浅析Golang开发中goroutine的正确使用姿势
作者:飞翔码农
很多初级的Gopher在学习了goroutine之后,在项目中其实使用率不高,尤其一些跨语言过来的人,对并发编程理解不深入,可能很多人只知道go func(),或者掌控不够,谨慎一些,尽量少使用或者不使用,用的话就是go func(),主要列一下我们这边的主要使用方法。
goroutine在项目中的使用方法
看一下样例代码,实际上,我们生产环境中就是这么使用的。
package logic
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
)
type UserData struct {
Age int
Name string
Postion string
}
type ServerLogic struct {
ctx context.Context
cancel func()
waiter sync.WaitGroup
ch chan UserData
}
func NewServerLogic(logCtx *context.Context, worker int, queue int) *ServerLogic {
logic := &ServerLogic{}
logic.InitWorker(worker, queue)
return logic
}
func (this *ServerLogic) InitWorker(workers int, queue int) {
this.ch = make(chan UserData, queue)
this.ctx, this.cancel = context.WithCancel(context.Background())
this.waiter.Add(workers)
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go this.Proc()
}
}
func (this *ServerLogic) Proc() {
defer this.waiter.Done()
for {
select {
case t := <-this.ch:
this.Dothing(t)
case <-this.ctx.Done():
return
}
}
}
func (this *ServerLogic) Dothing(data UserData) error {
//do code
time.Sleep(time.Second*30)
return nil
}
func (this *ServerLogic) Close() {
this.cancel()
this.waiter.Wait()
}
func (this *ServerLogic) PutData(user UserData) error {
select {
case this.ch<-user:
return nil
default:
return fmt.Errorf("queue overflow")
}
}
如果有人想直接使用的话,只需要把UserData struct换成自己的请求数据,把Dothing里面的代码换成让goroutine多任务执行的代码就可以在自己的项目中使用了。
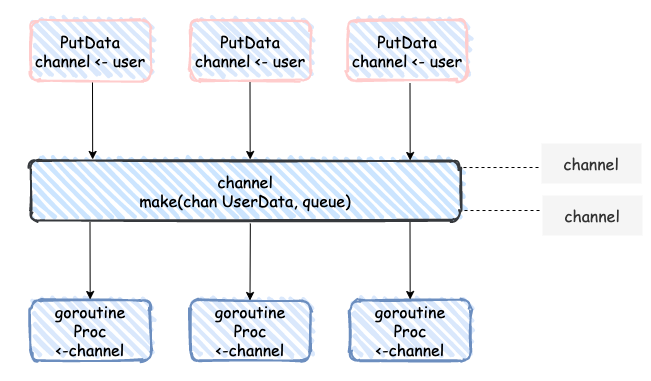
PutData有请求数据就放入channel,每个goroutine不停的循环从channel里面取数据,取到数据之后就执行相应的逻辑流程,可以看到整体的调度都是channel来控制的,通过channel的通信来传递数据。
不要通过共享内存来通信,要通过通信来共享内存
看看大概的代码分析
- InitWorker的时候会创建queue个channl,再创建workers个goroutine,执行go Proc()
- Proc方法,里面有for的无限循环,不停从步骤1里面创建的channl里面获取UserData数据,一旦获取数据成功,就会带着UserData数据去执行Dothing方法。需要注意的是,这是workers个goroutine都在执行Proc
- Dothing方法,就是让某一个goroutine拿到UserData数据去处理数据,执行逻辑
- Close方法,给所有的goroutine发送关闭的信号,channl里面不在有数据写入,waiter.Wait()等待现有的channel里面数据被消费完,goroutine就执行完毕退出。
- PutData方法,就是把请求的数据交给goroutine去执行。具体的做法,是把数据 塞到channl队列里面,如果queue个channl队列已满,就抛出溢出错误。
当然了PutData也可以等待channl队列里面的数据被Proc拿出,然后空出位置再塞数据到channl队列。
func (this *ServerLogic) PutData(user UserData) error {
timer := time.NewTimer(3*time.Second)
select {
case this.ch<-user:
return nil
case <-timer.C:
return fmt.Errorf("put timeout")
}
}
加一个超时器,总不能等到天荒地老把,如果超过三秒,仍然没有空出channl位置,现有的队列还没有消费完,就抛出塞数据超时的错误.
看一下样例的使用的代码
package main
import (
context2 "context"
"fmt"
"test/logic"
)
func main() {
context := context2.Background()
server := logic.NewServerLogic(&context, 1, 2)
rt1 := server.PutData(logic.UserData{
Age: 11,
Name: "test1",
Postion: "golang",
})
fmt.Println(rt1)
rt2 := server.PutData(logic.UserData{
Age: 12,
Name: "test2",
Postion: "golang",
})
fmt.Println(rt2)
rt3 := server.PutData(logic.UserData{
Age: 13,
Name: "test3",
Postion: "golang",
})
fmt.Println(rt3)
server.Close()
fmt.Println("end")
}
等待了大概三十多秒之后的结果,打印结果其实跟预想的是一样的。
<nil>
<nil>
queue overflow
end
NewServerLogic(&context, 1, 2)代码中,我们要求创建了1个goroutine,大小为2的channl队列。
所以第一个PutData和第二个PutData是塞数据成功的。等到第三次PutData的时候,因为我们channl队列的大小是2,已经被占满了,所以第三次就会提示溢出错误。
使用goroutine另一种方法
我看项目中还有一些其他人的使用方法,区别只是退出的时候没有使用context的cancel方法,而是使用了channel去通知退出goroutine,内部的原理其实是一样的。看一下下面的代码。
func(this *ServerLogic)InitWorker(workers int, queue int)
{
this.quit = make(chan bool)
this.ch = make(chan UserData, queue)
this.waiter.Add(workers)
for i :=0;i< workers; i++ {
go this.Proc()
}
}
func(this *ServerLogic)Proc()
{
defer this.waiter.Done()
for {
select {
case t := ←this.ch:
this.Dothing(t)
case ←this.quit:
return
}
}
}
func(this *ServerLogic)Close(){
close(this.quit)
this.waiter.Wait()
}只有关闭这里是不一样的,其他的基本一致。执行退出的时候在Close()方法中,close(this.quit)会给quit channel写入数据,Proc()方法会循环从channel和quit里面取数据,一旦从this.quit里面取出了数据,说明系统让关闭goroutine,然后Proc方法就终止。
go func()行不行
有人说,扯这么多,为啥go func()不行,我在项目里面使用go func()运行的好好,而且golang的HTTP库里也是使用的go c.serve(ctx)。
我的理解是主要看使用场景,如果你的服务对结果要求不是100%的成功,对并发的要求很高,那就可以使用go func(),go c.serve(ctx)也是类似,TCP本身就是不可靠的连接,HTTP也允许有极少量的失败状态。
如果你的服务里面只是想让多个goroutine处理你的数据,不希望这个goroutine太多影响你的主干服务,或者你为了提高数据处理效率,想让多个goroutine去请求第三方的服务,这样的话,就应该创建若干个goroutine去并发处理你的任务,也不建议直接go func(),goroutine数量不可控,会影响其他的主干服务或者占用服务器资源,如果请求第三方的服务,可能会因为并发太高被限制,或者把第三方服务打挂。我们就遇到过这种情况。
总之,使用场景很重要,不是一概而论的。
到此这篇关于浅析Golang开发中goroutine的正确使用姿势 的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Go goroutine内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家
