c++结构体排序方式(1条件,多条件)
作者:wo_jiushi_wo
这篇文章主要介绍了c++结构体排序方式(1条件,多条件),具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助,如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教
c++结构体排序(1条件,多条件)
最近做题的时候总会遇到排序问题,同样一个问题用结构体排序和用数组做差的不仅仅是代码的长度,还有理解的难易程度,很明显,用结构体排序更简单易懂。
但结构体不能直接用algorithm头文件里的sort函数,需要我们自己补充一个函数。这里就给大家一一列举出来。
一个判断条件
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct cj
{
int num;
string name;
int score;
};
bool cmp(cj a,cj b)
{
return a.score>b.score;
}
int main()
{
cj x[5]; //这里的5可以手动输入n代替
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
cin>>x[i].name>>x[i].score>>x[i].num;
sort(x,x+5,cmp);
cout<<'\n';
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<x[i].name<<'\t'<<
x[i].score<<'\t'<<x[i].num<<'\n';
system("pause");
return 0;
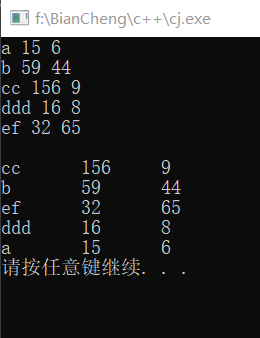
}这里的判断条件为score,效果如图
多个判断条件(以两个为例)
还是以上的代码,只要把cmp函数稍做修改就可以了。这里我们的第二给判断条件为num.
bool cmp(cj a,cj b)
{
if(a.score!=b.score)
return a.score>b.score;
else
return a.num>b.num;
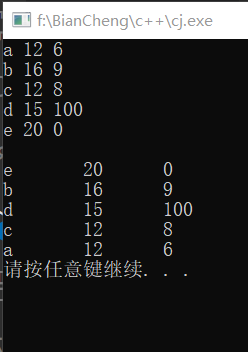
}效果如图
有更多条件也可以仿照两个条件的进行修改,要强调的是,多个条件中,越靠前的所起作用越大。
这里对于初学者不一定要懂为什么要这样写,只需要会用就好了。等到熟练之时可以再找资料更深层次地理解。有什么问题欢迎在评论区与我交流。
C++结构体自定义排序
声明:本机无C++环境,以下代码均没有编译测试,最近golang写的比较多,语法可能会有问题,请自行测试代码
sort排序函数简单使用
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[100];
bool cmp1(int x,int y) {
return x > y;
}
bool cmp2(int x,int y) {
return x < y;
}
int main()
{
//sort简单用法
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
/*
1到n输入
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a+1,a+1+n); //默认从小到大排序
*/
/*
0 到 n-1 输入
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a,a+n);
*/
//从大到小排序需要写自定义优先级函数
sort(a,a+n,cmp1); //采用cmp1函数排序 从大到小
sort(a,a+n,cmp2); //采用cmp2函数排序 从小到大
return 0;
}结构体的自定义排序
例如 对于时间排序 年月日
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*
//结构体排序两种写法 写法1 结构体内部 重载<运算符
struct node {
int year,month,day;
node() {year=0,month=0,day=0;}
node(int y,int m,int d) { year=y,month=m,day=d;}
bool operator< (const node &p) const { //重载<函数 内部写小于逻辑
if (year == p.year && month == p.month) {
return day < p.day;
}
if (year == p.year) {
return year < p.year;
}
return year < p.year;
}
};
//写法2 定义结构体后 写自定义排序函数
struct node {
int year,month,day;
node() {year=0,month=0,day=0;}
node(int y,int m,int d) { year=y,month=m,day=d;}
};
bool cmp(const node &p,const node &q) { //语句不同 实现排序效果同方法1 const不可省略
if (p.year != q.year) return p.year < q.year;
if (p.month != q.month) return p.month < q.month;
return p.day < q.day;
}
*/
node t[100];
int main()
{
t[0] = node{2019,1,20};
t[1] = node{2019,1,22};
t[2] = node{2018,2,1};
t[3] = node{2020,1,1};
/* 方法1
sort(t,t+4);
方法2
sort(t,t+4,cmp);
*/
for (int i=0;i<4;i++) {
printf("%d %d %d\n",t[i].year,t[i].month,t[i].day);
}
return 0;
}总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
