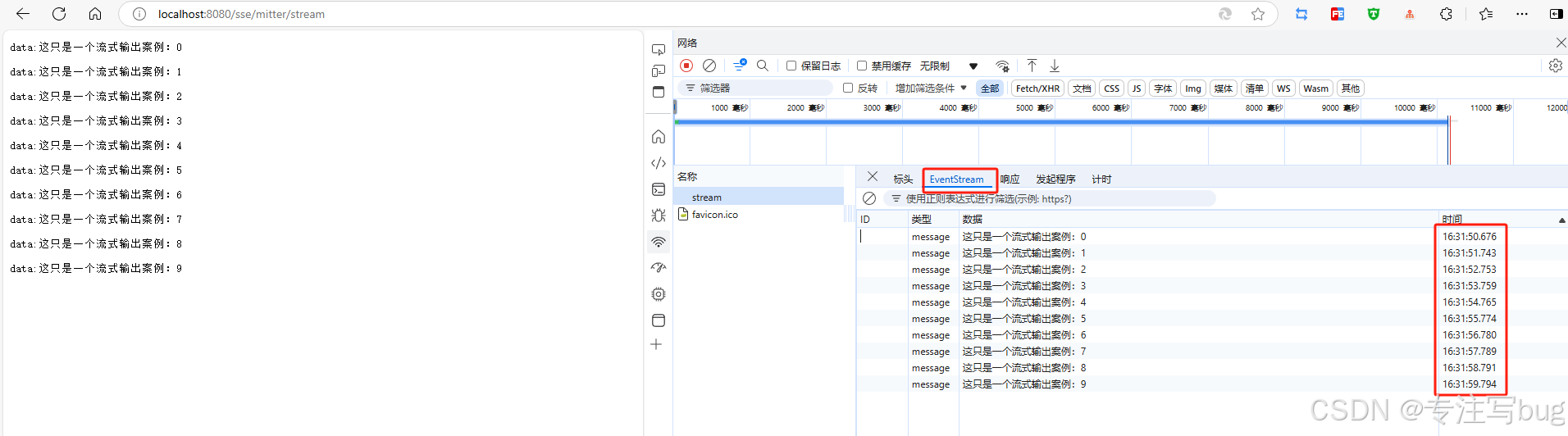
注意点
异常一 ResponseBodyEmitter is already set complete
这种问题通常是 设置超时时间timeout太小导致的。网上很多demo中说的这个单位是秒,但实际测试来看,单位应该是毫秒 ms。
补充:SpringBoot中SSE流式输出中止的核心代码
SpringBoot中SSE流式输出中止的核心代码
在大模型会话中,会有一个功能是停止生成功能。这个功能如果在前端实现,既取消监听后端的流式返回事件,会导致后端日志中报错连接中断等错误。
由此引出的需求,我的接口A中使用了sse流式返回,需要做一个接口B,B的功能是中止第一个接口的流式返回,以下是核心代码和思路:
方案一:需要借助redis,在输出时循环判定来解决。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SseEmitter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/startStreaming")
public SseEmitter startStreaming(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String requestId = request.getId(); // 获取请求的唯一标识符
String key = "shouldStopStreaming_" + requestId; // 生成唯一的key
SseEmitter emitter = new SseEmitter();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(/*输入流*/));
// SSE输出逻辑
String line;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
Boolean shouldStop = (Boolean) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (shouldStop != null && shouldStop) {
break; // 检查shouldStopStreaming标志,若为true则中断循环
}
// 发送数据给客户端
emitter.send(line);
}
// 删除key,确保不再需要该key时将其移除
redisTemplate.delete(key);
return emitter;
}
@RequestMapping("/stopStreaming")
@ResponseBody
public String stopStreaming(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestId = request.getId(); // 获取请求的唯一标识符
String key = "shouldStopStreaming_" + requestId; // 生成唯一的key
// 设置shouldStopStreaming为true,终止流式输出
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, true, 1, TimeUnit.HOURS); // 设置过期时间为1小时(可根据需要调整)
return "Streaming stopped";
}
}A接口定期从Redis中获取shouldStopStreaming的值,并检查是否应该中止流式输出。B接口使用RedisTemplate将shouldStopStreaming的值设置为true,以指示A接口中止输出。由于Redis的操作是原子性的,并且RedisTemplate提供了线程安全的访问,这样可以确保多个线程之间的协调和线程安全性。
方案二:使用本地缓存,结合SseEmitter特性实现(实际使用的此种方案)
private final Map<String, SseEmitter> sseCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(10);
## 对话接口中put一下前端随机生成的不唯一emitterId
sseCache.put(emitterId, emitter);
## 停止回答接口
@Override
public void stop(String emitterId) {
if (sseCache.containsKey(emitterId)) {
sseCache.get(emitterId).complete();
sseCache.remove(emitterId);
}
}到此这篇关于Springboot SseEmitter流式输出 的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Springboot SseEmitter流式输出 内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
