一文弄懂Mybatis中介者模式
作者:Cosolar
一、前言
中介者模式的核心思想是将对象间的交互行为集中在一个中介者对象中,从而降低对象之间的耦合度。在mybatis中,中介者模式被广泛应用于Session对象的创建和管理中。
具体来说,mybatis中的SqlSessionFactory就扮演了中介者的角色,它负责创建和管理SqlSession对象。SqlSession是mybatis中用于与数据库交互的核心对象,而SqlSessionFactory则是创建SqlSession对象的工厂类。
当应用程序需要执行一个操作(如查询、添加或更新记录)时,它将向SqlSessionFactory请求一个SqlSession对象。SqlSessionFactory根据需要的配置信息(如数据库连接信息、事务管理器等)创建一个新的SqlSession对象,并将其返回给应用程序。
一旦应用程序获得了SqlSession对象,它就可以使用SqlSession对象来执行数据库操作。当执行完操作后,应用程序需要调用SqlSession的close()方法关闭资源,SqlSession将会被归还给SqlSessionFactory进行资源回收。
通过将SqlSession对象的创建和管理职责交由SqlSessionFactory统一管理,不仅可以保证SqlSession对象的有效性和一致性,同时也可以避免重复创建和销毁SqlSession对象的开销,提高系统性能和稳定性。
Mybatis是一个我项目开发中常用的非常优秀的ORM框架,它可以帮我们快速、简便地操作数据库。本文将会按照Mybatis的原理手写一个ORM框架,并通过利用中介者模式来实现JDBC方式操作数据库的增强。
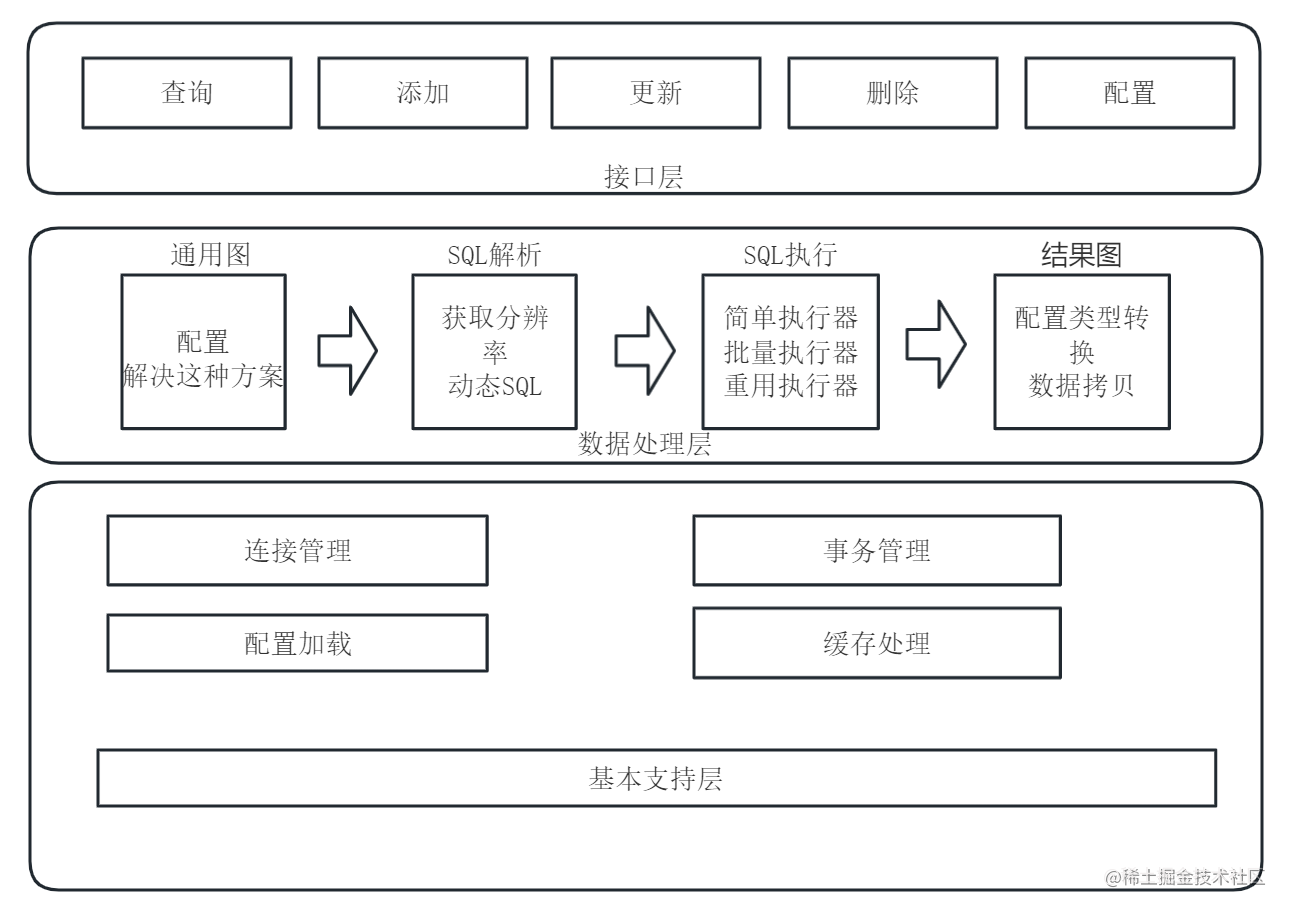
二、Mybatis工作原理
在开始实现ORM框架之前,我们需要先了解一下Mybatis的工作原理:
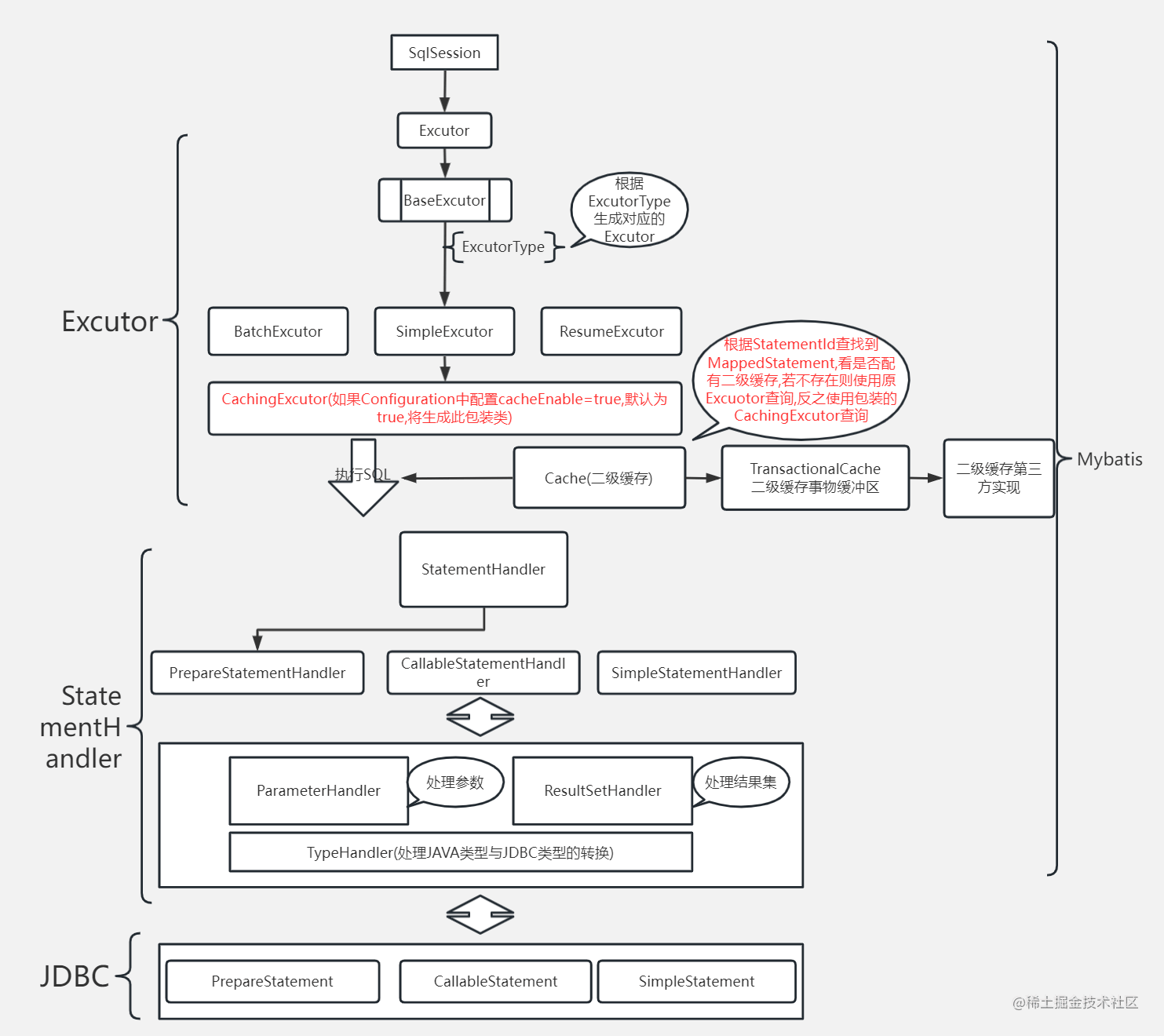
SqlSessionFactory:SqlSessionFactory是Mybatis的核心接口,它是一个工厂类,用于创建SqlSession对象。SqlSession是Mybatis的另一个核心接口,它提供了操作数据库的方法和事务管理的功能。
Configuration:Configuration是Mybatis的配置类,它包含了Mybatis的所有配置,如数据源、映射关系等,用于生成SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSession:SqlSession是Mybatis的会话类,它与数据库的连接是一一对应的,负责与数据库进行交互。SqlSession中包含了一系列的操作数据库的方法,如插入、更新、删除、查询等。
Mapper:Mapper是Mybatis的映射器,它定义了Java对象与SQL语句之间的映射关系,即将Java对象转化为SQL语句,或将SQL语句转化为Java对象。
Executor:Executor是Mybatis的执行器,它负责执行SQL语句,管理事务。Mybatis中有两种类型的执行器:SimpleExecutor和ReuseExecutor,SimpleExecutor会为每个SQL语句创建一个Statement对象,而ReuseExecutor则会复用Statement对象。
TypeHandler:TypeHandler是Mybatis的类型处理器,它用于将Java对象与数据库中的数据类型进行转换。Mybatis中内置了许多常用的类型处理器,如StringTypeHandler、IntegerTypeHandler等,可以根据需要进行扩展。
三、手写ORM框架
我们将按照Mybatis的工作原理来手写一个ORM框架,该框架支持基本的增删改查操作。
1. 创建Configuration类
首先,我们需要创建一个Configuration类,该类负责读取配置文件并生成SqlSessionFactory对象。
public class Configuration {
private final Properties properties = new Properties(); // 存储配置信息
public Configuration(String configLocation) {
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(configLocation);
properties.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Config file not found!");
} finally {
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(this);
}
// getter 方法省略...
}2. 创建SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession类
接下来,我们需要创建SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession类。
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
}public interface SqlSession {
int insert(String statementId, Object parameter);
int update(String statementId, Object parameter);
int delete(String statementId, Object parameter);
<T> T selectOne(String statementId, Object parameter);
<T> List<T> selectList(String statementId, Object parameter);
void close();
}3. 创建Executor类
然后,我们需要创建Executor类,该类负责执行SQL语句,并返回结果。
public interface Executor {
int insert(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter);
int update(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter);
int delete(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter);
<T> T selectOne(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter);
<E> List<E> selectList(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter);
}4. 创建MappedStatement类
我们还需要创建MappedStatement类,该类保存了SQL语句和参数映射关系的信息。
public class MappedStatement {
private String statementId; // SQL语句的ID
private String sql; // SQL语句
private Class<?> parameterType; // 参数类型
private Class<?> resultType; // 返回值类型
// getter、setter方法省略...
}5. 创建MapperRegistry和MapperProxy类
最后,我们需要创建MapperRegistry和MapperProxy类,用于将Java对象与SQL语句之间进行映射。
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
}
public <T> T getMapper(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> type) {
MapperProxyFactory<?> mapperProxyFactory = knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Mapper not found: " + type);
}
return (T) mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
}
}public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler {
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 获取MappedStatement对象
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(statementId);
// 调用Executor执行SQL
Object result = null;
switch (mappedStatement.getSqlCommandType()) {
case INSERT:
result = sqlSession.insert(statementId, args[0]);
break;
case UPDATE:
result = sqlSession.update(statementId, args[0]);
break;
case DELETE:
result = sqlSession.delete(statementId, args[0]);
break;
case SELECT:
if (method.getReturnType() == List.class) {
result = sqlSession.selectList(statementId, args[0]);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectOne(statementId, args[0]);
}
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown SqlCommandType: " + mappedStatement.getSqlCommandType());
}
return result;
}
}6. 在SqlSession中调用Executor
最后,在SqlSession的方法中,我们需要调用Executor来执行SQL语句。
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Executor executor;
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration) {
this.executor = new SimpleExecutor(configuration);
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public int insert(String statementId, Object parameter) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
return executor.insert(mappedStatement, parameter);
}
@Override
public int update(String statementId, Object parameter) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
return executor.update(mappedStatement, parameter);
}
@Override
public int delete(String statementId, Object parameter) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
return executor.delete(mappedStatement, parameter);
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statementId, Object parameter) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
return executor.selectOne(mappedStatement, parameter);
}
@Override
public <T> List<T> selectList(String statementId, Object parameter) {
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
return executor.selectList(mappedStatement, parameter);
}
@Override
public void close() {
// 关闭Executor等资源
}
}7. 创建MapperProxyFactory类
在创建MapperRegistry时,我们还需要创建一个MapperProxyFactory类,用于创建MapperProxy对象。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{mapperInterface},
new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface));
}
}到此为止,我们已经手写了一个简单的ORM框架,并且可以进行基本的增删改查操作。
四、利用中介者模式增强JDBC方式操作数据库
接下来,我们将利用中介者模式来增强JDBC方式操作数据库的功能。
1. 创建DataSource类
首先,我们需要创建一个DataSource类,该类负责管理数据库连接和释放资源。
public class DataSource {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public DataSource(String url, String username, String password) {
this.url = url;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = connectionHolder.get();
if (connection == null) {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
connectionHolder.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
public void releaseConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
connectionHolder.remove();
}
}2. 创建JdbcExecutor类
然后,我们需要创建JdbcExecutor类,该类继承自Executor类,用于执行JDBC操作。
public class JdbcExecutor extends Executor {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcExecutor(Configuration configuration, DataSource dataSource) {
super(configuration);
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public int insert(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(mappedStatement.getSql());
statement.setObject(1, parameter);
return statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
dataSource.releaseConnection(connection);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter) {
// 类似insert方法,此处省略...
}
@Override
public int delete(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter) {
// 类似insert方法,此处省略...
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter) {
// 类似insert方法,此处省略...
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter) {
// 类似insert方法,此处省略...
}
}3. 创建JdbcSqlSession类
我们还需要创建一个JdbcSqlSession类,该类继承自DefaultSqlSession类,用于创建JdbcExecutor对象。
public class JdbcSqlSession extends DefaultSqlSession {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcSqlSession(Configuration configuration, DataSource dataSource) {
super(configuration);
this.executor = new JdbcExecutor(configuration, dataSource);
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public void close() {
// 关闭DataSource等资源
}
}4. 创建JdbcMapperRegistry类
接下来,我们需要创建JdbcMapperRegistry类,该类继承自MapperRegistry类,用于创建JdbcMapperProxyFactory对象。
public class JdbcMapperRegistry extends MapperRegistry {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcMapperRegistry(Configuration configuration, DataSource dataSource) {
super();
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
super.addMapper(type);
JdbcMapperProxyFactory<?> mapperProxyFactory = new JdbcMapperProxyFactory<>(dataSource, type);
knownMappers.put(type, mapperProxyFactory);
}
}5. 创建JdbcMapperProxyFactory类
最后,我们需要创建JdbcMapperProxyFactory类,该类继承自MapperProxyFactory类,用于创建JdbcMapperProxy对象。
public class JdbcMapperProxyFactory<T> extends MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcMapperProxyFactory(DataSource dataSource, Class<T> mapperInterface) {
super(mapperInterface);
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{mapperInterface},
new JdbcMapperProxy<>(sqlSession, dataSource, mapperInterface));
}
}6. 创建JdbcMapperProxy类
最后,我们还需要创建JdbcMapperProxy类,该类继承自MapperProxy类,用于调用JdbcSqlSession的方法。
public class JdbcMapperProxy<T> extends MapperProxy<T> {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcMapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, DataSource dataSource, Class<T> mapperInterface) {
super(sqlSession, mapperInterface);
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 如果是Object类的方法,则直接调用父类的方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
// 获取MappedStatement对象
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(statementId);
// 根据配置文件中的useCache属性来判断是否开启缓存
if (mappedStatement.isUseCache()) {
// TODO: 如果开启了缓存,先从缓存中查找数据,如果不存在再调用JdbcSqlSession中的方法
}
// 调用JdbcSqlSession的方法
Object result;
JdbcSqlSession jdbcSqlSession = new JdbcSqlSession(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), dataSource);
try {
result = method.invoke(jdbcSqlSession.getMapper(mapperInterface), args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
jdbcSqlSession.close();
}
// 如果开启了缓存,则将查询结果添加到缓存中
if (mappedStatement.isUseCache()) {
// TODO: 将查询结果添加到缓存中
}
return result;
}
}到此为止,我们利用中介者模式增强了JDBC方式操作数据库的功能。通过使用中介者模式,我们可以让JDBC操作数据库更加方便快捷、灵活可扩展。
五、小结一下
Mybatis,这个神奇的ORM框架,让我们在操作数据库的道路上披荆斩棘。没错,你没有听错,它就是那个可以帮我们快速、简便地操作数据库的好伙伴。不过话说回来,你有没有想过,如果这个世界上没有Mybatis,那我们程序员岂不是要像远古时期恶劣的条件下编程,跟数据库打交道会变得异常的困难。
但是别担心,就算Mybatis哪天离我们而去了,我们也可以自己动手写一个ORM框架,用中介者模式来增强JDBC方式操作数据库,这样,我们就可以轻松愉悦地跟数据库玩耍啦。所以,让我们手握键盘,放声歌唱,继承Mybatis的精髓,创造更加属于我们自己的数据库操作方式吧!
我在本文中全面讲解了如何按照Mybatis的原理手写一个ORM框架,并利用中介者模式增强JDBC方式操作数据库的功能。在实际开发中,ORM框架可以帮助我们快速、简便地操作数据库,而中介者模式则可以让我们的程序更加灵活可扩展。同时,在使用ORM框架时,我们需要注意管理数据库连接和释放资源等问题,以保证软件系统的稳定性和安全性。
到此这篇关于一文弄懂Mybatis中介者模式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Mybatis中介者模式内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
