SpringBoot手写自定义starter源码
作者:刻苦的樊同学
1,前言
(1)SpringBoot的优点
SpringBoot是新一代流行的Spring应用开发框架,它具有更多的优点:
- 创建独立的Spring应用
- 内嵌Tomcat、Jetty或Undertow(无需部署war包)
- 提供自用的starter来简化构建配置
- 提供指标监控、运行状况检查和外部化配置
- 没有代码生成,也不需要XML配置(约定大于配置)
(2)SpringBoot-starter的作用
SpringBoot拥有很多方便使用的starter(Spring提供的starter命名规范spring-boot-starter-xxx.jar,第三方提供的starter命名规范xxx-spring-boot-starter.jar),比如spring-boot-starter-log4j、mybatis-spring-boot-starter.jar等,各自都代表了一个相对完整的功能模块。
SpringBoot-starter是一个集成接合器,完成两件事:
- 引入模块所需的相关jar包
- 自动配置各自模块所需的属性
2,为什么要自定义starter?
在我们的日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,我们经常将其放到一个特定的包下,然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,麻烦至极。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可,SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配,简直不要太爽。
3,自定义starter的实现方式
首先新建一个maven工程,切记,只是一个maven工程而已,并非springboot工程!
(1)引入自动配置依赖和自动提示依赖
自动提示就是在properties或yml配置文件中输入时自动提示!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--输入properties或yml会自动提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
(2)写一个TestBean,装载信息
public class TestBean {
private String msg;
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestBean{" +
"msg='" + msg + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(3)写一个Properties类
该类上面的注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")是获取配置文件的配置前缀为hello的值,然后赋值给msg变量
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
public class HelloServiceProperties {
private static final String MSG="hello world";
private String msg=MSG;
public static String getMSG() {
return MSG;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
(4)写一个自动配置类 MyAutoConfiguration
引用定义好的配置信息;在AutoConfiguration中实现所有starter应该完成的操作,并且把这个类加入spring.factories配置文件中进行声明
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({TestBean.class})//判断当前classpath下是否存在指定类,若是则将当前的配置装载入spring容器
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloServiceProperties.class)//激活自动配置(指定文件中的配置)
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloServiceProperties helloServiceProperties;//注入测试的配置信息类
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(TestBean.class) //当前上下文中没有TestBean实例时创建实例
public TestBean getTestService(){
TestBean testBean=new TestBean();
testBean.setMsg(helloServiceProperties.getMsg());
return testBean;
}
}
完成上面的操作还不够,最重要的一步是接下来的一步 在resources文件夹下新建文件夹META-INF/spring.factories,将上面的自定义配置类MyAutoConfiguration的全路径名+类名配置到该文件中(遵循spring.factories的格式),这样随着项目的启动就可以实现自动装配! 文件内容
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.ftx.tomcat.bean.MyAutoConfiguration
(5)把本maven项目打包,上传到maven私服
使用maven构建工具打包自定义starter项目
mvn clean install
然后上传到maven私服上,再新建一个springboot项目,把私服和starter项目的maven依赖配置到pom文件中
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ftx.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>write-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
</dependency>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>nexus</id>
<name>nexus</name>
<url>http://nexus.tiger2.cn/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
可以找到对应的jar包
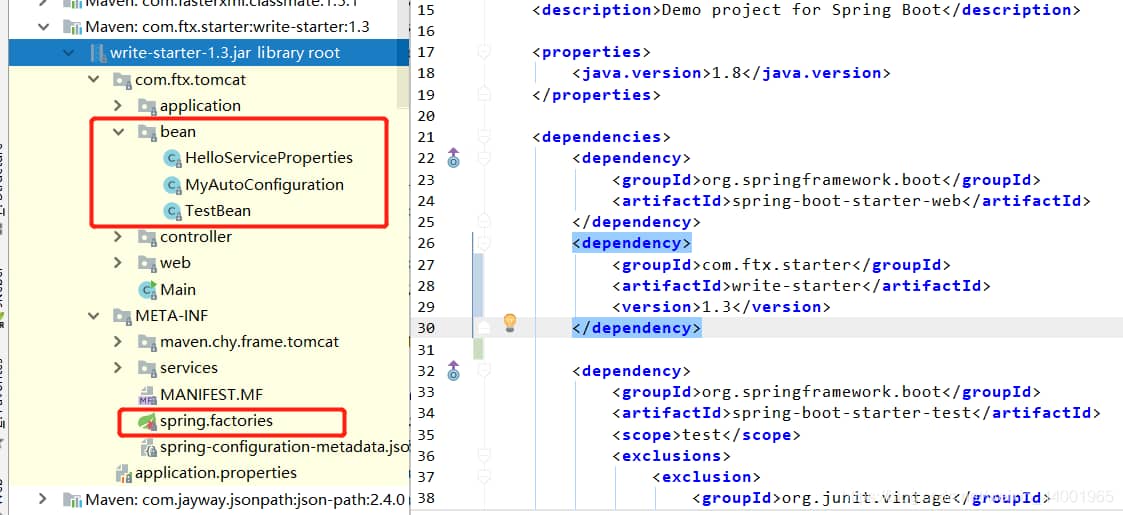
(6)测试
在新建的springboot项目中写一个TestController进行测试 注入TestBean,并使用TestBean
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
TestBean testBean;
@RequestMapping("/user")
public String user(){
User user=new User();
user.setName(testBean.getMsg());
return user.toString();
}
}
然后启动项目,访问//localhost:8080/test/user

因为TestBean的msg默认是hello world,可以在配置文件中自定义TestBean的msg信息
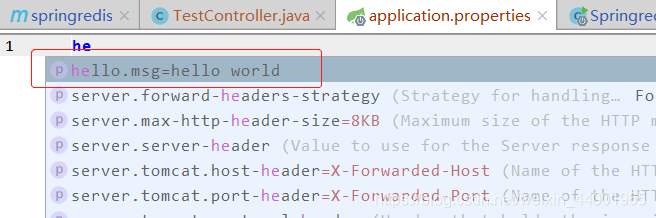
这就是自动提示的效果
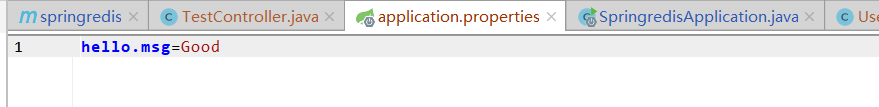
然后重启项目,重新访问//localhost:8080/test/user

到这里就已经结束了!还没看出来starter的好处吗?
到此这篇关于SpringBoot手写自定义starter源码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关自定义starter源码内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
