SpringSecurity入门使用教程
作者:骑鹤下江南。
1. 第一部分 SpringSecurity入门
1.1 Spring Security简介
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。它是用于保护基于Spring的应用程序的实际标准。Spring Security是一个框架,致力于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring Security的真正强大之处在于可以轻松扩展以满足自定义要求.

1.2 Spring Security框架功能简介
- 认证: 用户登录, 解决的是"你是谁?"
- 授权: 判断用户拥有什么权限,可以访问什么资源. 解决的是"你能干什么?"
- 安全防护,防止跨站请求,session 攻击等
1.3 SpringSecurity应用场景
- 用户登录, 传统基于web开发的项目的登录功能.
- 用户授权, 在系统中用户拥有哪些操作权限
- 单一登录, 一个账号只能在同一时间只能在一个地方进行登录, 如果在其他地方进行第二次登录,则剔除之前登录操作

集成cas,做单点登录,即多个系统只需登录一次,无需重复登录
集成oauth2 ,做登录授权, 可以用于app登录和第三方登录(QQ,微信等), 也可以实现cas的功能.
1.5 SpringSecurity入门案例
快速体验SpringSecurity功能
1.创建Spring Boot 工程
使用Spring Initializr 快速过构建Spring Boot工程
Spring Boot版本选择2.3.5 , 并选中Spring Web 模块
2.编写Controller
package com.boxuegu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* security入门案例
*/
@RestController
public class HelloSecurityController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello security";
}
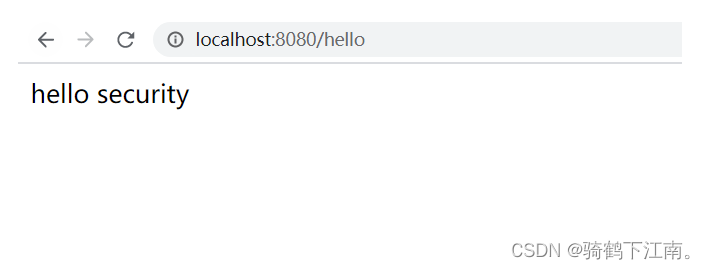
}3.访问http://localhost:8080/hello
4.添加SpringSecurity依赖
<!--添加Spring Security 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>5.重启Spring Boot启动类,再次访问http://localhost:8080/hello
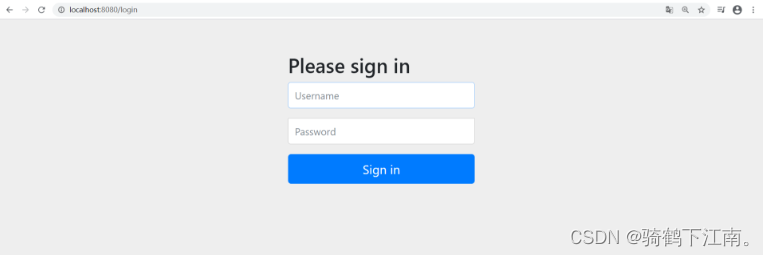
我们来观察下帮我们生成的表单页面
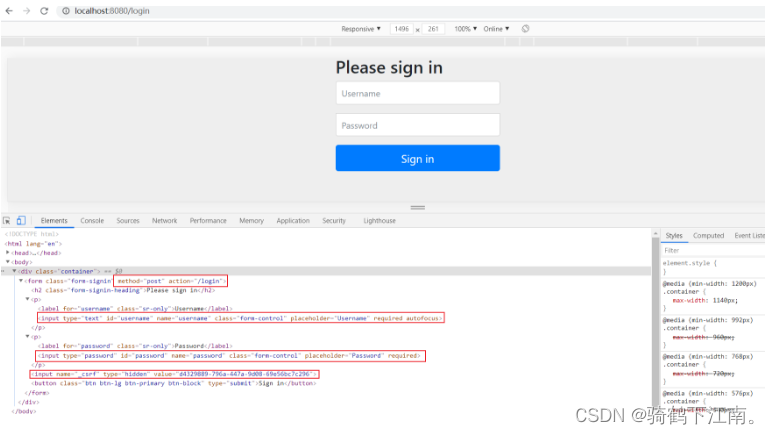
咱们先看看这个页面源代码,这里有三点需要大家注意下:
- 表单的提交方式和路径:
post/login - input输入项的name值:
usernamepassword - 隐藏域input的name: 值为:
_csrfvalue值为d4329889-796a-447a-9d08-69e56bc7c296
SpringBoot已经为SpringSecurity提供了默认配置,默认所有资源都必须认证通过才能访问。那么问题来了!此刻并没有连接数据库,也并未在内存中指定认证用户,如何认证呢?
其实SpringBoot已经提供了默认用户名user,密码在项目启动时随机生成
认证通过后可以继续访问处理器资源:

2. 第二部分 SpringSecurity认证
2.1建表语句
/*
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : localhost
Source Server Type : MySQL
Source Server Version : 50540
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Schema : security_management
Target Server Type : MySQL
Target Server Version : 50540
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 31/10/2020 14:35:33
*/
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `t_permission` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '编号',
`permission_name` varchar(30) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限名称',
`permission_tag` varchar(30) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限标签',
`permission_url` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限地址',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 9 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of t_permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (1, '查询所有用户', 'user:findAll', '/user/findAll');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (2, '用户添加或修改', 'user:saveOrUpdate', '/user/saveOrUpadate');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (3, '用户删除', 'user:delete', '/delete/{id}');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (4, '根据ID查询用户', 'user:getById', '/user/{id}');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (5, '查询所有商品', 'product:findAll', '/product/findAll');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (6, '商品添加或修改', 'product:saveOrUpdate', '/product/saveOrUpadate');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (7, '商品删除', 'product:delete', '/product//delete/{id}');
INSERT INTO `t_permission` VALUES (8, '商品是否显示', 'product:show', '/product/show/{id}/{isShow}');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_role` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '编号',
`ROLE_NAME` varchar(30) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色名称',
`ROLE_DESC` varchar(60) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色描述',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 6 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of t_role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (1, 'ADMIN', '超级管理员');
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (2, 'USER', '用户管理');
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (3, 'PRODUCT', '商品管理员');
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (4, 'PRODUCT_INPUT', '商品录入员');
INSERT INTO `t_role` VALUES (5, 'PRODUCT_SHOW', '商品审核员');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_role_permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_role_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `t_role_permission` (
`RID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色编号',
`PID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '权限编号',
PRIMARY KEY (`RID`, `PID`) USING BTREE,
INDEX `FK_Reference_12`(`PID`) USING BTREE,
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_11` FOREIGN KEY (`RID`) REFERENCES `t_role` (`ID`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_12` FOREIGN KEY (`PID`) REFERENCES `t_permission` (`ID`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of t_role_permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 1);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (2, 1);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 2);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (2, 2);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 3);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (2, 3);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 4);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (2, 4);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 5);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (3, 5);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (4, 5);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (5, 5);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 6);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (3, 6);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (4, 6);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 7);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (3, 7);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (4, 7);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (1, 8);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (3, 8);
INSERT INTO `t_role_permission` VALUES (5, 8);
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`status` int(1) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户状态1-启用 0-关闭',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 6 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_bin ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of t_user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `t_user` VALUES (1, 'admin', '$2a$10$m8WqgTzr0TO.XG.aR91.jegJJmDnGSvWs69aMWPR.WNvCzemHpLum', 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user` VALUES (2, 'zhaoyang', '$2a$10$m8WqgTzr0TO.XG.aR91.jegJJmDnGSvWs69aMWPR.WNvCzemHpLum', 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user` VALUES (3, 'user1', '$2a$10$m8WqgTzr0TO.XG.aR91.jegJJmDnGSvWs69aMWPR.WNvCzemHpLum', 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user` VALUES (4, 'user2', '$2a$10$m8WqgTzr0TO.XG.aR91.jegJJmDnGSvWs69aMWPR.WNvCzemHpLum', 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user` VALUES (5, 'user3', '$2a$10$Wk1jWJPoMQ5s7UIp0S/tu.WTcUZUspUUQH6K3BQpa8uHXWRUQc3/a', 1);
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for t_user_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user_role` (
`UID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户编号',
`RID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色编号',
PRIMARY KEY (`UID`, `RID`) USING BTREE,
INDEX `FK_Reference_10`(`RID`) USING BTREE,
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_10` FOREIGN KEY (`RID`) REFERENCES `t_role` (`ID`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_9` FOREIGN KEY (`UID`) REFERENCES `t_user` (`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of t_user_role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `t_user_role` VALUES (1, 1);
INSERT INTO `t_user_role` VALUES (2, 2);
INSERT INTO `t_user_role` VALUES (3, 4);
INSERT INTO `t_user_role` VALUES (4, 5);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;2.2 SpringSecurity认证基本原理与认证2种方式
在工程中添加Spring Security的依赖
<!--添加Spring Security 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency> 在使用SpringSecurity框架,该框架会默认自动地替我们将系统中的资源进行保护,每次访问资源的时候都必须经过一层身份的校验,如果通过了则重定向到我们输入的url中,否则访问是要被拒绝的。那么SpringSecurity框架是如何实现的呢? Spring Security功能的实现主要是由一系列过滤器相互配合完成。也称之为过滤器链
2.2.1 过滤器链介绍

过滤器是一种典型的AOP思想,下面简单了解下这些过滤器链,后续再源码剖析中在涉及到过滤器链在仔细讲解.
org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
根据请求封装获取WebAsyncManager,从WebAsyncManager获取/注册的安全上下文可调用处理拦截器
org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter主要是使用SecurityContextRepository在session中保存或更新一个SecurityContext,并将SecurityContext给以后的过滤器使用,来为后续fifilter建立所需的上下文。SecurityContext中存储了当前用户的认证以及权限信息。
org.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter
向请求的Header中添加相应的信息,可在http标签内部使用security:headers来控制
org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter
csrf又称跨域请求伪造,SpringSecurity会对所有post请求验证是否包含系统生成的csrf的token信息,如果不包含,则报错。起到防止csrf攻击的效果。
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter
匹配URL为/logout的请求,实现用户退出,清除认证信息。
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
表单认证操作全靠这个过滤器,默认匹配URL为/login且必须为POST请求。
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
如果没有在配置文件中指定认证页面,则由该过滤器生成一个默认认证页面。
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
由此过滤器可以生产一个默认的退出登录页面
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter
此过滤器会自动解析HTTP请求中头部名字为Authentication,且以Basic开头的头信息。
org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter
通过HttpSessionRequestCache内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存HttpServletRequest
org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
针对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的API
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
当SecurityContextHolder中认证信息为空,则会创建一个匿名用户存入到SecurityContextHolder中。spring security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程,只不过是一个匿名的身份。
org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter
securityContextRepository限制同一用户开启多个会话的数量
org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter
异常转换过滤器位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个链路中出现的异常
org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor
获取所配置资源访问的授权信息,根据SecurityContextHolder中存储的用户信息来决定其是否有权限。
Spring Security默认加载15个过滤器, 但是随着配置可以增加或者删除一些过滤器.
2.2.2 认证方式
1.HttpBasic认证
HttpBasic登录验证模式是Spring Security实现登录验证最简单的一种方式,也可以说是最简陋的一种方式。它的目的并不是保障登录验证的绝对安全,而是提供一种“防君子不防小人”的登录验证。
在使用的Spring Boot早期版本为1.X版本,依赖的Security 4.X版本,那么就无需任何配置,启动项目访问则会弹出默认的httpbasic认证。现在使用的是spring boot2.0以上版本(依赖Security 5.X版本),HttpBasic不再是默认的验证模式,在spring security 5.x默认的验证模式已经是表单模式。
HttpBasic模式要求传输的用户名密码使用Base64模式进行加密。如果用户名是 “admin” ,密码是“ admin”,则将字符串"admin:admin" 使用Base64编码算法加密。加密结果可能是:YWtaW46YWRtaW4=。HttpBasic模式真的是非常简单又简陋的验证模式,Base64的加密算法是可逆的,想要破解并不难.

2.formLogin登录认证模式
Spring Security的HttpBasic模式,该模式比较简单,只是进行了通过携带Http的Header进行简单的登录验证,而且没有定制的登录页面,所以使用场景比较窄。对于一个完整的应用系统,与登录验证相关的页面都是高度定制化的,非常美观而且提供多种登录方式。这就需要Spring Security支持我们自己定制登录页面, spring boot2.0以上版本(依赖Security 5.X版本)默认会生成一个登录页面.

2.3 表单认证
2.3.1 自定义表单登录页面
在config包下编写SecurityConfiguration配置类
package com.boxuegu.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
/**
* Security配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* http请求处理方法
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*http.httpBasic()//开启httpbasic认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问*/
http.formLogin()//开启表单认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;
}
}问题一: localhost将您重定向次数过多

因为设置登录页面为login.html 后面配置的是所有请求都登录认证,陷入了死循环. 所以需要将login.html放行不需要登录认证
http.formLogin().loginPage("/login.html")//开启表单认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()//放行登录页面
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;问题二: 访问login.html 报404错误
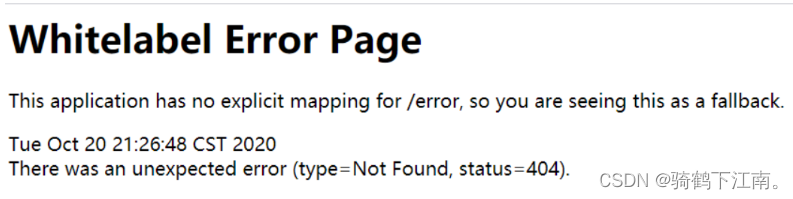
spring boot整合thymeleaf 之后 所有的静态页面以放在resources/templates下面,所以得通过请求访问到模板页面, 将/login.html修改为/toLoginPage
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLoginPage")//开启表单认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/toLoginPage").permitAll()//放行登录页面
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;问题三: 访问login.html 后发现页面没有相关样式

因为访问login.html需要一些js , css , image等静态资源信息, 所以需要将静态资源放行, 不需要认证
/**
* WebSecurity
*
* @param web
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
//解决静态资源被拦截的问题
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/css/**", "/images/**", "/js/**", "/favicon.ico");
}Spring Security中,安全构建器HttpSecurity和WebSecurity的区别是 :
WebSecurity不仅通过HttpSecurity定义某些请求的安全控制,也通过其他方式定义其他某些请求可以忽略安全控制;HttpSecurity仅用于定义需要安全控制的请求(当然HttpSecurity也可以指定某些请求不需要安全控制);- 可以认为
HttpSecurity是WebSecurity的一部分,WebSecurity是包含HttpSecurity的更大的一个概念; - 构建目标不同
- WebSecurity
构建目标是整个Spring Security安全过滤器FilterChainProxy`, HttpSecurity的构建目标仅仅是FilterChainProxy中的一个SecurityFilterChain。
- WebSecurity
2.3.2 表单登录
通过讲解过滤器链中我们知道有个过滤器UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter是处理表单登录的. 那么下面我们来通过源码观察下这个过滤器.
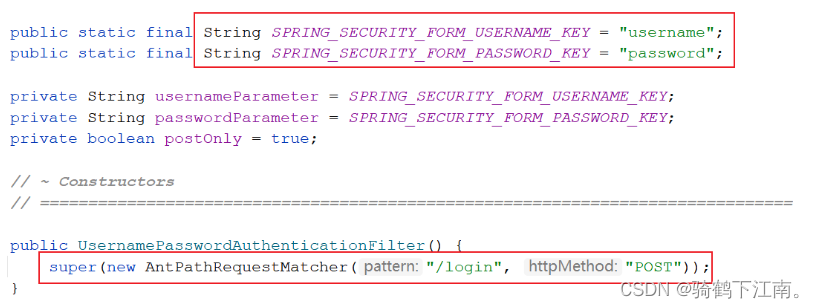
在源码中可以观察到, 表单中的input的name值是username和password, 并且表单提交的路径为/login, 表单提交方式method为post, 这些可以修改为自定义的值.
代码如下:
/**
* http请求处理方法
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*http.httpBasic()//开启httpbasic认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问*/
http.formLogin()//开启表单认证
.loginPage("/toLoginPage")//自定义登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")// 登录处理Url
.usernameParameter("username").passwordParameter("password"). //修改自定义表单name值.
.successForwardUrl("/")// 登录成功后跳转路径
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/toLoginPage").permitAll()//放行登录页面
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;
// 关闭csrf防护
http..csrf().disable();
}页面代码:

代码修改后重启完成登录:
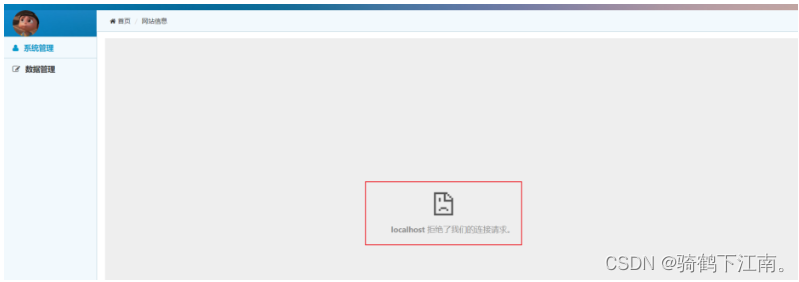
这个时候又出现新的问题了. 这个是什么原因呢? 我们来看出现问题的具体是哪里?

发现行内框架iframe这里出现问题了. Spring Security下,X-Frame-Options默认为DENY,非Spring Security环境下,X-Frame-Options的默认大多也是DENY,这种情况下,浏览器拒绝当前页面加载任何Frame页面,设置含义如下:
- DENY:浏览器拒绝当前页面加载任何Frame页面 此选择是默认的.
- SAMEORIGIN:frame页面的地址只能为同源域名下的页面
允许iframe加载
http.formLogin()//开启表单认证
.loginPage("/toLoginPage")//自定义登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")// 登录处理Url
.usernameParameter("username").passwordParameter("password"). //修改自定义表单name值.
.successForwardUrl("/")// 登录成功后跳转路径
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/toLoginPage").permitAll()//放行登录页面与静态资源
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;
// 关闭csrf防护
http.csrf().disable();
// 允许iframe加载页面
http.headers().frameOptions().sameOrigin();2.3.3 基于数据库实现认证功能
之前我们所使用的用户名和密码是来源于框架自动生成的, 那么我们如何实现基于数据库中的用户名和密码功能呢? 要实现这个得需要实现security的一个UserDetailsService接口, 重写这个接口里面loadUserByUsername即可
编写MyUserDetailsService并实现UserDetailsService接口,重写loadUserByUsername方法
package com.boxuegu.service.impl;
import com.boxuegu.domain.User;
import com.boxuegu.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* 基于数据库中完成认证
*/
@Service
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
/**
* 根据username查询用户实体
*
* @param username
* @return
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userService.findByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username);// 用户名没有找到
}
// 先声明一个权限集合, 因为构造方法里面不能传入null
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 需要返回一个SpringSecurity的UserDetails对象
UserDetails userDetails =
new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(),
"{noop}" + user.getPassword(),// {noop}表示不加密认证。
true, // 用户是否启用 true 代表启用
true,// 用户是否过期 true 代表未过期
true,// 用户凭据是否过期 true 代表未过期
true,// 用户是否锁定 true 代表未锁定
authorities);
return userDetails;
}
}在SecurityConfiguration配置类中指定自定义用户认证
/**
* 身份验证管理器
*
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(myUserDetailsService);// 使用自定义用户认证
}2.3.4 密码加密认证
在基于数据库完成用户登录的过程中,我们所是使用的密码是明文的,规则是通过对密码明文添加{noop}前缀。那么下面 Spring Security 中的密码编码进行一些探讨。
Spring Security 中PasswordEncoder就是我们对密码进行编码的工具接口。该接口只有两个功能: 一个是匹配验证。另一个是密码编码。

BCrypt算法介绍
任何应用考虑到安全,绝不能明文的方式保存密码。密码应该通过哈希算法进行加密。 有很多标准的算法比如SHA或者MD5,结合salt(盐)是一个不错的选择。 Spring Security 提供了BCryptPasswordEncoder类,实现Spring的PasswordEncoder接口使用BCrypt强哈希方法来加密密码。BCrypt强哈希方法 每次加密的结果都不一样,所以更加的安全。
bcrypt算法相对来说是运算比较慢的算法,在密码学界有句常话:越慢的算法越安全。黑客破解成本越高.通过salt和const这两个值来减缓加密过程,它的加密时间(百ms级)远远超过md5(大概1ms左右)。对于计算机来说,Bcrypt 的计算速度很慢,但是对于用户来说,这个过程不算慢。bcrypt是单向的,而且经过salt和cost的处理,使其受攻击破解的概率大大降低,同时破解的难度也提升不少,相对于MD5等加密方式更加安全,而且使用也比较简单
bcrypt加密后的字符串形如:$2a$10$wouq9P/HNgvYj2jKtUN8rOJJNRVCWvn1XoWy55N3sCkEHZPo3lyWq
其中$是分割符,无意义;2a是bcrypt加密版本号;10是const的值;而后的前22位是salt值;再然后的字符串就是密码的密文了;这里的const值即生成salt的迭代次数,默认值是10,推荐值12。
在项目中使用BCrypt
首先看下PasswordEncoderFactories 密码器工厂
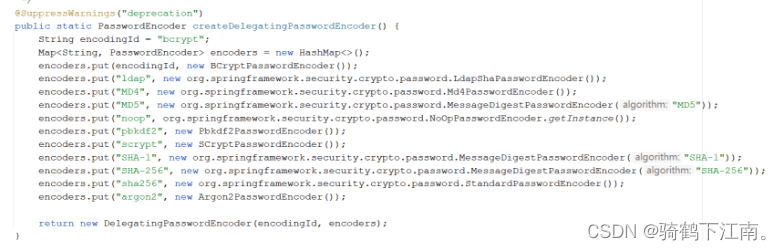
之前我们在项目中密码使用的是明文的是noop , 代表不加密使用明文密码, 现在用BCrypt只需要将noop换成bcrypt即可
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userService.findByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username);// 用户名没有找到
}
// 先声明一个权限集合, 因为构造方法里面不能传入null
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 需要返回一个SpringSecurity的UserDetails对象
UserDetails userDetails =
new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(),
"{bcrypt}" + user.getPassword(),// {noop}表示不加密认证。{bcrypt} 加密认证
true, // 用户是否启用 true 代表启用
true,// 用户是否过期 true 代表未过期
true,// 用户凭据是否过期 true 代表未过期
true,// 用户是否锁定 true 代表未锁定
authorities);
return userDetails;
}同时需要将数据库中的明文密码修改为加密密码
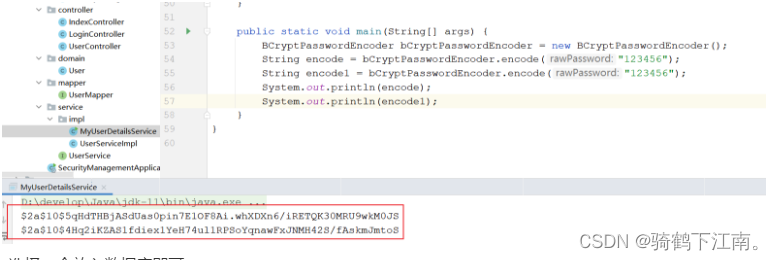
选择一个放入数据库即可.

2.3.5 获取当前登录用户
在传统web系统中, 我们将登录成功的用户放入session中, 在需要的时候可以从session中获取用户, 那么Spring Security中我们如何获取当前已经登录的用户呢?
SecurityContextHolder
保留系统当前的安全上下文SecurityContext,其中就包括当前使用系统的用户的信息。
SecurityContext
安全上下文,获取当前经过身份验证的主体或身份验证请求令牌
代码实现:
/**
* 获取当前登录用户
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/loginUser")
@ResponseBody
public UserDetails getCurrentUser() {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails)
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
return userDetails;
}除了上述方法, Spring Security 还提供了2种方式可以获取.
/**
* 获取当前登录用户
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/loginUser1")
@ResponseBody
public UserDetails getCurrentUser() {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails)
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
return userDetails;
}
/**
* 获取当前登录用户
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/loginUser2")
@ResponseBody
public UserDetails getCurrentUser(Authentication authentication) {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) authentication.getPrincipal();
return userDetails;
}
/**
* 获取当前登录用户
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/loginUser3")
@ResponseBody
public UserDetails getCurrentUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetails userDetails) {
return userDetails;
}2.3.5 remember me 记住我
在大多数网站中,都会实现RememberMe这个功能,方便用户在下一次登录时直接登录,避免再次输入用户名以及密码去登录,Spring Security针对这个功能已经帮助我们实现, 下面我们来看下他的原理图.
简单的Token生成方法
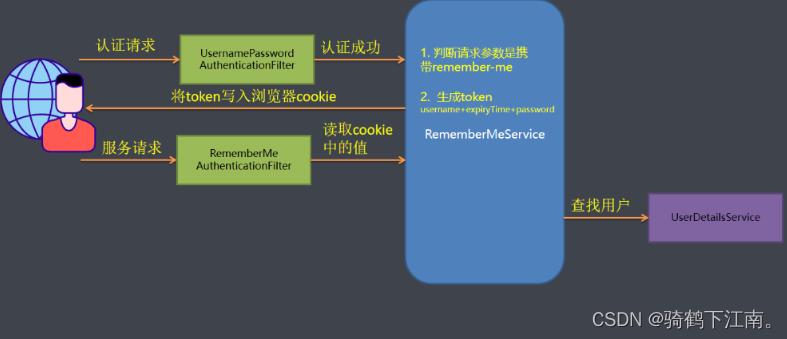
Token=MD5(username+分隔符+expiryTime+分隔符+password)
注意: 这种方式不推荐使用, 有严重的安全问题. 就是密码信息在前端浏览器cookie中存放. 如果cookie被盗取很容易破解.
代码实现:
前端页面需要增加remember-me的复选框
<div class="form-group">
<div >
<!--记住我 name为remember-me value值可选true yes 1 on 都行-->
<input type="checkbox" name="remember-me" value="true"/>记住我
</div>
</div>后台代码开启remember-me功能
.and().rememberMe()//开启记住我功能
.tokenValiditySeconds(1209600)// token失效时间默认2周
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")// 自定义表单name值登录成功后前台cookie
持久化的Token生成方法

存入数据库Token包含:
token: 随机生成策略,每次访问都会重新生成
series: 登录序列号,随机生成策略。用户输入用户名和密码登录时,该值重新生成。使用remember-me功能,该值保持不变
expiryTime: token过期时间。
CookieValue=encode(series+token)
代码实现:
后台代码
/**
* http请求处理方法
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*http.httpBasic()//开启httpbasic认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问*/
http.formLogin()//开启表单认证
.loginPage("/toLoginPage")//自定义登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")// 登录处理Url
//.usernameParameter().passwordParameter(). 修改自定义表单name值.
.successForwardUrl("/")// 登录成功后跳转路径
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/toLoginPage").permitAll()//放行登录页面与静态资源
.anyRequest().authenticated()//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;
.and().rememberMe()//开启记住我功能
.tokenValiditySeconds(1209600)// token失效时间默认2周
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")// 自定义表单name值
.tokenRepository(getPersistentTokenRepository());// 设置tokenRepository
// 关闭csrf防护
http.csrf().disable();
// 允许iframe加载页面
http.headers().frameOptions().sameOrigin();
}
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
/**
* 持久化token,负责token与数据库之间的相关操作
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository getPersistentTokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
tokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);//设置数据源
// 启动时创建一张表, 第一次启动的时候创建, 第二次启动的时候需要注释掉, 否则会报错
tokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return tokenRepository;
}项目启动成功后,观察数据库,会帮助我们创建persistent_logins表

再次完成登录功能.
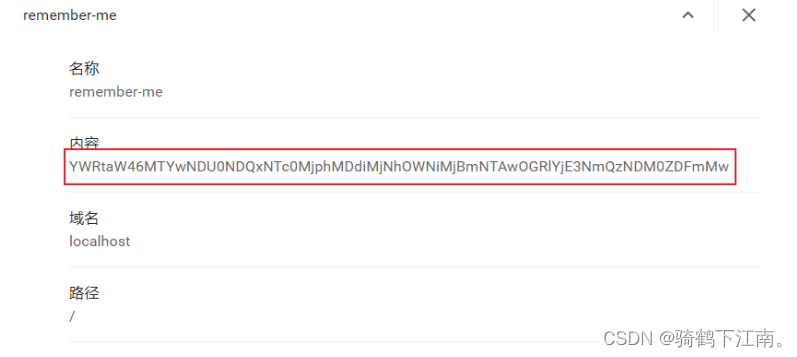
观察数据库,会插入一条记录.说明持久化token方式已经生效

再观察cookie值

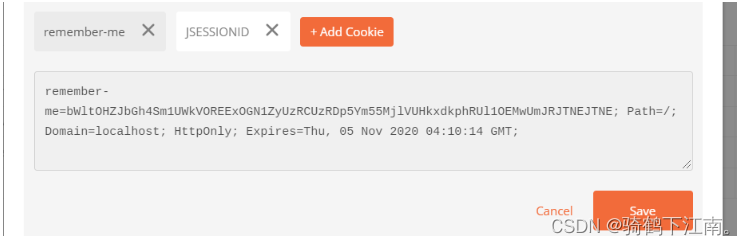
Cookie窃取伪造演示
使用网页登录系统,记录remember-me的值
使用postman 伪造cookie
安全验证
/**
* 根据用户ID查询用户
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public User getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
//获取认证信息
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// 判断认证信息是否来源于RememberMe
if (RememberMeAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication.getClass())) {
throw new RememberMeAuthenticationException("认证信息来源于RememberMe,请重新登录");
}
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
}
在重要操作步骤可以加以验证, true代表自动登录,则引导用户重新表单登录, false正常进行
#### 2.3.6 自定义登录成功处理和失败处理
在某些场景下,用户登录成功或失败的情况下用户需要执行一些后续操作,比如登录日志的搜集, 或者在现在目前前后端分离的情况下用户登录成功和失败后需要给前台页面返回对应的错误信息, 有前台主导登录成功或者失败的页面跳转. 这个时候需要要到用到AuthenticationSuccessHandler与AnthenticationFailureHandler.
**自定义成功处理:**
实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口,并重写onAnthenticationSuccesss()方法.
**自定义失败处理:**
实现AuthenticationFailureHandler接口,并重写onAuthenticationFailure()方法;
1. 代码实现登录成功或失败的自定义处理
- SecurityConfiguration类
```java
.successHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义登录成功处理
.failureHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义登录失败处理MyAuthenticationService类
package com.boxuegu.service.impl;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 自定义登录成功或失败处理类
*/
@Service
public class MyAuthenticationService implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler, AuthenticationFailureHandler {
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("登录成功后续处理....");
//重定向到index页
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/");
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("登录失败后续处理....");
//重定向到login页
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/toLoginPage");
}
}异步用户登录实现
前端页面改造
<form id="formLogin" action="/login" method="post">
<div class="panel loginbox">
.....
<div style="padding:30px;">
<input type="button" onclick="login()"
class="button button-block bg-main text-big input-big" value="登录">
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
function login() {
$.ajax({
type: "POST",//方法类型
dataType: "json",//服务器预期返回类型
url: "/login", // 登录url
data: $("#formLogin").serialize(),
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
if (data.code == 200) {
window.location.href = "/";
} else {
alert(data.message);
}
}
});
}
</script>MyAuthenticationService类改造
@Autowired
ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("登录成功后续处理....");
//redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/");
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("code", HttpStatus.OK.value());// 设置响应码
result.put("message", "登录成功");// 设置响应信息
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(result));
}
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("登录失败后续处理....");
//redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/toLoginPage");
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("code", HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value());// 设置响应码
result.put("message", exception.getMessage());// 设置错误信息
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(result));
}2.3.7 退出登录
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter
匹配URL为/logout的请求,实现用户退出,清除认证信息。
只需要发送请求,请求路径为/logout即可, 当然这个路径也可以自行在配置类中自行指定, 同时退出操作也有对应的自定义处理LogoutSuccessHandler,退出登录成功后执行,退出的同时如果有remember-me的数据,同时一并删除
前端页面
<a class="button button-little bg-red" href="/logout" rel="external nofollow" >
<span class="icon-power-off"></span>退出登录</a></div>后台代码
package com.boxuegu.service.impl;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 自定义登录成功,失败,退出处理类
*/
@Service
public class MyAuthenticationService implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler,
AuthenticationFailureHandler, LogoutSuccessHandler {
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
................
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("退出成功后续处理....");
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/toLoginPage");
}
}.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout")//设置退出url
.logoutSuccessHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义退出处理2.4 图形验证码验证
图形验证码一般是防止恶意,人眼看起来都费劲,何况是机器。不少网站为了防止用户利用机器人自动注册、登录、灌水,都采用了验证码技术。所谓验证码,就是将一串随机产生的数字或符号,生成一幅图片, 图片里加上一些干扰, 也有目前需要手动滑动的图形验证码. 这种可以有专门去做的第三方平台. 比如极验(https://www.geetest.com/), 那么本次课程讲解主要针对图形验证码.
spring security添加验证码大致可以分为三个步骤:
- 根据随机数生成验证码图片;
- 将验证码图片显示到登录页面;
- 认证流程中加入验证码校验。
Spring Security的认证校验是由UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器完成的,所以我们的验证码校验逻辑应该在这个过滤器之前。验证码通过后才能到后续的操作. 流程如下:

代码实现:
自定义验证码过滤器ValidateCodeFilter
package com.boxuegu.filter;
import com.boxuegu.controller.ValidateCodeController;
import com.boxuegu.exception.ValidateCodeException;
import com.boxuegu.service.impl.MyAuthenticationService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.ServletRequestBindingException;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 验证码验证filter 需要继承OncePerRequestFilter确保在一次请求只通过一次filter,而不需要重复执行
*/
@Component
public class ValidateCodeFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
MyAuthenticationService myAuthenticationService;
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 判断是否是登录请求,只有登录请求才去校验验证码
if (httpServletRequest.getRequestURI().equals("/login")
&& httpServletRequest.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("post")) {
try {
validate(httpServletRequest);
} catch (ValidateCodeException e) {
myAuthenticationService.onAuthenticationFailure(httpServletRequest, httpServletResponse, e);
return;
}
}
//如果不是登录请求,直接调用后面的过滤器链
filterChain.doFilter(httpServletRequest, httpServletResponse);
}
private void validate(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletRequestBindingException {
//获取ip
String remoteAddr = request.getRemoteAddr();
//拼接redis的key
String redisKey = ValidateCodeController.REDIS_KEY_IMAGE_CODE + "-" + remoteAddr;
//从redis中获取imageCode
String redisImageCode =
stringRedisTemplate.boundValueOps(redisKey).get();
String imageCode = request.getParameter("imageCode");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(imageCode)) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码的值不能为空!");
}
if (redisImageCode == null) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码已过期!");
}
if (!redisImageCode.equals(imageCode)) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码不正确!");
}
// 从redis中删除imageCode
stringRedisTemplate.delete(redisKey);
}
}自定义验证码异常类
package com.boxuegu.exception;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
/**
* 验证码异常类
*/
public class ValidateCodeException extends AuthenticationException {
public ValidateCodeException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}security配置类
@Autowired
ValidateCodeFilter validateCodeFilter;
/**
* http请求处理方法
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/*http.httpBasic()//开启httpbasic认证
.and().authorizeRequests().
anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问*/
// 加在用户名密码过滤器的前面
http.addFilterBefore(validateCodeFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
http.formLogin()//开启表单认证
.loginPage("/toLoginPage")//自定义登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")// 登录处理Url
//.usernameParameter().passwordParameter(). 修改自定义表单name值.
.successForwardUrl("/")// 登录成功后跳转路径
.successHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义登录成功处理
.failureHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义登录失败处理
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout")//设置退出url
.logoutSuccessHandler(myAuthenticationService)//自定义退出处理
.and().authorizeRequests().
antMatchers("/toLoginPage","/code/**").permitAll()//放行登录页面与静态资源
.anyRequest().authenticated()//所有请求都需要登录认证才能访问;
.and().rememberMe()//开启记住我功能
.tokenValiditySeconds(1209600)// token失效时间默认2周
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")// 自定义表单name值
.tokenRepository(getPersistentTokenRepository());// 设置tokenRepository
// 关闭csrf防护
http.csrf().disable();
// 允许iframe加载页面
http.headers().frameOptions().sameOrigin();
}2.5 session管理
Spring Security可以与Spring Session库配合使用,只需要做一些简单的配置就可以实现一些功能,如(会话过期、一个账号只能同时在线一个、集群session等)
2.5.1 会话超时
配置session会话超时时间,默认为30分钟,但是Spring Boot中的会话超时时间至少为60秒
#session设置 #配置session超时时间 server.servlet.session.timeout=60
当session超时后, 默认跳转到登录页面.
自定义设置session超时后地址
设置session管理和失效后跳转地址
http.sessionManagement()//设置session管理
.invalidSessionUrl("/toLoginPage")// session无效后跳转的路径, 默认是登录页面2.5.2 并发控制
并发控制即同一个账号同时在线个数,同一个账号同时在线个数如果设置为1表示,该账号在同一时间内只能有一个有效的登录,如果同一个账号又在其它地方登录,那么就将上次登录的会话过期,即后面的登录会踢掉前面的登录
修改超时时间
#session设置 #配置session超时时间 server.servlet.session.timeout=600
设置最大会话数量
http.sessionManagement().//设置session管理
invalidSessionUrl("/toLoginPage")// session无效后跳转的路径, 默认是登录页面
.maximumSessions(1)//设置session最大会话数量 ,1同一时间只能有一个用户登录
.expiredUrl("/toLoginPage");//设置session过期后跳转路径阻止用户第二次登录
sessionManagement也可以配置 maxSessionsPreventsLogin:boolean值,当达到maximumSessions设置的最大会话个数时阻止登录。
http.sessionManagement().//设置session管理
invalidSessionUrl("/toLoginPage")// session无效后跳转的路径, 默认是登录页面
.maximumSessions(1)//设置session最大会话数量 ,1同一时间只能有一个用户登录
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true)//当达到最大会话个数时阻止登录。
.expiredUrl("/toLoginPage");//设置session过期后跳转路径2.5.3 集群session
实际场景中一个服务会至少有两台服务器在提供服务,在服务器前面会有一个nginx做负载均衡,用户访问nginx,nginx再决定去访问哪一台服务器。当一台服务宕机了之后,另一台服务器也可以继续提供服务,保证服务不中断。如果我们将session保存在Web容器(比如tomcat)中,如果一个用户第一次访问被分配到服务器1上面需要登录,当某些访问突然被分配到服务器二上,因为服务器二上没有用户在服务器一上登录的会话session信息,服务器二还会再次让用户登录,用户已经登录了还让登录就感觉不正常了。
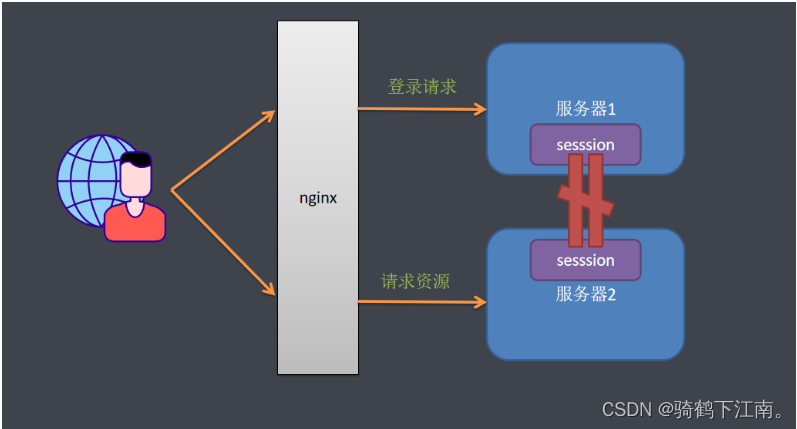
解决这个问题的思路是用户登录的会话信息不能再保存到Web服务器中,而是保存到一个单独的库(redis、mongodb、jdbc等)中,所有服务器都访问同一个库,都从同一个库来获取用户的session信息,如用户在服务器一上登录,将会话信息保存到库中,用户的下次请求被分配到服务器二,服务器二从库中检查session是否已经存在,如果存在就不用再登录了,可以直接访问服务了。
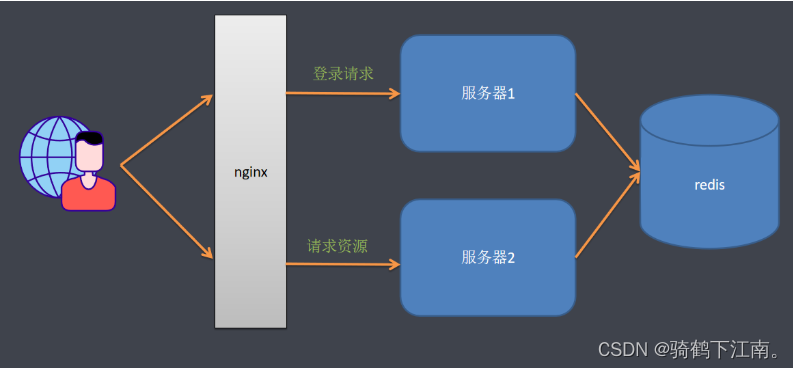
引用依赖
<!-- 基于redis实现session共享 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>设置session存储类型
#使用redis共享session spring.session.store-type=redis
测试
- 使用其中一个服务去登录 http://localhost:8080/login
- 使用另一个服务访问任意接口 ,则不需要再重新登录就可以直接访问
2.6 csrf防护机制
2.6.1 什么是csrf?
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery),中文名称:跨站请求伪造
你这可以这么理解CSRF攻击:攻击者盗用了你的身份,以你的名义发送恶意请求。CSRF能够做的事情包括:以你名义发送邮件,发消息,盗取你的账号,甚至于购买商品,虚拟货币转账…造成的问题包括:个人隐私泄露以及财产安全。
CSRF这种攻击方式在2000年已经被国外的安全人员提出,但在国内,直到06年才开始被关注,08年,国内外的多个大型社区和交互网站分别爆出CSRF漏洞,如:NYTimes.com(纽约时报)、Metafilter(一个大型的BLOG网站),YouTube和百度HI…而现在,互联网上的许多站点仍对此毫无防备,以至于安全业界称CSRF为“沉睡的巨人”。
2.6.2 CSRF的原理
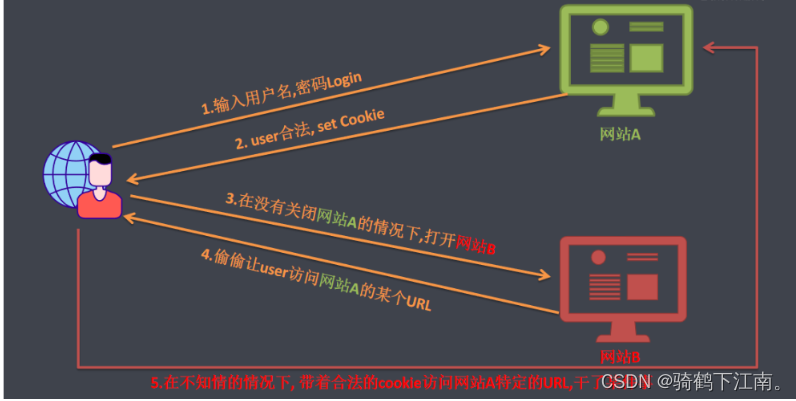
从上图可以看出,要完成一次CSRF攻击,受害者必须依次完成三个步骤:
1.登录受信任网站A,并在本地生成Cookie。
2.在不登出A的情况下,访问危险网站B。
3. 触发网站B中的一些元素
2.6.3 CSRF的防御策略
在业界目前防御 CSRF 攻击主要有三种策略:验证 HTTP Referer 字段;在请求地址中添加 token 并验证;在 HTTP 头中自定义属性并验证。
验证 HTTP Referer 字段
根据 HTTP 协议,在 HTTP 头中有一个字段叫 Referer,它记录了该 HTTP 请求的来源地址。在通常情况下,访问一个安全受限页面的请求来自于同一个网站,在后台请求验证其 Referer 值,如果是以自身安全网站开头的域名,则说明该请求是是合法的。如果 Referer 是其他网站的话,则有可能是黑客的 CSRF 攻击,拒绝该请求。
在请求地址中添加 token 并验证
CSRF 攻击之所以能够成功,是因为黑客可以完全伪造用户的请求,该请求中所有的用户验证信息都是存在于 cookie 中,因此黑客可以在不知道这些验证信息的情况下直接利用用户自己的 cookie 来通过安全验证。要抵御 CSRF,关键在于在请求中放入黑客所不能伪造的信息,并且该信息不存在于 cookie 之中。可以在 HTTP 请求中以参数的形式加入一个随机产生的 token,并在服务器端建立一个拦截器来验证这个 token,如果请求中没有 token 或者 token 内容不正确,则认为可能是 CSRF 攻击而拒绝该请求。
在 HTTP 头中自定义属性并验证
这种方法也是使用 token 并进行验证,和上一种方法不同的是,这里并不是把 token 以参数的形式置于 HTTP 请求之中,而是把它放到 HTTP 头中自定义的属性里。
2.6.4 security中的csrf防御机制
org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter
csrf又称跨站请求伪造,SpringSecurity会对所有post请求验证是否包含系统生成的csrf的token信息,如果不包含,则报错。起到防止csrf攻击的效果。(1. 生成token 2.验证token)
开启csrf防护
//开启csrf防护, 可以设置哪些不需要防护
http.csrf().ignoringAntMatchers("/user/save");页面需要添加token值
<input type="hidden" th:name="${_csrf.parameterName}" th:value="${_csrf.token}"/>3.第三部分 SpringSecurity授权
3.1 授权简介
在第二部分中我们讲解的都是用户认证, 不管是用户名密码,还是图形验证码等,最终的目的都是一个: 让系统知道你到底是谁在访问你的系统, 解决的问题是, 你是谁? 这部分主要讲解你能在系统中做什么事情, 针对这个有的叫做: 授权, 有的叫做:鉴权, 还有叫权限控制. 最终的目的就是你能在系统中能过做什么?
3.1.1 Spring Security 对授权的定义

安全权限控制问题其实就是控制能否访问url
3.1.2 Spring Security 授权原理

在我们应用系统里面,如果想要控制用户权限,需要有2部分数据。
系统配置信息数据:写着系统里面有哪些URL,每一个url拥有哪些权限才允许被访问。
另一份数据就是用户权限信息:请求用户拥有权限
系统用户发送一个请求:系统配置信息和用户权限信息作比对,如果比对成功则允许访问。
当一个系统授权规则比较简单,基本不变时候,系统的权限配置信息可以写在我们的代码里面去的。比如前台门户网站等权限比较单一,可以使用简单的授权配置即可完成,如果权限复杂, 例如办公OA, 电商后台管理系统等就不能使用写在代码里面了. 需要RBAC权限模型设计.
3.2 Spring Security 授权
3.2.1 内置权限表达式
Spring Security 使用Spring EL来支持,主要用于Web访问和方法安全上, 可以通过表达式来判断是否具有访问权限. 下面是Spring Security常用的内置表达式. ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer定义了所有的表达式
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| permitAll | 指定任何人都允许访问。 |
| denyAll | 指定任何人都不允许访问 |
| anonymous | 指定匿名用户允许访问。 |
| rememberMe | 指定已记住的用户允许访问。 |
| authenticated | 指定任何经过身份验证的用户都允许访问,不包含anonymous |
| fullyAuthenticated | 指定由经过身份验证的用户允许访问,不包含anonymous和rememberMe |
| hasRole(role) | 指定需要特定的角色的用户允许访问, 会自动在角色前面插入’ROLE_’ |
| hasAnyRole([role1,role2]) | 指定需要任意一个角色的用户允许访问, 会自动在角色前面插入’ROLE_’ |
| hasAuthority(authority) | 指定需要特定的权限的用户允许访问 |
| hasAnyAuthority([authority,authority]) | 指定需要任意一个权限的用户允许访问 |
| hasIpAddress(ip) | 指定需要特定的IP地址可以访问 |
3.2.2 url安全表达式
基于web访问使用表达式保护url请求路径.
设置url访问权限
// 设置/user/** 访问需要ADMIN角色
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("ADMIN");
// 设置/user/** 访问需要PRODUCT角色和IP地址为127.0.0.1 .hasAnyRole("PRODUCT,ADMIN")
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/product/**")
.access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN,PRODUCT') and hasIpAddress('127.0.0.1')");
// 设置自定义权限不足信息.
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);MyAccessDeniedHandler自定义权限不足类
package com.boxuegu.handle;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 自定义权限不足信息
*/
@Component
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse resp, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN);
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.getWriter().write("权限不足,请联系管理员!");
}
}设置用户对应的角色权限
// 先声明一个权限集合, 因为构造方法里面不能传入null
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
if ("admin".equalsIgnoreCase(user.getUsername())) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
} else {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_PRODUCT"));
}3.2.3 在Web 安全表达式中引用自定义Bean授权
定义自定义授权类
package com.boxuegu.service.impl;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* 自定义授权类
*/
@Component
public class MyAuthorizationService {
/**
* 检查用户是否有对应的访问权限
*
* @param authentication 登录用户
* @param request 请求对象
* @return
*/
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request) {
User user = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();
// 获取用户所有权限
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = user.getAuthorities();
// 获取用户名
String username = user.getUsername();
// 如果用户名为admin,则不需要认证
if (username.equalsIgnoreCase("admin")) {
return true;
} else {
// 循环用户的权限, 判断是否有ROLE_ADMIN权限, 有返回true
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
String role = authority.getAuthority();
if ("ROLE_ADMIN".equals(role)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}配置类
//使用自定义Bean授权
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/**").
access("@myAuthorizationService.check(authentication,request)");携带路径变量
/**
* 检查用户是否有对应的访问权限
*
* @param authentication 登录用户
* @param request 请求对象
* @param id 参数ID
* @return
*/
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, Integer id) {
if (id > 10) {
return false;
}
return true;
}//使用自定义Bean授权,并携带路径参数
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/delete/{id}").
access("@myAuthorizationService.check(authentication,request,#id)");3.2.4 Method安全表达式
针对方法级别的访问控制比较复杂,spring security提供了4种注解分别是 @PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize,
@PreFilter,@PostFilter.
开启方法级别的注解配置
在security配置类中添加注解
/** * Security配置类 */ @Configuration @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)//开启注解支持 public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter /** * Security配置类 */ @Configuration @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)//开启注解支持 public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
在方法上使用注解
@ProAuthorize : 注解适合进入方法前的权限验证
/**
* 查询所有用户
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/findAll")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")//需要ADMIN权限
public String findAll(Model model) {
List<User> userList = userService.list();
model.addAttribute("userList", userList);
return "user_list";
}
/**
* 用户修改页面跳转
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/update/{id}")
@PreAuthorize("#id<10")//针对参数权限限定 id<10可以访问
public String update(@PathVariable Integer id, Model model) {
User user = userService.getById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user_update";
}@PostAuthorize: @PostAuthorize在方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限,Spring EL提供返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取到返回对象的 returnObject
/**
* 根据ID查询用户
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@ResponseBody
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.username== authentication.principal.username")//判断查询用户信息是否是当前登录用户信息.否则没有权限
public User getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
} returnObject : 代表return返回的值
@PreFilter: 可以用来对集合类型的参数进行过滤, 将不符合条件的元素剔除集合
/**
* 商品删除-多选删除
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/delByIds")
@PreFilter(filterTarget = "ids", value = "filterObject%2==0")//剔除参数为基数的值
public String delByIds(@RequestParam(value = "id") List<Integer> ids) {
for (Integer id : ids) {
System.out.println(id);
}
return "redirect:/user/findAll";
}@PostFilter: 可以用来对集合类型的返回值进行过滤, 将不符合条件的元素剔除集合
/**
* 查询所有用户-返回json数据
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/findAllTOJson")
@ResponseBody
@PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0")//剔除返回值ID为偶数的值
public List<User> findAllTOJson() {
List<User> userList = userService.list();
return userList;
}3.3 基于数据库的RBAC数据模型的权限控制
我们开发一个系统,必然面临权限控制的问题,不同的用户具有不同的访问、操作、数据权限。形成理论的权限控制模型有:自主访问控制(DAC: Discretionary Access Control)、强制访问控制(MAC: Mandatory Access Control)、基于属性的权限验证(ABAC: Attribute-Based Access Control)等。最常被开发者使用也是相对易用、通用的就是RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)
3.3.1 RBAC权限模型简介
RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)即:基于角色的权限控制。模型中有几个关键的术语:
- 用户:系统接口及访问的操作者
- 权限:能够访问某接口或者做某操作的授权资格
- 角色:具有一类相同操作权限的总称
RBAC权限模型核心授权逻辑如下:
某用户是什么角色?某角色具有什么权限?通过角色对应的权限推导出用户的权限 3.3.2 RBAC的演化进程
用户与权限直接关联

想到权限控制,人们最先想到的一定是用户与权限直接关联的模式,简单地说就是:某个用户具有某些权限。如图:
- 张三具有所有权限他可能是一个超级管理员.
- 李四,王五 具有添加商品和审核商品的权限有可能是一个普通业务员
这种模型能够清晰的表达用户与权限之间的关系,足够简单。但同时也存在问题:
- 现在用户是张三、李四,王五以后随着人员增加,每一个用户都需要重新授权
- 操作人员的他的权限发生变更后,需要对每个一个用户重新授予新的权限
用户与角色关联
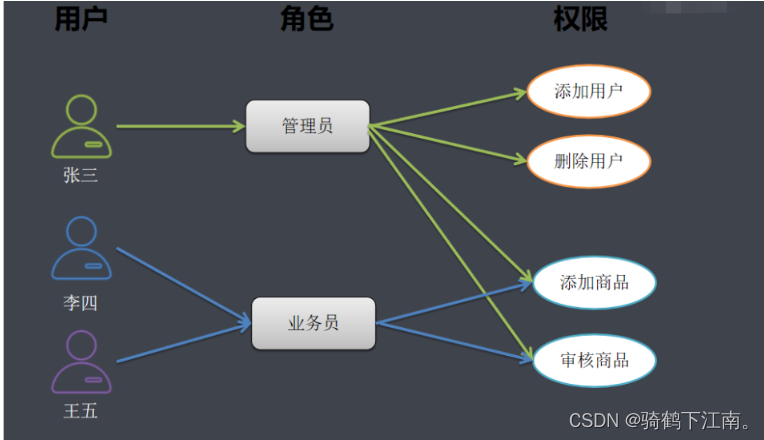
这样只需要维护角色和权限之间的关系就可以了. 如果业务员的权限发生变更, 只需要变动业务员角色和权限之前的关系进行维护就可以了. 用户和权限就分离开来了. 如下图

3.3.3 基于RBAC设计权限表结构
- 一个用户有一个或多个角色
- 一个角色包含多个用户
- 一个角色有多种权限
- 一个权限属于多个角色
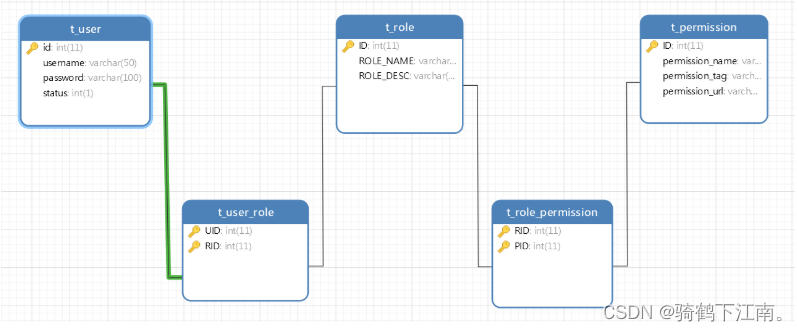
3.3.4 基于Spring Security 实现RBAC权限管理
动态查询数据库中用户对应的权限
package com.boxuegu.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.boxuegu.domain.Permission;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
public interface PermissionMapper extends BaseMapper<Permission> {
/**
* 根据用户ID查询权限
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Select("SELECT p.* FROM t_permission p,t_role_permission rp,t_role r,t_user_role ur,t_user u " +
"WHERE p.id = rp.PID AND rp.RID = r.id AND r.id = ur.RID AND ur.UID = u.id AND u.id =#{id}")
List<Permission> findByUserId(Integer id);
}给登录用户授权
// 先声明一个权限集合, 因为构造方法里面不能传入null
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 查询用户对应所有权限
List<Permission> permissions = permissionService.findByUserId(user.getId());
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
// 授权
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission.getPermissionTag()));
}设置访问权限
// 查询数据库所有权限列表
List<Permission> permissions = permissionService.list();
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
//添加请求权限
http.authorizeRequests().
antMatchers(permission.getPermissionUrl()).hasAuthority(permission.getPermissionTag());
}3.4 基于页面端标签的权限控制
在jsp页面或者thymeleaf模板页面中我们可以使用spring security提供的权限标签来进行权限控制.要想使用thymeleaf为SpringSecurity提供的标签属性,首先需要引入thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity依赖支持。
在pom 文件中的引入springsecurity的标签依赖thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5。
<!--添加thymeleaf为SpringSecurity提供的标签 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>在html文件里面申明使用
!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security">3.4.1 常用SpringSecurity的标签属性介绍
判断用户是否已经登陆认证,引号内的参数必须是isAuthenticated()。
sec:authorize=“isAuthenticated()”
获得当前用户的用户名,引号内的参数必须是name。
sec:authentication=“name”判断当前用户是否拥有指定的权限。引号内的参数为权限的名称。
sec:authorize=“hasRole(‘role’)”
3.4.2 SpringSecurity标签的使用
<div class="leftnav">
<div class="leftnav-title">
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
<span sec:authentication="name"></span>
<img src="images/y.jpg" class="radius-circle rotate-hover" height="50" alt=""/></div>
</div>
<div sec:authorize="hasAuthority('user:findAll')">
<h2><span class="icon-user"></span>系统管理</h2>
<ul style="display:block">
<li><a href="/user/findAll" target="right"><span class="icon-caret-right"></span>用户管理</a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:void(0)" onclick="toCors()" target="right"><span
class="icon-caret-right"></span>跨域测试</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div sec:authorize="hasAuthority('product:findAll')">
<h2><span class="icon-pencil-square-o"></span>数据管理</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="/product/findAll" target="right"><span class="icon-caret-right"></span>商品管理</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>签属性,首先需要引入thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity依赖支持。
在pom 文件中的引入springsecurity的标签依赖thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5。
<!--添加thymeleaf为SpringSecurity提供的标签 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>在html文件里面申明使用
!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security">3.4.1 常用SpringSecurity的标签属性介绍
判断用户是否已经登陆认证,引号内的参数必须是isAuthenticated()。
sec:authorize=“isAuthenticated()”
获得当前用户的用户名,引号内的参数必须是name。
sec:authentication=“name”判断当前用户是否拥有指定的权限。引号内的参数为权限的名称。
sec:authorize=“hasRole(‘role’)”
3.4.2 SpringSecurity标签的使用
<div class="leftnav">
<div class="leftnav-title">
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
<span sec:authentication="name"></span>
<img src="images/y.jpg" class="radius-circle rotate-hover" height="50" alt=""/></div>
</div>
<div sec:authorize="hasAuthority('user:findAll')">
<h2><span class="icon-user"></span>系统管理</h2>
<ul style="display:block">
<li><a href="/user/findAll" target="right"><span class="icon-caret-right"></span>用户管理</a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:void(0)" onclick="toCors()" target="right"><span
class="icon-caret-right"></span>跨域测试</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div sec:authorize="hasAuthority('product:findAll')">
<h2><span class="icon-pencil-square-o"></span>数据管理</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="/product/findAll" target="right"><span class="icon-caret-right"></span>商品管理</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>到此这篇关于如何使用SpringSecurity的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringSecurity使用内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- springsecurity实现拦截器的使用示例
- SpringSecurity整合JWT的使用示例
- SpringSecurity拦截器链的使用详解
- SpringSecurity实现权限认证与授权的使用示例
- SpringSecurity默认登录页的使用示例教程
- 使用SpringSecurity+defaultSuccessUrl不跳转指定页面的问题解决方法
- springsecurity实现用户登录认证快速使用示例代码(前后端分离项目)
- Spring Security 使用 OncePerRequestFilter 过滤器校验登录过期、请求日志等操作
- Spring Security使用多种加密方式进行密码校验的代码示例
- 新版SpringSecurity5.x使用与配置详解
