SpringBoot项目接收前端参数的11种方式
作者:袁庭新
1 搭建项目
1.通过Spring Initializr选项创建一个项目名称为【sb_receive_param】的SpringBoot项目。
2.给项目添加Spring Web依赖。
3.在com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo包下创建User实体类。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Cat cat;
private List<Course> courses;
}4.在com.cy.sb_receive_param.controller包下创建UserController类。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RequestMapping("users")
@RestController
public class UserController {
}5.解决在前后端分离项目中的跨域问题。通过实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,并重写addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry)方法来实现。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class CrossOriginConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* addMapping("/**"):配置可以被跨域的路径,可以任意配置,可以具体到直接请求路径
* allowedOrigins("*"):允许所有的请求域名访问我们的跨域资源,可以固定单条或者多条内容,如"http://www.yx.com",只有该域名可以访问我们的跨域资源
* allowedHeaders("*"):允许所有的请求header访问,可以自定义设置任意请求头信息
* allowedMethods():允许所有的请求方法访问该跨域资源服务器,如GET、POST、DELETE、PUT、OPTIONS、HEAD等
* maxAge(3600):配置客户端可以缓存pre-flight请求的响应的时间(秒)。默认设置为1800秒(30分钟)
*/
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "DELETE", "PUT", "OPTIONS", "HEAD")
.maxAge(3600);
}
}2 Spring Boot接收前端参数方式
2.1 传非JSON数据
2.1.1 注解介绍
@RequestParam主要用于在Spring MVC后台控制层获取参数,它有三个常用参数。
参数名 | 描述 |
defaultValue | 表示设置默认值 |
required | 表示该参数是否必传 |
value | 值表示接收传入的参数的key |
@PathVariable用于将请求URL中的模板变量映射到功能处理方法的参数上,即取出URL模板中的变量作为参数。
2.1.2 案例演示
1.方式一
1.在UserController类中添加add1()请求处理方法。前端请求参数的key需和后端控制层处理请求的方法参数名称一致。
@RequestMapping("add1")
public void add1(String username, String password) {
System.out.println("username=" + username + ", password=" + password);
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试(GET和POST请求都支持)。
localhost:8080/users/add1?username=tom&password=123456
3.创建param01.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
username: '王小虎',
password: '123456'
}
},
mounted() {
axios.get('http://localhost:8888/users/add1', {
params: {
username: this.username,
password: this.password
}
}).then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>2.方式二
1.在UserController类中添加add2()请求处理方法。如果前端请求参数的key与后端控制层处理请求的方法参数名称不一致,使用@RequestParam注解来解决。
@RequestMapping("add2")
public void add2(@RequestParam("name") String username, @RequestParam("pwd") String password) {
System.out.println("username=" + username + ", password=" + password);
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试(GET和POST请求都支持)。
localhost:8080/users/add2?name=tom&pwd=123456
3.创建param02.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
username: '张小三',
password: '654321'
}
},
mounted() {
axios.get('http://localhost:8888/users/add2', {
params: {
name: this.username,
pwd: this.password
}
}).then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>3.接收前端传数组参数
1.在UserController类中添加delete1()请求处理方法。
@DeleteMapping("batch_delete1")
public void delete1(@RequestParam(name = "ids") List<Integer> ids) {
for (Integer id : ids) {
System.out.println(id);
}
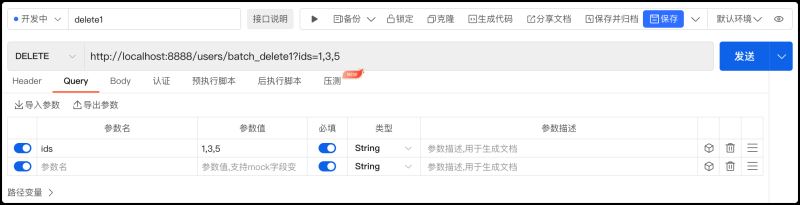
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试,在【Query】选项下添加ids参数,参数值设置为1,3,5。
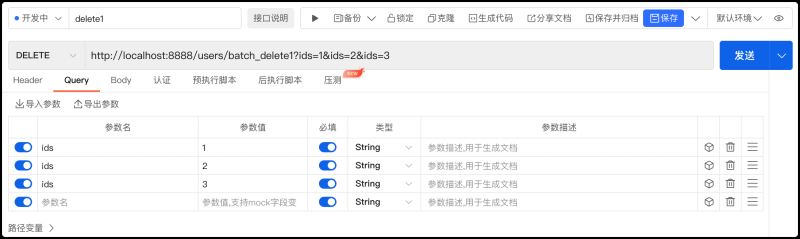
3.使用ApiPost工具测试,在【Query】选项下添加ids参数,将参数的值单独一个个进行添加。
4.创建param03.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
ids: [1, 3, 5]
}
},
mounted() {
axios.delete('http://localhost:8888/users/batch_delete1', {
params: {
ids: this.ids.join(',')
}
}).then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>4.方式四
1.在UserController类中添加add3()请求处理方法。前端请求参数的key需和后端控制层处理请求方法的参数pojo实体类的属性名称一致。
@RequestMapping("add3")
public void add3(User user) {
System.out.println(user);
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试(GET和POST请求都支持)。
localhost:8080/users/add3?id=1&username=tom&password=123
3.创建param04.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
id: 1,
username: '王小明',
password: '123456'
}
},
mounted() {
axios.get('http://localhost:8888/users/add3', {
params: {
id: this.id,
username: this.username,
password: this.password
}
})
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>5.方式五
1.在UserController类中添加add4()请求处理方法。使用@PathVariable注解将请求URL中的模板变量映射到功能处理方法的参数上,如果模板变量名称和方法的参数名称不同需要在@PathVariable注解上显示的指定映射关系。
@RequestMapping("add4/{username}/{pwd}")
public void add4(@PathVariable String username, @PathVariable("pwd") String password) {
System.out.println("username=" + username + ", password=" + password);
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试(GET和POST请求都支持)。
localhost:8080/users/add4/tom/123456
3.创建param05.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
username: '袁庭新',
password: '123456'
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post(`http://localhost:8888/users/add4/${this.username}/${this.password}`)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>6.方式六
1.在UserController类中添加add5()请求处理方法。通过HttpServletRequest对象获取数据,前端请求参数的key需和getParameter(String name)方法传递的参数名称一致。
@RequestMapping("add5")
public void add5(HttpServletRequest request) {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username=" + username + ", password=" + password);
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试(GET和POST请求都支持)。
localhost:8080/users/add5?username=tom&password=123
3.创建param06.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
username: '袁庭新',
password: '123456'
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/add5', null, {
params: {
username: this.username,
password: this.password
}
})
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>2.2 传JSON数据
2.2.1 注解介绍
@RequestBody该注解会把接收到的参数转为JSON格式。如果前端通过application/json类型提交JSON格式的数据给后端控制层处理请求的方法,方法的参数必须使用@RequestBody注解进行修饰,才能接收来自前端提交的JSON数据。
2.2.2 案例演示
1.接收前端传数组参数
1.在UserController类中添加delete2()请求处理方法。
@DeleteMapping("batch_delete2")
public void delete2(@RequestBody ArrayList<Integer> ids) {
for (Integer id : ids) {
System.out.println(id);
}
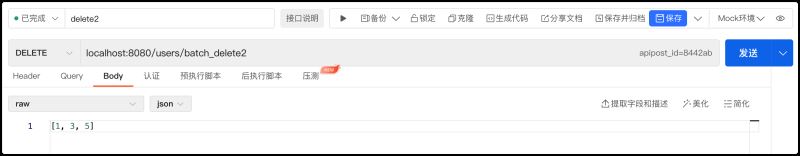
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试,在【Body】选项选项下发送JSON格式数据[1, 3, 5]给后台。
3.创建param07.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
ids: [1, 3, 5]
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/batch_delete2', this.ids)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>2.单个实体接收参数
1.在UserController类中添加add6()请求处理方法。
@RequestMapping("add6")
public User add6(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试,需将提交的数据类型设置为application/json格式(GET和POST请求都支持)。
{
"id": 1,
"username": "tom",
"password": "123456"
}3.创建param08.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
user: {
username: '袁庭新',
password: '123456'
}
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/add6', this.user)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>3.实体嵌套实体接收参数
1.在pojo包下创建Cat实体类。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Cat {
private Integer id;
private String breed;
private String name;
}2.在pojo包下的User实体类中声明Cat类型的属性。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Cat cat;
}3.在UserController类中添加add7()请求处理方法。
@RequestMapping("add7")
public User add7(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}4.使用ApiPost工具测试,需将提交的数据类型设置为application/json格式(GET和POST请求都支持)。
{
"id": 1,
"username": "袁庭新",
"password": "123456",
"cat": {
"id": 1,
"breed": "蓝白",
"name": "花花"
}
}5.创建param09.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
user: {
id: 1,
username: '袁庭新',
password: '123456',
cat: {
id: 1,
breed: '蓝白',
name: '花花'
}
}
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/add7', this.user)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>4.实体嵌套List集合接收参数
1.在pojo包下创建Course实体类。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Course {
private Integer id;
private String courseName;
private String lecturer;
}2.在pojo包下的User实体类中声明List<Course>类型的属性。
package com.cy.sb_receive_param.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private List<Course> courses;
}3.在UserController类中添加add8()请求处理方法。
@RequestMapping("add8")
public User add8(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}4.使用ApiPost工具测试,需将提交的数据类型设置为application/json格式(GET和POST请求都支持)。
{
"id": 1,
"username": "tom",
"password": "123456",
"courses": [
{
"id": 1,
"courseName": "Java",
"lecturer": "袁庭新老师"
},
{
"id": 2,
"courseName": "Python",
"lecturer": "李小红老师"
}
]
}5.创建param10.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
user: {
id: 1,
username: 'tom',
password: '123456',
cat: {
id: 1,
breed: '蓝白',
name: '花花'
},
courses: [
{
id: 1,
courseName: "Java",
lecturer: "袁庭新老师"
},
{
id: 2,
courseName: "Python",
lecturer: "张晓东老师"
}
]
}
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/add8', this.user)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>5.Map集合接收参数
1.在UserController类中添加add9()请求处理方法。
@RequestMapping("add9")
public Map<String, Object> add9(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> map) {
String username = (String) map.get("username");
System.out.println("username : " + username);
Map<String, Object> catMap = (Map<String, Object>) map.get("cat");
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> catSet = catMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : catSet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
List<Map<String, Object>> courseMapList = (List<Map<String, Object>>) map.get("courses");
for (Map<String, Object> courseMap : courseMapList) {
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> courseSet = courseMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : courseSet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
return map;
}2.使用ApiPost工具测试,需将提交的数据类型设置为application/json格式(GET和POST请求都支持)。
{
"id": 1,
"username": "tom",
"password": "123456",
"courses": [
{
"id": 1,
"courseName": "Java",
"lecturer": "袁庭新老师"
},
{
"id": 2,
"courseName": "Python",
"lecturer": "李小红老师"
}
]
}3.创建param11.html页面,通过Axios发送请求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>前后端参数传递</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
const app = {
data() {
return {
user: {
id: 1,
username: 'tom',
password: '123456',
cat: {
id: 1,
breed: '蓝白',
name: '花花'
},
courses: [
{
id: 1,
courseName: "Java",
lecturer: "袁庭新老师"
},
{
id: 2,
courseName: "Python",
lecturer: "张晓东老师"
}
]
}
}
},
mounted() {
axios.post('http://localhost:8888/users/add9', this.user)
.then(response => {
console.log('success', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('fail', error.data);
});
}
}
Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>3 总结
本文介绍了在Spring Boot项目中接收前端数据的多种方式。通过创建Spring Boot项目、配置Web依赖和跨域问题,展示了如何使用@RequestParam、@PathVariable、@RequestBody等注解接收不同类型的参数,包括基本类型、数组、复杂对象及嵌套结构。通过实例演示了如何在Controller中处理GET、POST等请求,并通过前端页面发送请求验证后端接收逻辑。
以上就是SpringBoot项目接收前端参数的11种方式的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot接收前端参数的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
