C/C++ Zlib库封装MyZip压缩类的详细过程
作者:微软技术分享
Zlib是一个开源的数据压缩库,提供了一种通用的数据压缩和解压缩算法。它最初由Jean-Loup Gailly和Mark Adler开发,旨在成为一个高效、轻量级的压缩库,其被广泛应用于许多领域,包括网络通信、文件压缩、数据库系统等。其压缩算法是基于DEFLATE算法,这是一种无损数据压缩算法,通常能够提供相当高的压缩比。
在软件开发中,文件的压缩和解压缩是一项常见的任务,而ZIP是一种被广泛应用的压缩格式。为了方便地处理ZIP压缩和解压缩操作,开发者通常使用各种编程语言和库来实现这些功能。本文将聚焦于一个简化的C++实现,通过分析代码,我们将深入了解其设计和实现细节。
类的功能实现
MyZip类旨在提供简单易用的ZIP压缩和解压缩功能。通过成员函数Compress和UnCompress,该类使得对目录的ZIP压缩和ZIP文件的解压变得相对容易。
ZIP压缩函数 Compress
Compress函数通过zlib库提供的ZIP压缩功能,递归地将目录下的文件添加到ZIP文件中。其中,nyCollectfileInDirtoZip函数负责遍历目录,而nyAddfiletoZip函数则用于添加文件到ZIP中。这种设计使得代码模块化,易于理解。
ZIP解压函数 UnCompress
UnCompress函数通过zlib库提供的ZIP解压功能,将ZIP文件解压到指定目录。函数中使用了unz系列函数来遍历ZIP文件中的文件信息,并根据文件类型进行相应的处理。这包括创建目录和写入文件,使得解压后的目录结构与ZIP文件一致。
将如上的压缩与解压方法封装成MyZip类,调用zip.Compress()实现压缩目录,调用zip.UnCompress()则实现解压缩目录。这些函数使用了zlib库的ZIP压缩和解压缩功能,并可以在项目中被应用,该类代码如下所示;
#define ZLIB_WINAPI
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <Shlwapi.h>
#include <zip.h>
#include <unzip.h>
#include <zlib.h>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(lib, "Shlwapi.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "zlibstat.lib")
class MyZip
{
private:
// 向ZIP文件中添加文件
bool nyAddfiletoZip(zipFile zfile, const std::string& fileNameinZip, const std::string& srcfile)
{
if (NULL == zfile || fileNameinZip.empty())
{
return false;
}
int nErr = 0;
zip_fileinfo zinfo = { 0 };
tm_zip tmz = { 0 };
zinfo.tmz_date = tmz;
zinfo.dosDate = 0;
zinfo.internal_fa = 0;
zinfo.external_fa = 0;
// 构建新文件名
char sznewfileName[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
memset(sznewfileName, 0x00, sizeof(sznewfileName));
strcat_s(sznewfileName, fileNameinZip.c_str());
if (srcfile.empty())
{
strcat_s(sznewfileName, "\\");
}
// 在ZIP中打开新文件
nErr = zipOpenNewFileInZip(zfile, sznewfileName, &zinfo, NULL, 0, NULL, 0, NULL, Z_DEFLATED, Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION);
if (nErr != ZIP_OK)
{
return false;
}
// 如果有源文件,读取并写入ZIP文件
if (!srcfile.empty())
{
FILE* srcfp = _fsopen(srcfile.c_str(), "rb", _SH_DENYNO);
if (NULL == srcfp)
{
return false;
}
int numBytes = 0;
char* pBuf = new char[1024 * 100];
if (NULL == pBuf)
{
return false;
}
// 逐块读取源文件并写入ZIP
while (!feof(srcfp))
{
memset(pBuf, 0x00, sizeof(pBuf));
numBytes = fread(pBuf, 1, sizeof(pBuf), srcfp);
nErr = zipWriteInFileInZip(zfile, pBuf, numBytes);
if (ferror(srcfp))
{
break;
}
}
delete[] pBuf;
fclose(srcfp);
}
// 关闭ZIP文件中的当前文件
zipCloseFileInZip(zfile);
return true;
}
// 递归地将目录下的文件添加到ZIP
bool nyCollectfileInDirtoZip(zipFile zfile, const std::string& filepath, const std::string& parentdirName)
{
if (NULL == zfile || filepath.empty())
{
return false;
}
bool bFile = false;
std::string relativepath = "";
WIN32_FIND_DATAA findFileData;
char szpath[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
if (::PathIsDirectoryA(filepath.c_str()))
{
strcpy_s(szpath, sizeof(szpath) / sizeof(szpath[0]), filepath.c_str());
int len = strlen(szpath) + strlen("\\*.*") + 1;
strcat_s(szpath, len, "\\*.*");
}
else
{
bFile = true;
strcpy_s(szpath, sizeof(szpath) / sizeof(szpath[0]), filepath.c_str());
}
HANDLE hFile = ::FindFirstFileA(szpath, &findFileData);
if (NULL == hFile)
{
return false;
}
do
{
// 构建相对路径
if (parentdirName.empty())
relativepath = findFileData.cFileName;
else
relativepath = parentdirName + "\\" + findFileData.cFileName;
// 如果是目录,递归处理子目录
if (findFileData.dwFileAttributes == FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY)
{
if (strcmp(findFileData.cFileName, ".") != 0 && strcmp(findFileData.cFileName, "..") != 0)
{
nyAddfiletoZip(zfile, relativepath, "");
char szTemp[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
strcpy_s(szTemp, filepath.c_str());
strcat_s(szTemp, "\\");
strcat_s(szTemp, findFileData.cFileName);
nyCollectfileInDirtoZip(zfile, szTemp, relativepath);
}
continue;
}
char szTemp[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
if (bFile)
{
strcpy_s(szTemp, filepath.c_str());
}
else
{
strcpy_s(szTemp, filepath.c_str());
strcat_s(szTemp, "\\");
strcat_s(szTemp, findFileData.cFileName);
}
// 将文件添加到ZIP
nyAddfiletoZip(zfile, relativepath, szTemp);
} while (::FindNextFileA(hFile, &findFileData));
FindClose(hFile);
return true;
}
// 替换字符串中的所有指定子串
std::string& replace_all(std::string& str, const std::string& old_value, const std::string& new_value)
{
while (true)
{
std::string::size_type pos(0);
if ((pos = str.find(old_value)) != std::string::npos)
str.replace(pos, old_value.length(), new_value);
else
break;
}
return str;
}
// 创建多级目录
BOOL CreatedMultipleDirectory(const std::string& direct)
{
std::string Directoryname = direct;
if (Directoryname[Directoryname.length() - 1] != '\\')
{
Directoryname.append(1, '\\');
}
std::vector< std::string> vpath;
std::string strtemp;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
// 遍历目录字符串,逐级创建目录
for (int i = 0; i < Directoryname.length(); i++)
{
if (Directoryname[i] != '\\')
{
strtemp.append(1, Directoryname[i]);
}
else
{
vpath.push_back(strtemp);
strtemp.append(1, '\\');
}
}
std::vector< std::string>::iterator vIter = vpath.begin();
for (; vIter != vpath.end(); vIter++)
{
bSuccess = CreateDirectoryA(vIter->c_str(), NULL) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
return bSuccess;
}
public:
// 压缩目录
bool Compress(const std::string& dirpathName, const std::string& zipfileName, const std::string& parentdirName)
{
bool bRet = false;
zipFile zFile = NULL;
// 根据ZIP文件是否存在选择打开方式
if (!::PathFileExistsA(zipfileName.c_str()))
{
zFile = zipOpen(zipfileName.c_str(), APPEND_STATUS_CREATE);
}
else
{
zFile = zipOpen(zipfileName.c_str(), APPEND_STATUS_ADDINZIP);
}
if (NULL == zFile)
{
return bRet;
}
// 将目录下的文件添加到ZIP
if (nyCollectfileInDirtoZip(zFile, dirpathName, parentdirName))
{
bRet = true;
}
zipClose(zFile, NULL);
return bRet;
}
// 解压目录
bool UnCompress(const std::string& strFilePath, const std::string& strTempPath)
{
int nReturnValue;
string tempFilePath;
string srcFilePath(strFilePath);
string destFilePath;
// 打开ZIP文件
unzFile unzfile = unzOpen(srcFilePath.c_str());
if (unzfile == NULL)
{
return false;
}
unz_global_info* pGlobalInfo = new unz_global_info;
nReturnValue = unzGetGlobalInfo(unzfile, pGlobalInfo);
if (nReturnValue != UNZ_OK)
{
return false;
}
unz_file_info* pFileInfo = new unz_file_info;
char szZipFName[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
char szExtraName[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
char szCommName[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < pGlobalInfo->number_entry; i++)
{
nReturnValue = unzGetCurrentFileInfo(unzfile, pFileInfo, szZipFName, MAX_PATH, szExtraName, MAX_PATH, szCommName, MAX_PATH);
if (nReturnValue != UNZ_OK)
return false;
string strZipFName = szZipFName;
// 如果是目录,创建相应目录
if (pFileInfo->external_fa == FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY || (strZipFName.rfind('/') == strZipFName.length() - 1))
{
destFilePath = strTempPath + "//" + szZipFName;
CreateDirectoryA(destFilePath.c_str(), NULL);
}
else
{
string strFullFilePath;
tempFilePath = strTempPath + "/" + szZipFName;
strFullFilePath = tempFilePath;
int nPos = tempFilePath.rfind("/");
int nPosRev = tempFilePath.rfind("\\");
if (nPosRev == string::npos && nPos == string::npos)
continue;
size_t nSplitPos = nPos > nPosRev ? nPos : nPosRev;
destFilePath = tempFilePath.substr(0, nSplitPos + 1);
// 创建多级目录
if (!PathIsDirectoryA(destFilePath.c_str()))
{
destFilePath = replace_all(destFilePath, "/", "\\");
int bRet = CreatedMultipleDirectory(destFilePath);
}
strFullFilePath = replace_all(strFullFilePath, "/", "\\");
// 创建文件并写入数据
HANDLE hFile = CreateFileA(strFullFilePath.c_str(), GENERIC_WRITE, 0, NULL, OPEN_ALWAYS, FILE_FLAG_WRITE_THROUGH, NULL);
if (hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
return false;
}
nReturnValue = unzOpenCurrentFile(unzfile);
if (nReturnValue != UNZ_OK)
{
CloseHandle(hFile);
return false;
}
uLong BUFFER_SIZE = pFileInfo->uncompressed_size;
void* szReadBuffer = NULL;
szReadBuffer = (char*)malloc(BUFFER_SIZE);
if (NULL == szReadBuffer)
{
break;
}
// 逐块读取ZIP文件并写入目标文件
while (TRUE)
{
memset(szReadBuffer, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
int nReadFileSize = 0;
nReadFileSize = unzReadCurrentFile(unzfile, szReadBuffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (nReadFileSize < 0)
{
unzCloseCurrentFile(unzfile);
CloseHandle(hFile);
return false;
}
else if (nReadFileSize == 0)
{
unzCloseCurrentFile(unzfile);
CloseHandle(hFile);
break;
}
else
{
DWORD dWrite = 0;
BOOL bWriteSuccessed = WriteFile(hFile, szReadBuffer, BUFFER_SIZE, &dWrite, NULL);
if (!bWriteSuccessed)
{
unzCloseCurrentFile(unzfile);
CloseHandle(hFile);
return false;
}
}
}
free(szReadBuffer);
}
unzGoToNextFile(unzfile);
}
delete pFileInfo;
delete pGlobalInfo;
if (unzfile)
{
unzClose(unzfile);
}
return true;
}
};如何使用类
压缩文件时可以通过调用zip.Compress()函数实现,该函数接受3个参数,第一个参数是需要压缩的目录名,第二个参数是压缩后保存的文件名,第三个参数则是压缩后主目录的名字,我们以压缩D:\\csdn目录下的所有文件为例,代码如下所示;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
MyZip zip;
// 压缩目录
std::string compress_src = "D:\\csdn"; // 压缩目录
std::string compress_dst = "D:\\test.zip"; // 压缩后
bool compress_flag = zip.Compress(compress_src, compress_dst, "lyshark");
std::cout << "压缩状态: " << compress_flag << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}压缩后可以看到对应的压缩包内容,如下所示;
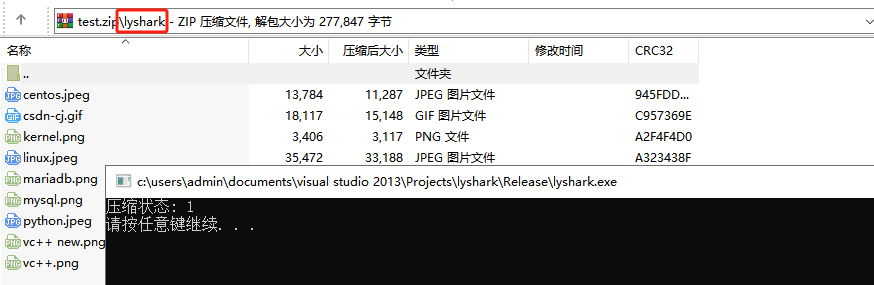
解压缩与压缩类似,通过调用zip.UnCompress实现,该方法需要传入两个参数,被压缩的文件名和解压到的目录名,如果目录不存在则会创建并解压。
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
MyZip zip;
// 解压缩目录
std::string uncompress_src = "D:\\test.zip"; // 被解压文件
std::string uncompress_dst = "D:\\dst"; // 解压到
bool compress_flag = zip.UnCompress(uncompress_src, uncompress_dst);
std::cout << "解压缩状态: " << compress_flag << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}输出效果如下所示;

到此这篇关于C/C++ Zlib库封装MyZip压缩类的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++封装Zlib库内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
