关于使用ContextClassLoader遇到的问题
作者:sunct
这篇文章主要介绍了关于使用ContextClassLoader遇到的问题,ContextClassLoader是通过Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()返回该线程上下文的ClassLoader,需要的朋友可以参考下
关于使用ContextClassLoader遇到的问题
对ContextClassLoader有一些疑惑:
- 父线程加载的Class,子线程是否可以使用该Class? 答:可以
- 子线程加载的Class,父线程是否可以使用该Class? 答:不可以
- 如果一个线程加载的Class,其他线程是否可以使用该Class ? 答:不可以
- 怎么使用ContextClassLoader才是正确姿势呢? 答:取出->更改->还原(finally语句块)。
关于上述4点疑问,做了以下测试:
父线程加载的Class,子线程是否可以使用该Class?
/**
* Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
* 如果父线程加载了某个class, 那么子线程也可以使用该class
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
MyClassLoader classLoader = new MyClassLoader();
classLoader.setClassFile(new File("D:\\UserService3Impl.class"));
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
try {
classLoader.loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Class<?> userClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
System.out.println(userClass);
UserService3 userObj = (UserService3)userClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> " + userObj.getUserNo());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread.start();
}
}运行结果:
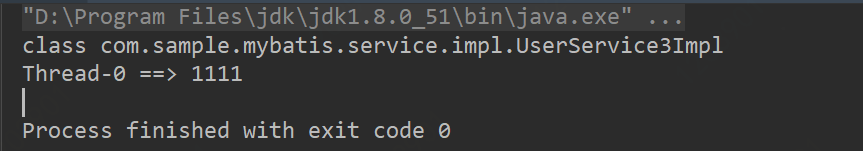
结论:父线程加载的Class,子线程是可以使用该Class
子线程加载的Class,父线程是否可以使用该Class?
/**
* Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
* 如果子线程加载了某个class, 那么父线程不能共享到该class
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
MyClassLoader classLoader = new MyClassLoader();
classLoader.setClassFile(new File("D:\\UserService3Impl.class"));
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
try {
classLoader.loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread.start();
thread.join();
Class<?> userClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
System.out.println(userClass);
UserService3 userObj = (UserService3) userClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> " + userObj.getUserNo());
}
}运行结果:
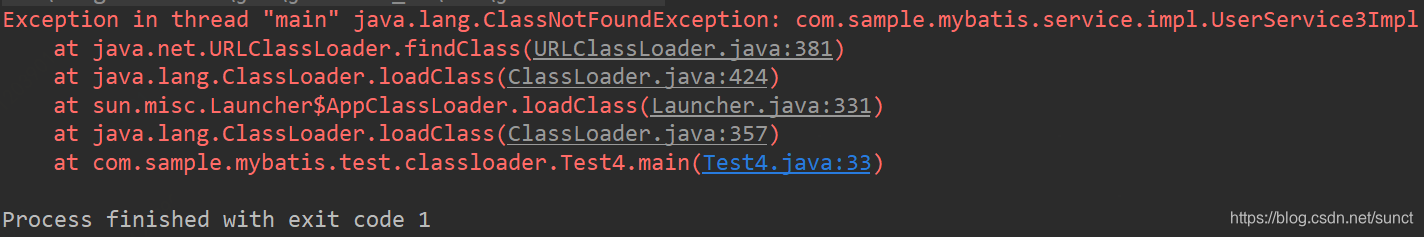
结论:子线程加载的Class,父线程是不可以使用该Class
如果一个线程加载的Class,其他线程是否可以使用该Class?
测试代码:
/**
* 如果两个线程不是父子线程, 线程之间不会共享加载过的class
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
MyClassLoader classLoader = new MyClassLoader();
classLoader.setClassFile(new File("D:\\UserService3Impl.class"));
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
Class<?> userClass = null;
try {
userClass = classLoader.loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
System.out.println(userClass);
UserService3 userObj = (UserService3) userClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> " + userObj.getUserNo());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread.start();
thread.join();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Class<?> userClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("com.sample.mybatis.service.impl.UserService3Impl");
System.out.println(userClass);
UserService3 userObj = (UserService3) userClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> " + userObj.getUserNo());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
thread2.start();
}
}运行结果:
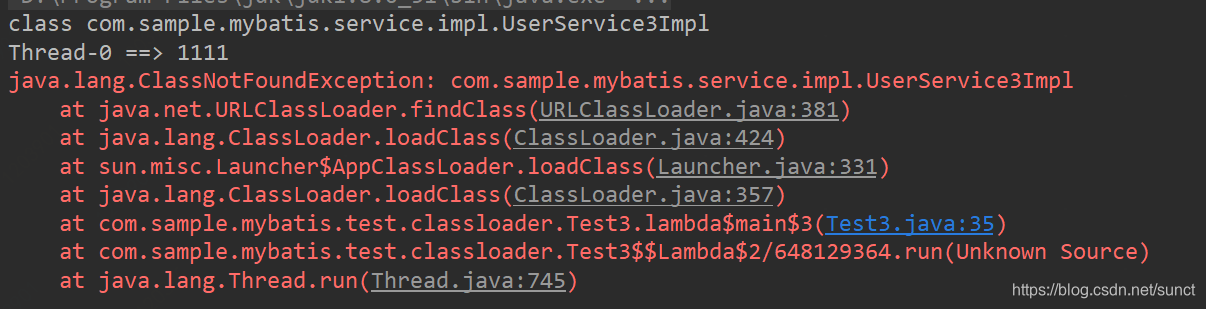
总结:如果一个线程加载的Class,其他线程是不可以使用该Class
怎么使用ContextClassLoader才是正确姿势呢?
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); //取出
try {
MyClassLoader classLoader = new MyClassLoader();
classLoader.setClassFile(new File("D:\\UserService3Impl.class"));
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader); //设置
//其他逻辑。。。
}finally {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(ccl); //还原
}到此这篇关于关于使用ContextClassLoader遇到的问题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ContextClassLoader使用详解内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
