Java线程之ThreadLocal解析
作者:奋斗的小面包
ThreadLocal实现原理
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
首先,每个Thread 里面都有一个成员 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 类型的成员变量
static class ThreadLocalMap {
//内部存储其实是一个 entry 的数组结构
private Entry[] table;
} static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}看到这里我们应该清楚了 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 的数据结构,如下图
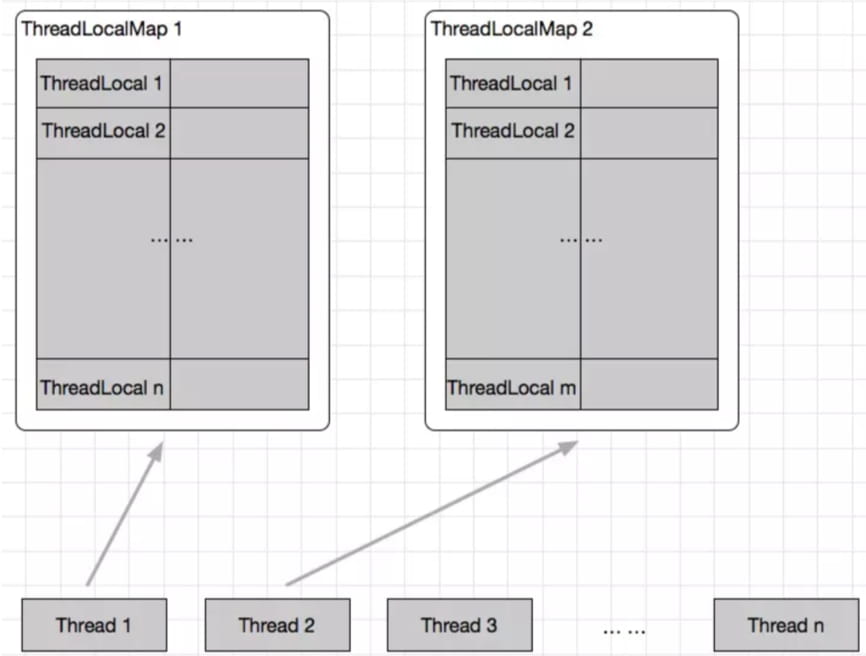
因为ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 类型的变量 是Thread 的成员变量,所以其有线程隔离性.
那么ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap中的数据是从什么地方写入或者读取的呢?那时就ThreadLocal这个类所实现的功能了。
ThreadLocal
这里我们着重分析一个 ThreadLocal的 get() 方法 、set(T value)方法 、 remove()方法
public T get() {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取当前线程的threadLocals 成员变量
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//获取以当前TheadLocal对象为key 的key-value 键值对
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//返回value
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//否则调用setInitialValue方法返回默认值
return setInitialValue(); 1
}1
private T setInitialValue() {
//我们可以重载该方法,初始化默认值
T value = initialValue(); 2
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
//创建ThreadLocalMap,并存储到Thread 中
createMap(t, value); 3
return value;
}
//我们可以重载该方法,初始化默认值
2
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
//创建
3
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
//赋值给当前线程
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}set() 方法类似
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}remove()方法
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}threadLocal 使用风险
最大的风险就是产生的内存泄漏风险,
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}通过构造函数我们知道 key 为弱引用,value 为强引用。
当threadLocal变量被置为null时,Heap中的threadLocal对象失去了引用,将被GC回收。同时Entry的key也将被回收。Entry中只剩下没有key的Value,此时存在强引用链threadlocalmap–>Entry–>Value,若当前线程迟迟不能结束,则Heap中的Value始终不能被GC回收,造成内存泄漏。所以必须建议 最好的办法在不使用ThreadLocal的时候,调用remove()方法,通过显示 的设置value = null 清除数据。
为了避免内存泄漏,ThreadLocalMap在调用get()方法和set()方法时操作数组时,也会去调用expungeStaleEntry()方法来清除Entry中key为null的Value,但是这种清理是不及时,因为我们不保证时候还会触发get()方法和set()等方法。因此也会引发内存泄漏的风险。只有remove()方法,显式调用expungeStaleEntry()方法,才是王道。
使用场景
场景1
线程内保存全局变量,可以让不同方法直接使用,避免参数传递麻烦,例如数据源切换
@Configuration
public class DataSourceProxyConfig {
//数据源1
@Bean("originOrder")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.order")
public DataSource dataSourceMaster() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//数据源2
@Bean("originStorage")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.storage")
public DataSource dataSourceStorage() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//数据源3
@Bean("originPay")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.pay")
public DataSource dataSourcePay() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//数据源4
@Bean(name = "order")
public DataSourceProxy masterDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originOrder") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
//数据源5
@Bean(name = "storage")
public DataSourceProxy storageDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originStorage") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
//数据源6
@Bean(name = "pay")
public DataSourceProxy payDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originPay") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Bean("dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource(@Qualifier("order") DataSource dataSourceOrder,
@Qualifier("storage") DataSource dataSourceStorage,
@Qualifier("pay") DataSource dataSourcePay) {
//动态数据源,这是spring 为我们提供的
DynamicRoutingDataSource dynamicRoutingDataSource = new DynamicRoutingDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>(3);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.ORDER.name(), dataSourceOrder);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.STORAGE.name(), dataSourceStorage);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.PAY.name(), dataSourcePay);
dynamicRoutingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSourceOrder);
//数据源以键值对的形式存储
dynamicRoutingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataSourceMap);
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKeys().addAll(dataSourceMap.keySet());
return dynamicRoutingDataSource;
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(@Qualifier("dynamicDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
}public class DynamicRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
log.info("当前数据源 [{}]", DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey());
//调用我们的ThreadLocal 获取数据源的key
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey();
}
}public class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> CONTEXT_HOLDER = ThreadLocal.withInitial(DataSourceKey.ORDER::name);
private static List<Object> dataSourceKeys = new ArrayList<>();
public static void setDataSourceKey(DataSourceKey key) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(key.name());
}
public static String getDataSourceKey() {
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get();
}
public static void clearDataSourceKey() {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
}
public static List<Object> getDataSourceKeys() {
return dataSourceKeys;
}
}在程序代码中我们就可以使用DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(),进行数据源的切换了。
在业务代码执行完成后,记得显示调用clearDataSourceKey()方法清除数据。
为了方便使用,我们完成一下,就是可以在需要切换数据源 Service 或 Mapper 方法上添加 @DataSource 注解,来实现数据源的切换功能
本实现出自ruoyi项目,感谢若依
声明一个切面,拦截包含 @DataSource注解的方法
@Component
public class DataSourceAspect
{
protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.ruoyi.common.annotation.DataSource)"
+ "|| @within(com.ruoyi.common.annotation.DataSource)")
public void dsPointCut()
{
}
@Around("dsPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable
{
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource(point);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(dataSource))
{
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceType(dataSource.value().name());
}
try
{
return point.proceed();
}
finally
{
// 销毁数据源 在执行方法之后
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clearDataSourceType();
}
}
/**
* 获取需要切换的数据源
*/
public DataSource getDataSource(ProceedingJoinPoint point)
{
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
DataSource dataSource = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(signature.getMethod(), DataSource.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(dataSource))
{
return dataSource;
}
return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(signature.getDeclaringType(), DataSource.class);
}
}@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface DataSource
{
/**
* 切换数据源名称
*/
public DataSourceType value() default DataSourceType.MASTER;
}这样就可以在方法上直接使用@DataSource 注解实现数据源的切换功能了。再次强调,一定要显示调用remove 方法确保内存回收。
场景2
每个线程需要一个独享的对象,比如非线程安全的工具类 例如SimpleDateFormt
class SimpleDateFormtHolder {
private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>() {
protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyy-MM-dd");
}
};
public static SimpleDateFormat getSimpleDateFormt() {
return threadLocal.get();
}
public static void setSimpleDateFormt(SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat) {
threadLocal.set(simpleDateFormat);
}
public static void removeSimpleDateFormt() {
threadLocal.remove();
}
}到此这篇关于Java线程之ThreadLocal解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ThreadLocal解析内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
