Java中的Semaphore信号量简析
作者:小晨想好好学习
这篇文章主要介绍了Java中的Semaphore信号量简析,Semaphore:信号量,用来限制能同时访问共享资源的线程上限,使用Semaphore实现简单连接池,对比享元模式下的实现(用wait和notify),性能和可读性要更好,需要的朋友可以参考下
一、是什么?
Semaphore:信号量,用来限制能同时访问共享资源的线程上限
二、简单使用
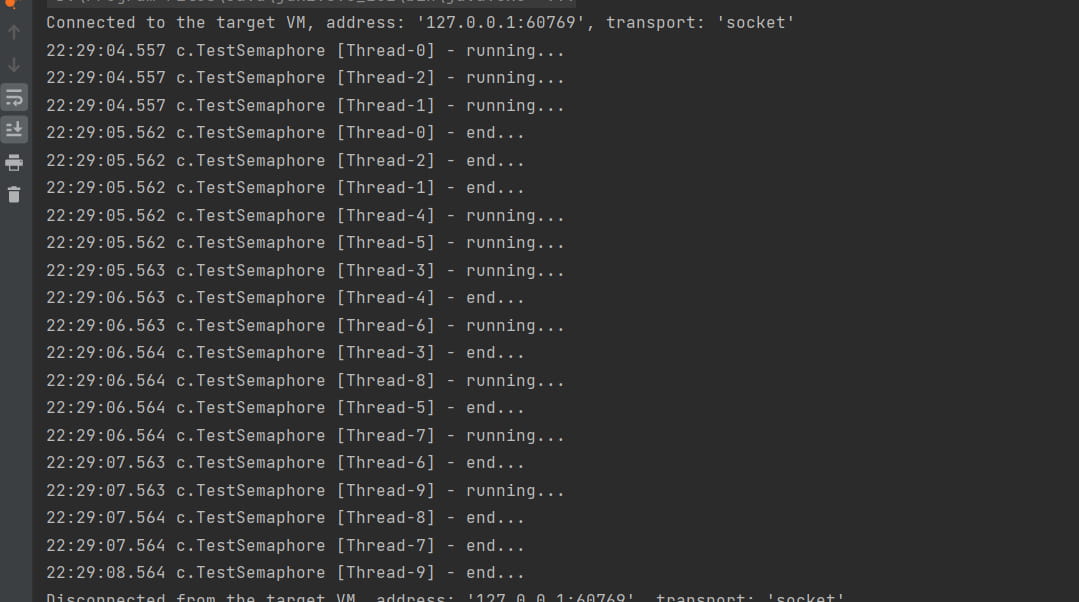
public class TestSemaphore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 semaphore 对象
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
// 2. 10个线程同时运行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
log.debug("running...");
sleep(1);
log.debug("end...");
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}).start();
}
}
}结果:始终只有三个线程处于正在运行的状态
三、semaphore应用
- 使用semaphore限流,在访问高峰期时,让请求线程阻塞。当然它只适合限制单机线程数量,并且是仅限制线程数,而不是限制资源数(例如连接数)
- 使用Semaphore实现简单连接池,对比享元模式下的实现(用wait和notify),性能和可读性要更好
class Pool {
// 1. 连接池大小
private final int poolSize;
// 2. 连接对象数组
private Connection[] connections;
// 3. 连接状态数组 0 表示空闲, 1 表示繁忙
private AtomicIntegerArray states;
private Semaphore semaphore;
// 4. 构造方法初始化
public Pool(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
// 让许可数与资源数一致
this.semaphore = new Semaphore(poolSize);
this.connections = new Connection[poolSize];
this.states = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[poolSize]);
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connections[i] = new MockConnection("连接" + (i+1));
}
}
// 5. 借连接
public Connection borrow() {// t1, t2, t3
// 获取许可
try {
semaphore.acquire(); // 没有许可的线程,在此等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
// 获取空闲连接
if(states.get(i) == 0) {
if (states.compareAndSet(i, 0, 1)) {
log.debug("borrow {}", connections[i]);
return connections[i];
}
}
}
// 不会执行到这里
return null;
}
// 6. 归还连接
public void free(Connection conn) {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
if (connections[i] == conn) {
states.set(i, 0);
log.debug("free {}", conn);
semaphore.release();
break;
}
}
}
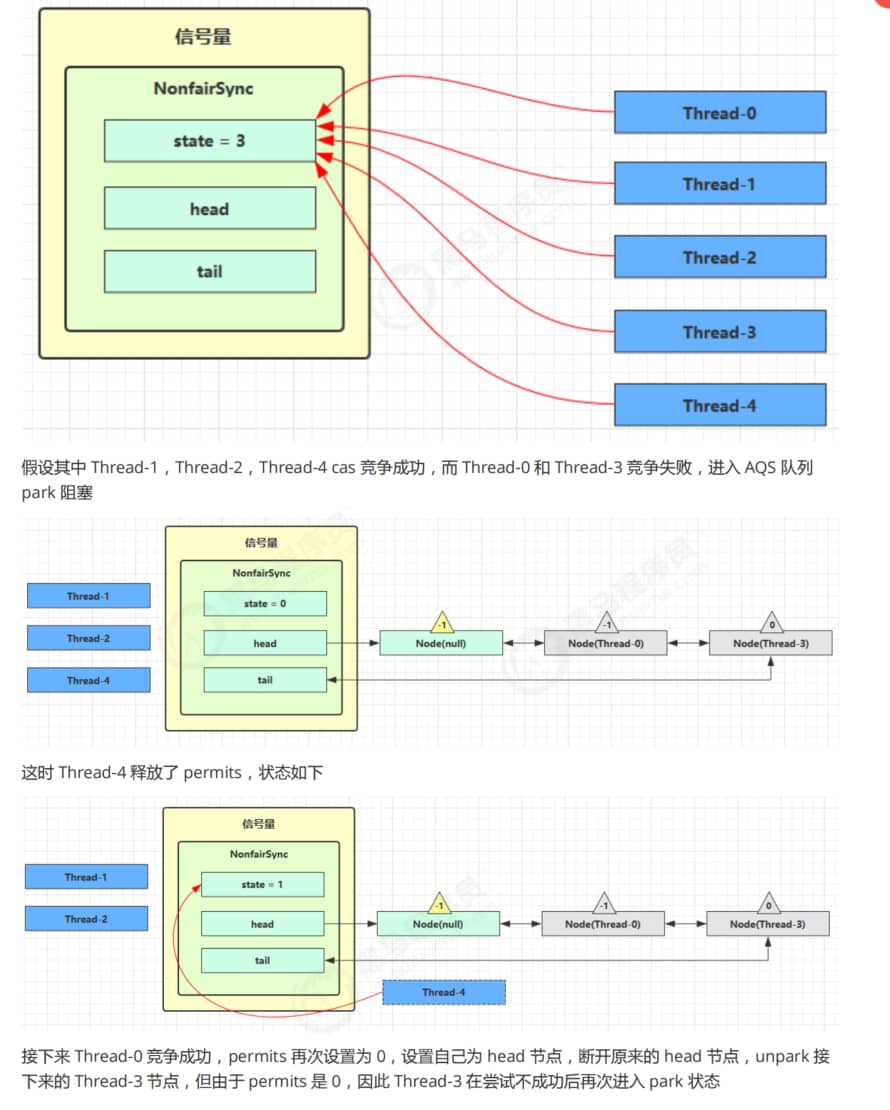
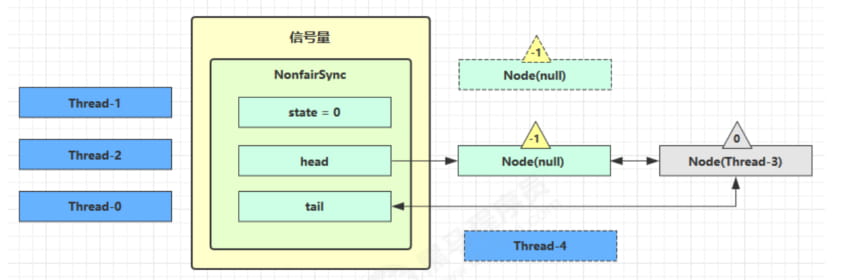
}四、Semaphore原理
到此这篇关于Java中的Semaphore信号量简析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Semaphore信号量内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
