Vue中keep-alive组件的原理与缓存详解
作者:北辰alk
Vue 的 keep-alive 是一个内置组件,用于缓存不活动的组件实例,避免重复渲染,从而优化应用性能,下面就跟随小编一起来看看其核心实现原理和缓存内容吧
Vue 的 keep-alive 是一个内置组件,用于缓存不活动的组件实例,避免重复渲染,从而优化应用性能。它常用于需要保留组件状态或避免重复加载的场景(如标签页切换、路由视图缓存)。以下是其核心实现原理和缓存内容的详细解析:
一、keep-alive 的核心作用
缓存组件实例:当组件被切换时,不会销毁,而是保留在内存中
保留组件状态:保持当前组件的所有状态(data、DOM 结构等)
避免重复渲染:再次激活时直接复用缓存,跳过创建/挂载过程
二、实现原理
1. 缓存管理策略
LRU 算法(最近最少使用):当缓存数量超过 max 限制时,自动移除最久未使用的实例
缓存存储结构:使用 JavaScript 对象存储缓存实例,数组记录访问顺序
2. 核心源码解析(Vue 2.x 简化版)
export default {
name: 'keep-alive',
abstract: true, // 标记为抽象组件,不渲染 DOM 元素
props: {
include: [String, RegExp, Array], // 白名单
exclude: [String, RegExp, Array], // 黑名单
max: [String, Number] // 最大缓存数
},
created() {
this.cache = Object.create(null) // 缓存池 { key: VNode }
this.keys = [] // 缓存键的访问顺序
},
destroyed() {
// 清理所有缓存
for (const key in this.cache) {
pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys)
}
},
render() {
const slot = this.$slots.default
const vnode = getFirstComponentChild(slot) // 获取包裹的第一个组件
const componentOptions = vnode?.componentOptions
if (componentOptions) {
const name = getComponentName(componentOptions)
// 检查是否匹配 include/exclude
if (
(this.include && (!name || !matches(this.include, name))) ||
(this.exclude && name && matches(this.exclude, name))
) {
return vnode
}
const key = vnode.key == null
? componentOptions.Ctor.cid + (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : '')
: vnode.key
// 命中缓存
if (this.cache[key]) {
vnode.componentInstance = this.cache[key].componentInstance
// 更新访问顺序
remove(this.keys, key)
this.keys.push(key)
} else {
this.cache[key] = vnode
this.keys.push(key)
// 清理超出 max 的旧缓存
if (this.max && this.keys.length > parseInt(this.max)) {
pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, this.keys[0], this.keys)
}
}
vnode.data.keepAlive = true // 标记为 keep-alive 组件
}
return vnode
}
}
3. 缓存生命周期
| 生命周期 | 触发时机 | 典型用途 |
|---|---|---|
| activated | 组件被激活(进入缓存视图) | 刷新数据、启动动画 |
| deactivated | 组件被停用(离开缓存视图) | 停止定时器、保存临时状态 |
三、缓存的具体内容
1. 缓存对象结构
{
cache: {
'component1::key1': {
componentInstance: ComponentInstance, // 组件实例
data: {
keepAlive: true, // 特殊标记
// ...其他 VNode 信息
},
// ...完整 VNode 信息
},
'component2::key2': { ... }
},
keys: ['component1::key1', 'component2::key2']
}
2. 具体缓存内容
| 内容类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 组件实例 | 完整的 Vue 组件实例(包含 data、methods、生命周期等) |
| DOM 结构 | 组件对应的真实 DOM 节点 |
| 状态数据 | 所有响应式数据、计算属性、观察者等 |
| 事件监听器 | 通过 v-on 或 $on 绑定的事件 |
| 插槽内容 | <slot> 中的子组件和 DOM 结构 |
四、使用示例
1. 基础用法
<template>
<keep-alive>
<component :is="currentComponent"></component>
</keep-alive>
</template>
2. 配置缓存策略
<template>
<keep-alive
:include="['Home', 'User']"
:exclude="['Login']"
:max="5"
>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</template>
五、注意事项
不要缓存过多组件:合理设置 max 防止内存泄漏
动态组件必须定义 name:用于 include/exclude 匹配
避免缓存高频变化组件:如实时数据展示组件
路由缓存需结合 key:确保相同路由不同参数的组件独立缓存
<keep-alive> <router-view :key="$route.fullPath"></router-view> </keep-alive>
六、实现流程图解
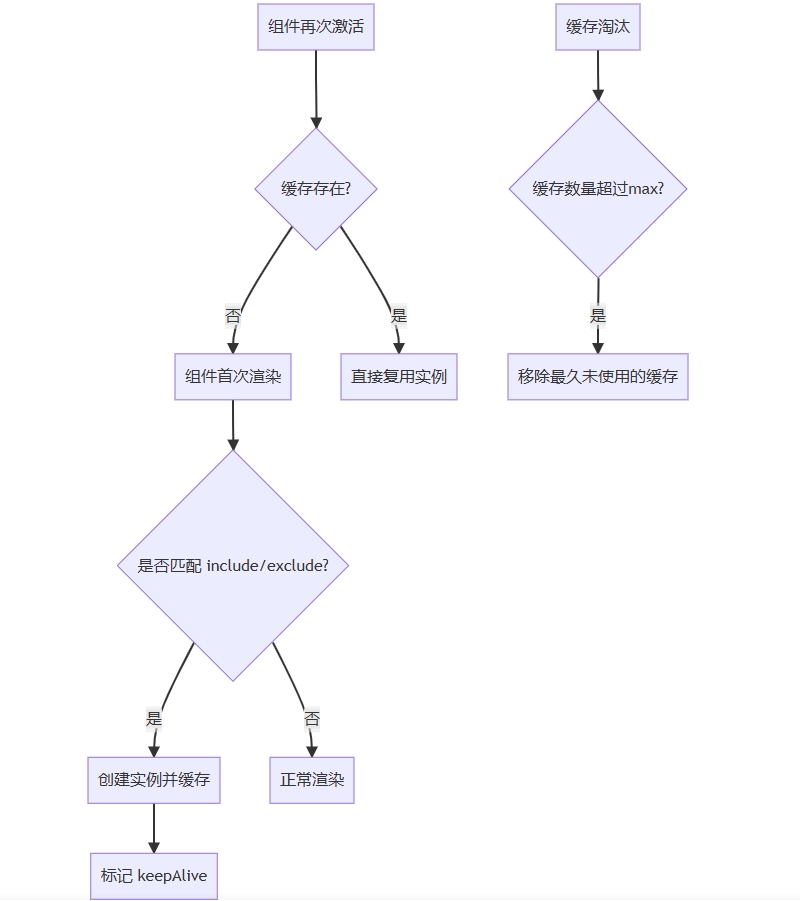
通过这种机制,keep-alive 在保证性能优化的同时,智能管理内存使用,是 Vue 性能优化体系中的重要组成部分。
以上就是Vue中keep-alive组件的原理与缓存详解的详细内容,更多关于Vue keep-alive组件的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
