详解C#如何使用重载方法实现不同类型数据的计算
作者:wenchm
一、涉及到的相关知识
1.重载的方法
重载方法就是方法名称相同,但是每个方法中参数的数据类型、个数或顺序不同的方法。如果一个类中存在两个以上的同名方法,并且方法的参数类型、个数或者顺序不同,当调用这样的方法时,编译器会根据传入的参数自动进行判断,决定调用哪个方法。
2.Convert.ToInt32(String)方法
将数字的指定字符串表示形式转换为等效的 32 位带符号整数。
public static int ToInt32 (string? value);
参数
value String 包含要转换的数字的字符串。
返回
Int32 一个与 value 中数字等效的 32 位带符号整数,如果 value 为 null,则为 0(零)。
例外
FormatException
value 不由一个可选符号后跟一系列数字 (0-9) 组成。
OverflowException
value 表示小于 Int32.MinValue 或大于 Int32.MaxValue 的数字。
在C#中,Convert.ToInt32(string)方法用于将字符串转换为整数。如果字符串包含非数字字符,例如小数点,该方法将引发异常。例如,字符串是"123.456",包含非数字字符"."。因此,直接使用Convert.ToInt32(string)会引发异常。
为了避免异常,可以先使用Decimal.Parse(string)方法将字符串转换为小数,然后再使用Convert.ToInt32(decimal)方法将小数转换为整数。
string str = "123.456"; decimal decimalValue = Decimal.Parse(str); int intValue = Convert.ToInt32(decimalValue);
或者,使用string.Split()方法将字符串按指定的分隔符拆分为一个字符串数组。例如,可以使用小数点"."作为分隔符,然后取第一个元素作为整数部分。
3.判断字符串是否带有小数点
string str = "123.456";
string[] parts = str.Split('.');
// 如果有小数点,取小数点前面的部分作为整数
// 如果没有小数点,整个字符串就是整数部分
string integerPart = parts.Length > 0 ? parts[0] : str;
int intValue = Convert.ToInt32(integerPart);使用正则表达式@"^\d+\.\d+$"判断字符串是否含有“.”,然后执行相应操作。
二、实例
1.示例
//重载加法运算
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
namespace _111
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private GroupBox? groupBox1;
private GroupBox? groupBox2;
private RadioButton? radioButton3;
private RadioButton? radioButton2;
private RadioButton? radioButton1;
private TextBox? textBox1;
private Label? label2;
private Label? label1;
private TextBox? textBox2;
private TextBox? textBox3;
private Button? button1;
private Label? label3;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
Load += Form1_Load;
}
private void Form1_Load(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
//
// radioButton1
//
radioButton1 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 17),
Name = "radioButton1",
Size = new Size(40, 21),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = true,
Text = "int",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// radioButton2
//
radioButton2 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 39),
Name = "radioButton2",
Size = new Size(90, 21),
TabIndex = 1,
TabStop = true,
Text = "int+double",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// radioButton3
//
radioButton3 = new RadioButton
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(11, 61),
Name = "radioButton3",
Size = new Size(67, 21),
TabIndex = 2,
TabStop = true,
Text = "double",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
//
// label1
//
label1 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(6, 23),
Name = "label1",
Size = new Size(44, 17),
TabIndex = 0,
Text = "加数:"
};
//
// label2
//
label2 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(6, 53),
Name = "label2",
Size = new Size(56, 17),
TabIndex = 1,
Text = "被加数:"
};
//
// textBox1
//
textBox1 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(56, 17),
Name = "textBox1",
Size = new Size(91, 23),
TabIndex = 2
};
//
// textBox2
//
textBox2 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(56, 47),
Name = "textBox2",
Size = new Size(91, 23),
TabIndex = 3
};
//
// groupBox1
//
groupBox1 = new GroupBox
{
Location = new Point(12, 12),
Name = "groupBox1",
Size = new Size(153, 92),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = false,
Text = "数据运算"
};
groupBox1.Controls.Add(textBox2);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(textBox1);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(label2);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(label1);
groupBox1.SuspendLayout();
//
// groupBox2
//
groupBox2 = new GroupBox
{
Location = new Point(171, 12),
Name = "groupBox2",
Size = new Size(127, 92),
TabIndex = 0,
TabStop = false,
Text = "选择数据类型"
};
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton3);
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton2);
groupBox2.Controls.Add(radioButton1);
groupBox2.SuspendLayout();
//
// textBox3
//
textBox3 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(88, 107),
Name = "textBox3",
Size = new Size(100, 23),
TabIndex = 1
};
//
// button1
//
button1 = new Button
{
Location = new Point(223, 107),
Name = "button1",
Size = new Size(75, 23),
TabIndex = 2,
Text = "开始计算",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
button1.Click += Button1_Click;
//
// label3
//
label3 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(12, 113),
Name = "label3",
Size = new Size(68, 17),
TabIndex = 3,
Text = "运算结果:"
};
//
// Form1
//
AutoScaleDimensions = new SizeF(7F, 17F);
AutoScaleMode = AutoScaleMode.Font;
ClientSize = new Size(309, 136);
Controls.Add(label3);
Controls.Add(button1);
Controls.Add(textBox3);
Controls.Add(groupBox2);
Controls.Add(groupBox1);
Name = "Form1";
Text = "重载加法运算";
groupBox1.ResumeLayout(false);
groupBox1.PerformLayout();
groupBox2.ResumeLayout(false);
groupBox2.PerformLayout();
}
private void Button1_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox3!.Text = "";
try
{
if (radioButton1!.Checked)
{
if (!IsDecimalNumber(textBox1!.Text) && !IsDecimalNumber(textBox2!.Text))
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToInt32(textBox1!.Text), Convert.ToInt32(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("文本内数字不能是小数","警示");
}
}
else if (radioButton2!.Checked)
{
if (!IsDecimalNumber(textBox1!.Text))
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToInt32(textBox1!.Text), Convert.ToDouble(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("加数不能是小数", "警示");
}
}
else if (radioButton3!.Checked)
{
textBox3!.Text = Add(Convert.ToDouble(textBox1!.Text) ,Convert.ToDouble(textBox2!.Text)).ToString();
}
}
catch { }
}
public static int Add(int x, int y)//定义一个静态方法Add,返回值为int类型,有两个int类型的参数
{
return x + y;
}
public static double Add(int x, double y)//重新定义方法Add,它与第一个方法的返回值类型及参数类型不同
{
return x + y;
}
public static double Add(double x, double y)//重新定义方法Add,它与第一个方法的返回值类型及参数类型不同
{
return x + y;
}
/// <summary>
/// 使用正则表达式判断字符串是否为带小数的数字
/// ^\d+\.\d+$ : ^ 表示字符串开始, \d+ 表示一个或多个数字,
/// \.? 表示可能存在的小数点, \d+ 表示小数点后面的一个或多个数字,
/// $ 表示字符串结束
/// </summary>
public static bool IsDecimalNumber(string str)
{
return MyRegex().IsMatch(str);
}
[GeneratedRegex(@"^\d+\.\d+$")]
private static partial Regex MyRegex();
}
}2.生成成果

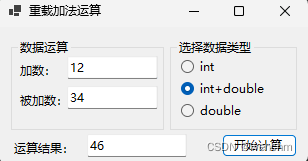







到此这篇关于详解C#如何使用重载方法实现不同类型数据的计算的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C#重载方法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
