SpringBoot日志配置全过程
作者:A尘埃
SpringBoot日志配置
如果使用Spring Boot Starters,那么默认使用的日志框架是Logback。Spring Boot底层对Java Util Logging、Commons Logging、Log4J及SLF4J日志框架也进行了适配,只需相关配置就可以实现日志框架的相互切换。
SpringBoot默认日志事打印在console控制台中,不会保存到文件中。
实际项目中必须保存到文件中进行日志分析
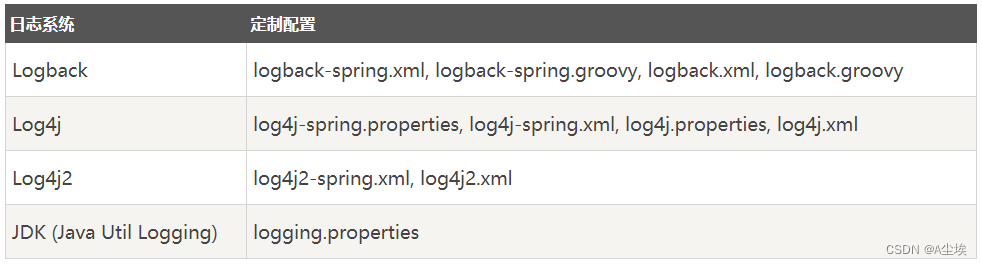
根据不同的日志系统,可以按如下规则组织配置文件名,就能被正确加载:
- Spring Boot官方推荐优先使用带有-spring的文件名作为定义的日志配置(使用logback-spring.xml而不是logback.xml名称)
- 若命名为logback-spring.xml的日志配置文件,Spring Boot可以为它添加一些Spring Boot特有的配置项
- 建议尽可能不使用Java Util Logging方式,因为Java Util Logging从可执行jar运行时会导致一些已知的类加载问题
自定义日志配置:
- 通过将相应的库添加到classpath可以激活各种日志系统
- 在classpath根目录下提供合适的配置文件可以进一步定制日志系统
- 配置文件也可以通过Spring Environment的logging.config属性指定
日志分级:(TRACE < DEBUG < INFO< WARN < ERROR < FATAL)从低到高
- TRACE,最低级别的日志记录,用于输出最详细的调试信息,通常用于开发调试目的。在生产环境中,应该关闭 TRACE 级别的日志记录,以避免输出过多无用信息
- DEBUG,是用于输出程序中的一些调试信息,通常用于开发过程中。像 TRACE 一样,在生产环境中应该关闭 DEBUG 级别的日志记录。
- INFO,用于输出程序正常运行时的一些关键信息,比如程序的启动、运行日志等。通常在生产环境中开启 INFO 级别的日志记录。
- WARN,是用于输出一些警告信息,提示程序可能会出现一些异常或者错误。在应用程序中,WARN 级别的日志记录通常用于记录一些非致命性异常信息,以便能够及时发现并处理这些问题。
- ERROR,是用于输出程序运行时的一些错误信息,通常表示程序出现了一些不可预料的错误。在应用程序中,ERROR 级别的日志记录通常用于记录一些致命性的异常信息,以便能够及时发现并处理这些问题。
Logback日志不提供FATAL级别,它被映射到ERROR级别。Spring Boot只会输出比当前级别高的日志,默认的日志级别是INFO,因此低于INFO级别的日志记录都不输出
Spring Boot中默认配置ERROR、WARN和INFO级别的日志输出到控制台。
通过启动您的应用程序—debug标志来启用“调试”模式(开发时推荐开启),以下两种方式皆可:
- 在运行命令后加入–debug标志,例如:java -jar springTest.jar --debug
- 在application.properties中配置debug=true,该属性置为true的时候,核心Logger(包含嵌入式容器、hibernate、spring)会输出更多内容,但是你自己应用的日志并不会输出为DEBUG级别。
除了这五种级别以外,还有一些日志框架定义了其他级别,例如 Python 中的 CRITICAL、PHP 中的 FATAL 等。CRITICAL 和 FATAL 都是用于表示程序出现了致命性错误或者异常,即不可恢复的错误。
使用xml配置日志保存
(并不需要pom配置slf4j依赖,使用这个默认不用配置pom依赖,最新的spring-boot-starter-web中已经集成了)
启动一个项目,直接将logback-spring.xml文件复制到resources目录下就可以实现日志文件记录。
步骤如下:
- 在项目resources目录下创建一个logback-spring.xml日志配置文件
名称只要是logback开头
备注:要配置logback-spring.xml,springboot会默认加载此文件,为什么不配置logback.xml,因为logback.xml会先application.properties加载,而logback-spring.xml会后于application.properties加载,这样我们在application.properties文中设置日志文件名称和文件路径才能生效。
- 内容如下
Spring Boot 默认日志输出如下:
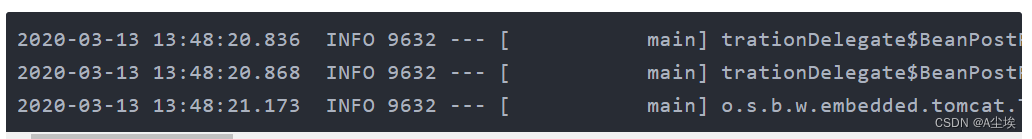
上述输出的日志信息,从左往右含义解释如下:
- 日期时间:精确到毫秒
- 日志级别:ERROR,WARN,INFO,DEBUG or TRACE
- 进程:id
- 分割符:用于区分实际的日志记录
- 线程名:括在方括号中
- 日志名字:通常是源类名
- 日志信息说明
依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId> </dependency>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="60 seconds" debug="false">
<contextName>logback</contextName>
<!--输出到控制台-->
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<!--<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg%n</pattern>
<!-- <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} -%5p ${PID:-} [%15.15t] %-30.30C{1.} : %m%n</pattern>-->
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--按天生成日志-->
<appender name="logFile" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<Prudent>true</Prudent>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<FileNamePattern>
poslog/%d{yyyy-MM-dd}/%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
</FileNamePattern>
<maxHistory>7</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<Pattern>
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger - %msg%n
</Pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="console" />
<appender-ref ref="logFile" />
</root>
</configuration>- 编写打印日志
@SpringBootTest
public class LoggerTest {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerTest.class);
@Test
public void test() {
logger.trace("trace 级别的日志");
logger.debug("debug 级别的日志");
logger.info("info 级别的日志");
logger.warn("warn 级别的日志");
logger.error("error 级别的日志");
}
}- 启动测试
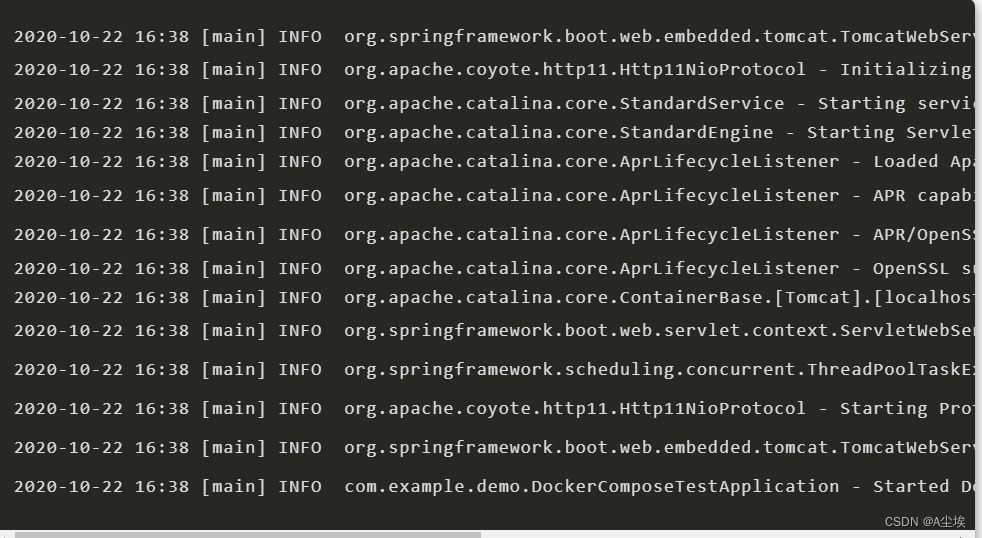
在当前文件夹下会创建一个【poslog/2020-10/22】的文件夹,里面会按天生成日志:【2020-10-22.log】,例如:
控制台输出:
分类logback.xml配置
需在application.properties中设置logging.file.name或logging.file.path属性
1)logging.file.name,设置文件,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。例如:
logging.file.name=info.log
2)logging.file.path,设置目录,会在该目录下创建spring.log文件,并写入日志内容,例如:
logging.file.path=/workspace/log
如果只配置logging.file.name,会在项目的当前路径下生成一个xxx.log日志文件。如果只配置logging.file.path,在/workspace/log文件夹生成一个为spring.log日志文件。
二者不能同时使用,如若同时使用,则只有logging.file.name生效。默认情况下,日志文件的大小达到10MB时会切分一次,产生新的日志文件,默认级别为:ERROR、WARN、INFO。
所有支持的日志记录系统都可以在Spring环境中设置记录级别,格式为:“logging.level.* = LEVEL”。
虽然Spring Boot中application.properties配置文件提供了日志的配置,但是个人更倾向于logback.xml的配置方式。
日志配置到d盘了:
根节点包含的属性
- scan:当此属性设置为true时,配置文件如果发生改变,将会被重新加载,默认值为true
- scanPeriod:设置监测配置文件是否有修改的时间间隔,如果没有给出时间单位,默认单位是毫秒。当scan为true时,此属性生效。默认的时间间隔为1分钟
- debug:当此属性设置为true时,将打印出logback内部日志信息,实时查看logback运行状态。默认值为false
子节点
- root节点是必选节点,用来指定最基础的日志输出级别,只有一个level属性。
- level:用来设置打印级别,大小写无关,其值包含如下:TRACE、DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR、ALL和OFF
- level不能设置为INHERITED或者同义词NULL,默认是DEBUG。
- root节点中可以包含零个或多个元素,标识这个appender将会添加到这个loger
子节点设置上下文名称
每个logger都关联到logger上下文,默认上下文名称为“default”。但可以使用设置成其他名字,用于区分不同应用程序的记录。
设置后不能修改,通过%contextName设置来打印日志上下文名称,一般来说不用这个属性
子节点
appender用来格式化日志输出节点,有两个属性name和class,class用来指定哪种输出策略,常用就是控制台输出策略和文件输出策略。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<!-- 日志存放路径 -->
<property name="log.path" value="d:/logback" />
<!-- 日志输出格式 -->
<property name="log.pattern" value="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{20} - [%method,%line] - %msg%n" />
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>${log.pattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 系统日志输出 -->
<appender name="file_info" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${log.path}/sys-info.log</file>
<!-- 循环政策:基于时间创建日志文件 -->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- 日志文件名格式 -->
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/sys-info.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<!-- 日志最大的历史 60天 -->
<maxHistory>60</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${log.pattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<!-- 过滤的级别 只会打印debug不会有info日志-->
<!-- <level>DEBUG</level>-->
<!-- 匹配时的操作:接收(记录) -->
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<!-- 不匹配时的操作:拒绝(不记录) -->
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<appender name="file_error" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${log.path}/sys-error.log</file>
<!-- 循环政策:基于时间创建日志文件 -->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- 日志文件名格式 -->
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/sys-error.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<!-- 日志最大的历史 60天 -->
<maxHistory>60</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${log.pattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<!-- 过滤的级别 -->
<level>ERROR</level>
<!-- 匹配时的操作:接收(记录) -->
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<!-- 不匹配时的操作:拒绝(不记录) -->
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- 用户访问日志输出 -->
<appender name="sys-user" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${log.path}/sys-user.log</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- 按天回滚 daily -->
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/sys-user.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<!-- 日志最大的历史 60天 -->
<maxHistory>60</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${log.pattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 系统模块日志级别控制 -->
<logger name="com.example" level="debug" />
<!-- Spring日志级别控制 -->
<logger name="org.springframework" level="warn" />
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="console" />
</root>
<!--系统操作日志-->
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="file_info" />
<appender-ref ref=&##34;file_error" />
</root>
<!--系统用户操作日志-->
<logger name="sys-user" level="info">
<appender-ref ref="sys-user"/>
</logger>
</configuration> 注:1)控制台和日志文件的字符集;2)日志文件的存放位置,须要遵守Linux的命名规则。
在application.yml中进行设置日志级别
如果com.example: debug,那么项目com.example包里面的debug以上的日志也会输出
logging: level: com.example: info org.springframework: warn
或者properties方式
#com.yoodb.study.demo04包下所有class以DEBUG级别输出 logging.level.com.yoodb.study=DEBUG #用来指定自己创建的日志文件 logging.config=classpath:logback-spring.xml #指定输出文件位置 logging.file.path=D://workspace/log
Controller
注:在添加引用时,日志的包一定是org.slf4j.Logger、org.slf4j.LoggerFactory类
@RestController
public class HelloWorldController {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldController.class);
@RequestMapping("/")
public String helloworld(){
logger.debug("关注微信公众号“Java精选”,Spring Boot系列文章持续更新中,带你从入门到精通,玩转Spring Boot框架。");
return "Hello world!";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello/{name}")
public String helloName(@PathVariable String name){
logger.debug("访问 helloName,Name={}",name);
return "Hello "+name;
}
}要解决的核心问题:「谁」在「什么时间」对「什么」做了「什么事」
方案 1:AOP 切面 + 注解
①、定义日志注解,用于标记哪些方法需要记录业务操作日志
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Loggable{
String value() default "";
//可以添加更多的配置属性,如操作类型、级别
}②、创建AOP切面
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect{
@Autowired
private Logger logger;//SLF4j获取
@Around("@annotation(loggable)")
public Object logBusinessOperation(Proceeding joinPoint,Loggable loggable)throws Throwable{
//方法执行前的逻辑,例如记录开始事件、方法参数等
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try{
Object result = jointPoint.proceed();//执行目标方法
//方法执行后的逻辑,例如记录结束时间、返回值等
return result;
}catch(Exception e){
// 异常处理逻辑,如记录异常信息
throw e;
}finally{
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 构建日志信息并记录
logger.info("{} executed in {} ms", joinPoint.getSignature(), executionTime);
}
}
}③、配置SpringAOP+标记注解
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AopConfig{
//可能还需要其他的配置或bean
}④、业务中使用注解
public class SomeService{
@Loggable
public void someBusinessMethod(Object someParam){
//业务逻辑
}
}缺点:
- 日志粒度和详细度:切面虽然拦截了我们目标方法,但其中能拿到的信息上下文有限,无法构成一条操作日志所需的数据信息
- 业务操作场景划分:切面的定义和使用都是非业务化的,所以无法感知到新的业务操作范围和业务的定义划分边界是如何处理
- 级联操作断档:当业务操作是设计多表或者多个服务间的调用串联时,切面只能单独记录每个服务方法级别的数据信息,无法对调用链的部分进行业务串联
记录到的日志数据都是固定的模板数据,如:_XXX 修改了项目,XXX 新建了问题数据,XXX 删除了风险问题,因为我们无法通过每个切面对具体参数内容和业务场景进行捕获。那么_如果我们想要在日志内容中添加更多的业务上下文信息,如:XXX 修改了项目 ID=001 的数据,XXX 删除了产品 ID=002 的数据,这时候就可以通过使用 AOP + SpEL 表达式来实现。
方案2:AOP 切面 + SpEL
①、对方案1的注解进行内容扩展
@Repeatable(LogRecords.class)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElmenetType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface LogRecord{
String success();
String fail() default "";
String operator() default ""; //业务操作场景人
String type(); // 业务场景 模块范围
String subType() default ""; //业务子场景,主要是模块下的功能范围
String bizNo(); //业务场景的业务编号,
String extra() default "";//一些操作的扩展操作
String actionType(); //业务操作类型,比如编辑、新增、删除
}②、基于注解进行定义SpEL的解析器来对注解中的字段进行解析和使用
public class LogRecordParser{
public static Map<String,Object> parseLogRecord(Annotation logRecordAnnotation){
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
ExpressionParser parser = new ExpressionParser(new SpelFunction("parseLogRecord", LogRecordParser.class, "parseLogRecord"));
for(String attribute : logRecordAnnotation.getAttributeNames()){
Object value = logRecordAnnotation.getAttribute(attribute);
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(attribute);
TypeResolutionContext typeResolutionContext = new TypeResolutionContext();
typeResolutionContext.setMethod(new Method(null, null, null));
Object parsedValue = expression.getValue(typeResolutionContext);
result.put(attribute, parsedValue);
}
return result;
}
}③、表达式使用
系统中实际业务操作的使用场景,在注解的内容中填充了很多业务操作场景的数据,如果需要涉及操作前后数据的内容记录,还可以再次进行扩充 SpEL 的字段及解析逻辑,可以说是有了它,我们可以做的更多了!(但是注解也越来越长了)
优缺点:
- 解决了方案1中冗余重复代码层面的侵入,但会出现大量注解定义的出现,也带有一定的侵入性
- 日志内容还是需要系统自身根据上报场景进行封装,需要从产品的业务定义到研发编码达成统一共识
- 与方案1相比简化了一部分代码集成的复杂度,只需编写自定义注解即可
- 与方案1相比扩展了对操作的业务数据广度,数据范围大大增加,而且还可根据自身业务定义无限扩展
解决了业务操作日志的一个收集问题,能够清晰的记录各类操作场景、动作、数据前后的内容等
方案3:Binlog + 时间窗口
怎么从应用层对操作场景、数据进行抓包、处理逻辑、保存,所以复杂度都会集中到应用层。既然是这样我们能不能直接基于底层的 MySQL 本身来处理这件事儿呢?
Binlog 是数据库中二进制格式的文件,用于记录用户对数据库更新的 SQL 语句信息,例如更改数据库表和更改内容的 SQL 语句都会记录到 binlog 里。那么 Binlog 能用来记录业务层面的数据变化内容吗?
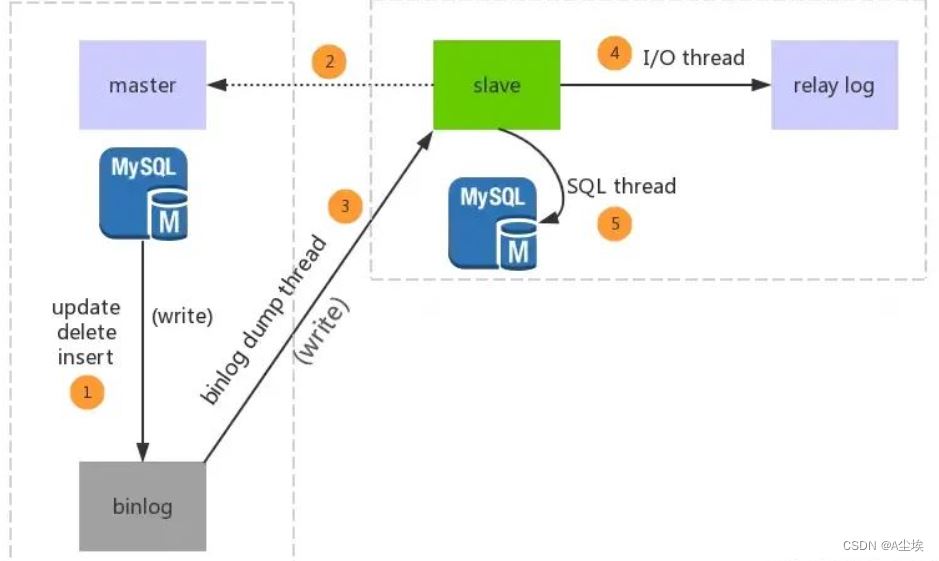
问题 1:无法对多表存在级联保存和更新的数据进行非常好的兼容支持,因为本身binlog数据是无序的,并且如果上游数据的操作不是包裹在一个事务中,也很难处理
解决问题 1:由于本身 binlog 的无序性,所以无法对大量 binlog 进行有序组合,如果本身是一个事务提交的还可以根据事务 KEY 进行组合,如果不是呢?这里可以考虑借鉴 Flink 的时间窗口机制:滚动的时间窗口将每个元素指定给指定窗口大小的窗口,滚动窗口具有固定大小,且不重叠。
例如,我们指定一个大小为 1 分钟的滚动窗口,在这种情况下,我们将每隔 1 分钟开启一个新的窗口,其中每一条数都会划分到唯一一个 1 分钟的窗口中,如下图所示:
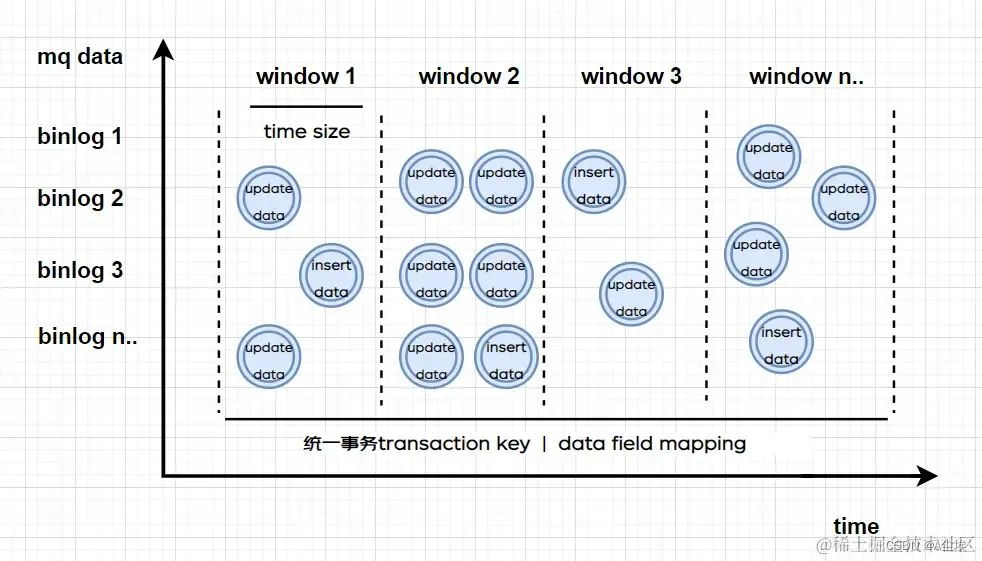
基于以上的窗口机制,我们就可以对数据先进行范围的框定,通过窗口的滑动机制和补偿机制对窗口中的数据进行关联处理。但光靠时间窗口还是无法对 binlog 进行关联,那我们就从关联数据本身下手,这类数据关联复杂主要是涉及表之间的引用关系,那我们在进行定义 binlog 解析时就把前后数据 + 表之间的引用字段都进行指定,这样在窗口中进行滑动关联时,就可以进行子表的引用字段关联了!这样关联字段补偿更新的机制就可以解决问题 1 了。
//部分的 binlog 数据变动结构的 RowChange 定义如下:
@Data
public static class RowChange {
private int tableId;
private List<RowDatas> rowDatas;
private String eventType;
private boolean isDdl;
}
@Data
public static class RowDatas {
private List<DataColumn> afterColumns;
private List<DataColumn> beforeColumns;
}
@Data
public static class DataColumn {
private int sqlType;
private boolean isNull;
private String mysqlType;
private String name;
private boolean isKey;
private int index;
private boolean updated;
private String value;
}
问题 2:关于更新人的问题,系统进行更新时如果未手动更新对应操作人,则系统无法识别,需要上游做对应场景的统一改造,但从系统承接来看,本身系统的操作人就是要跟着业务操作一起进行联动的
解决问题 2:关于更新人的问题其实是各系统需要自己排除解决的问题,因为本身业务在进行数据操作时就是需要留痕更新人信息,比较统一的方案就是基于底层的 ORM 框架来统一进行拦截处理,大家可以自行 GPT。
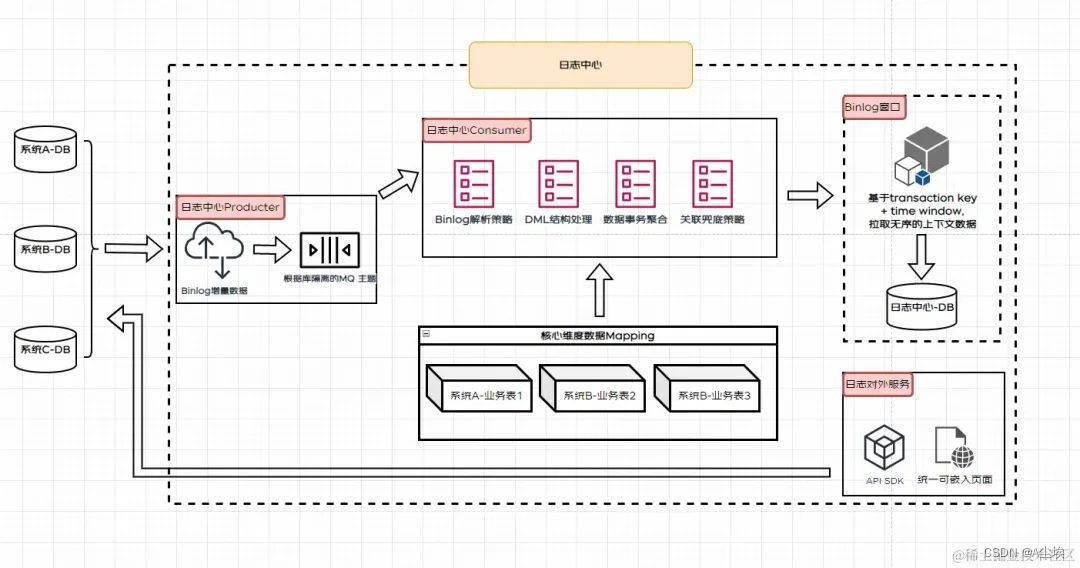
总结:
- 基于 binlog 后,我们对底层的数据变动感知更明显了,但是 binlog 的数据来源除了系统应用层还有很多其他来源,比如我们的数据库工单,日常跑批刷数等场景,这类的数据变动范围可能较大,而且感知较弱。
- 方案 3 的设计把方案 2 中的业务场景(也就是 actiontype subtype 等)弱化了,所以并不能很好的感知到很细颗粒度。
项目中应用日志
①、bootstrap.yml配置文件
mybatis-plus:
type-aliases-package: quick.pager.shop.model
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto
logging:
pattern:
console: "%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level [${spring.application.name}] [traceId:%X{X-B3-TraceId}][spanId:%X{X-B3-SpanId}][parentSpanId:%X{X-B3-ParentSpanId}] --- [%t] - [%class:%method: %line] - %msg%n"
file: "%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level [${spring.application.name}] [traceId:%X{X-B3-TraceId}][spanId:%X{X-B3-SpanId}][parentSpanId:%X{X-B3-ParentSpanId}] --- [%t] - [%class:%method: %line] - %msg%n"
level:
org.springframework: error
com.alibaba: error
org.apache.ibatis: error
io.seata: error
file:
path: ./logs/${spring.application.name}
max-size: 50MB
name: ${spring.application.name}②、service实现类中的使用日志
@Service
@Slf4j //lombok:1.18.12
public class GoodsSpuServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<GoodsSpuMapper, GoodsSpu> implements GoodsSpuService {
@Autowired
private GoodsClassMapper goodsClassMapper;
@Autowired
private BannerClient bannerClient;
@Override
public Response<Long> create(GoodsSpuSaveRequest request){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(request.getSpuName())){
return Response.toError(ResponseStatus.Code.FAIL_CODE, "spu名称不能为空!");
}
if(checkName(request.getSpuName(), null)){
return Response.toError(ResponseStatus.Code.FAIL_CODE, "spu名称已存在!");
}
GoodsSpu spu = this.conv(request);
spu.setCreateTime(DateUtils.dateTime());
spu.setDeleteStatus(Boolean.FALSE);
if (this.baseMapper.insert(spu) > 0) {
return Response.toResponse(spu.getId());
}
//添加日志
log.error("新增SPU失败 result = {}",JSON.toJSONString(request));
return Response.toError(ResponseStatus.Code.FAIL_CODE, "新增SPU失败");
}
@Override
public Response<Long> delete(final Long id){
int delete = this.baseMapper.deleteById(id);
if(delete>0){
return Response.toResponse(id);
}
//添加日志
log.error("删除SPU失败 id={}",id);
return Response.toError(ResponseStatus.Code.FAIL_CODE, "删除SPU失败");
}
}校验名称的唯一性
private Boolean checkName(final String name,final Long id){
List<GoodsSpu> spus = this.baseMapper.selectList(new LambdaQueryWrapper<GoodsSpu>()
.eq(GoodsSpu::getSpuName, name));
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(spus)){
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
return spus.stream()
.filter(item->Objects.isNull(id)?Boolean.TRUE:IConsts.ZERO!=item.getId().compareTo(id))
.anyMatch(item->item.getSpuName().equals(name));
}项目中注解和日志的结合
①、注解
/**
自定义操作日志记录注解
*/
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface OperLog{
//模块
public String title() default "";
//功能
public BusinessType businessType() default BusinessType.OTHER;
//操作人类别
public OperatorType operatorType() default OperatorType.MANAGE;
//是否保存请求的参数
public boolean isSaveRequestData() default true;
}/**
* 业务操作类型
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public enum BusinessType {
/**
* 其它
*/
OTHER,
/**
* 新增
*/
INSERT,
/**
* 修改
*/
UPDATE,
/**
* 删除
*/
DELETE,
/**
* 授权
*/
GRANT,
/**
* 导出
*/
EXPORT,
/**
* 导入
*/
IMPORT,
/**
* 强退
*/
FORCE,
/**
* 生成代码
*/
GENCODE,
/**
* 清空
*/
CLEAN,
}
/**
* 操作人类别
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public enum OperatorType {
/**
* 其它
*/
OTHER,
/**
* 后台用户
*/
MANAGE,
/**
* 手机端用户
*/
MOBILE
}②、切面
@Aspect
@Slf4j
@Document
public class OperLogAspect{
//配置织入点(注解)
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.ruoyi.system.log.annotation.OperLog)")
public void logPointCut(){}
//处理完请求后执行
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "logPointCut")
public void doAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint){
handleLog(joinPoint,null);
}
//拦截异常操作
@AfterThrowing(value = "logPointCut()",throwing = "e")
public void doAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e){
handleLog(joinPoint,e);
}
protected void handleLog(final JoinPoint joinPoint,final Exception e){
try{
// 获得注解
com.ruoyi.system.log.annotation.OperLog controllerLog = getAnnotationLog(joinPoint);
if (controllerLog == null) {
return;
}
// *========数据库日志=========*//
OperLog operLog = new OperLog();
operLog.setStatus(BusinessStatus.SUCCESS.ordinal());
// 请求的地址
HttpServletRequest request = ServletUtils.getRequest();
String ip = IpUtils.getIpAddr(request);
operLog.setOperIp(ip);
operLog.setOperUrl(request.getRequestURI());
operLog.setOperLocation(AddressUtils.getRealAddressByIP(ip));
String username = request.getHeader(Constants.CURRENT_USERNAME);
operLog.setOperName(username);
if (e != null) {
operLog.setStatus(BusinessStatus.FAIL.ordinal());
operLog.setErrorMsg(StringUtils.substring(e.getMessage(), 0, 2000));
}
//设置方法名称
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
Strng methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
operLog.setMethod(className + "." + methodName + "()");
//设置请求方式
operLog.setRequestMethod(request.getMethod());
//处理设置注解上的参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
getControllerMethodDescription(controllerLog, operLog, args);
//发布事件
SpringContextHolder.publishEvent(new OperLogEvent(operLog));
}catch(Exception exp){
//记录本地异常日志
log.error("==前置通知异常==");
log.error("异常信息:{}", exp.getMessage());
exp.printStackTrace();
}
}
//是否存在注解,如果存在就获取
private com.ruoyi.system.log.annotation.OperLog getAnnotationLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
if (method != null) {
return method.getAnnotation(com.ruoyi.system.log.annotation.OperLog.class);
}
return null;
}
//获取注解中对方法的描述信息,用于Controller层注解
public void getControllerMethodDescription(com.ruoyi.system.log.annotation.OperLog log, OperLog operLog, Object[] args)
throws Exception {
// 设置action动作
operLog.setBusinessType(log.businessType().ordinal());
// 设置标题
operLog.setTitle(log.title());
// 设置操作人类别
operLog.setOperatorType(log.operatorType().ordinal());
// 是否需要保存request,参数和值
if (log.isSaveRequestData()) {
// 获取参数的信息,传入到数据库中。
setRequestValue(operLog, args);
}
}
//获取请求的参数,放到log中
private void setRequestValue(OperLog operLog, Object[] args) throws Exception {
List<?> param = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(args)).stream().filter(p -> !(p instanceof ServletResponse))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
log.debug("args:{}", param);
String params = JSON.toJSONString(param, true);
operLog.setOperParam(StringUtils.substring(params, 0, 2000));
}
}工具类
/**
* 客户端工具类
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public class ServletUtils {
/**
* 获取String参数
*/
public static String getParameter(String name) {
return getRequest().getParameter(name);
}
/**
* 获取String参数
*/
public static String getParameter(String name, String defaultValue) {
return Convert.toStr(getRequest().getParameter(name), defaultValue);
}
/**
* 获取Integer参数
*/
public static Integer getParameterToInt(String name) {
return Convert.toInt(getRequest().getParameter(name));
}
/**
* 获取Integer参数
*/
public static Integer getParameterToInt(String name, Integer defaultValue) {
return Convert.toInt(getRequest().getParameter(name), defaultValue);
}
/**
* 获取request
*/
public static HttpServletRequest getRequest() {
return getRequestAttributes().getRequest();
}
/**
* 获取response
*/
public static HttpServletResponse getResponse() {
return getRequestAttributes().getResponse();
}
/**
* 获取session
*/
public static HttpSession getSession() {
return getRequest().getSession();
}
public static ServletRequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
return (ServletRequestAttributes) attributes;
}
/**
* 将字符串渲染到客户端
*
* @param response 渲染对象
* @param string 待渲染的字符串
* @return null
*/
public static String renderString(HttpServletResponse response, String string) {
try {
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().print(string);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 是否是Ajax异步请求
*
* @param request
*/
public static boolean isAjaxRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
String accept = request.getHeader("accept");
if (accept != null && accept.indexOf("application/json") != -1) {
return true;
}
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("X-Requested-With");
if (xRequestedWith != null && xRequestedWith.indexOf("XMLHttpRequest") != -1) {
return true;
}
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
if (StringUtils.inStringIgnoreCase(uri, ".json", ".xml")) {
return true;
}
String ajax = request.getParameter("__ajax");
if (StringUtils.inStringIgnoreCase(ajax, "json", "xml")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}/**
* 获取IP方法
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public class IpUtils {
public static String getIpAddr(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (request == null) {
return "unknown";
}
String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("X-Real-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
return "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ip) ? "127.0.0.1" : ip.split(",")[0];
}
public static boolean internalIp(String ip) {
byte[] addr = textToNumericFormatV4(ip);
if (null != addr) {
return internalIp(addr) || "127.0.0.1".equals(ip);
}
return false;
}
private static boolean internalIp(byte[] addr) {
final byte b0 = addr[0];
final byte b1 = addr[1];
// 10.x.x.x/8
final byte SECTION_1 = 0x0A;
// 172.16.x.x/12
final byte SECTION_2 = (byte) 0xAC;
final byte SECTION_3 = (byte) 0x10;
final byte SECTION_4 = (byte) 0x1F;
// 192.168.x.x/16
final byte SECTION_5 = (byte) 0xC0;
final byte SECTION_6 = (byte) 0xA8;
switch (b0) {
case SECTION_1:
return true;
case SECTION_2:
if (b1 >= SECTION_3 && b1 <= SECTION_4) {
return true;
}
case SECTION_5:
switch (b1) {
case SECTION_6:
return true;
}
default:
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将IPv4地址转换成字节
*
* @param text IPv4地址
* @return byte 字节
*/
public static byte[] textToNumericFormatV4(String text) {
if (text.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
String[] elements = text.split("\\.", -1);
try {
long l;
int i;
switch (elements.length) {
case 1:
l = Long.parseLong(elements[0]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 4294967295L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[0] = (byte) (int) (l >> 24 & 0xFF);
bytes[1] = (byte) (int) ((l & 0xFFFFFF) >> 16 & 0xFF);
bytes[2] = (byte) (int) ((l & 0xFFFF) >> 8 & 0xFF);
bytes[3] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
break;
case 2:
l = Integer.parseInt(elements[0]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 255L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[0] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
l = Integer.parseInt(elements[1]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 16777215L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[1] = (byte) (int) (l >> 16 & 0xFF);
bytes[2] = (byte) (int) ((l & 0xFFFF) >> 8 & 0xFF);
bytes[3] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
break;
case 3:
for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
l = Integer.parseInt(elements[i]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 255L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[i] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
}
l = Integer.parseInt(elements[2]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 65535L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[2] = (byte) (int) (l >> 8 & 0xFF);
bytes[3] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
break;
case 4:
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
l = Integer.parseInt(elements[i]);
if ((l < 0L) || (l > 255L)) {
return null;
}
bytes[i] = (byte) (int) (l & 0xFF);
}
break;
default:
return null;
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return null;
}
return bytes;
}
public static String getHostIp() {
try {
return InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
}
return "127.0.0.1";
}
public static String getHostName() {
try {
return InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
}
return "未知";
}
}/**
* 获取地址类
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public class AddressUtils {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AddressUtils.class);
public static final String IP_URL = "http://ip-api.com/json/%s?lang=zh-CN";
public static String getRealAddressByIP(String ip) {
String address = "XX XX";
// 内网不查询
if (IpUtils.internalIp(ip)) {
return "内网IP";
}
String rspStr = HttpUtil.get(String.format(IP_URL, ip));
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(rspStr)) {
log.error("获取地理位置异常 {}", ip);
return address;
}
JSONObject obj;
try {
obj = JSON.unmarshal(rspStr, JSONObject.class);
address = obj.getStr("country") + "," + obj.getStr("regionName") + "," + obj.getStr("city");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("获取地理位置异常 {}", ip);
}
return address;
}
}
系统日志事件
public class OperLogEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8905017895058642111L;
public OperLogEvent(OperLog source) {
super(source);
}
}@Slf4j
@Service
@Lazy(false)
public class SpringContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware,DisposableBean{
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
//取得存在在静态变量中的ApplicationContext
public static ApplicationCotnext getApplicationCotnext(){
return applicationContext;
}
//实现ApplicationContextAware接口, 注入Context到静态变量中
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
SpringContextHolder.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
//清除SpringContextHolder中的ApplicationContext为Null
public static void clearHolder() {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("清除SpringContextHolder中的ApplicationContext:" + applicationContext);
}
applicationContext = null;
}
//发布事件 SpringContextHolder.publishEvent(new OperLogEvent(operLog));
public static void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (applicationContext == null) {
return;
}
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
}
//实现DisposableBean接口, 在Context关闭时清理静态变量.
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public void destroy() {
SpringContextHolder.clearHolder();
}
//获取运行环境
public static String getActiveProfile() {
return applicationContext.getEnvironment().getActiveProfiles()[0];
}
}③、使用
//新增保存通知公告
@HasPermissions("system:notice:add")
@OperLog(title = "通知公告", businessType = BusinessType.INSERT)
@PostMapping("save")
public R addSave(@ReqeustBody Notice notice){
notice.setParkId(getParkId());
notice.setCreateBy(getLoginName());
return toAjax(noticeService.insertNotice(notice));
}总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
