Vue3中数据响应式原理与高效数据操作全解析
作者:Code_Cracke
这篇文章主要为大家详细介绍了Vue3中数据响应式原理与高效数据操作的相关知识,文中的示例代码讲解详细,感兴趣的小伙伴可以跟随小编一起学习一下
一、Vue3 数据响应式原理
(一)Proxy 替代 Object.defineProperty
在 Vue2 中,数据响应式是通过 Object.defineProperty 实现的。这种方法虽然能够监听对象属性的变化,但也存在一些局限性:
- 无法监听新增或删除的属性:如果动态地向对象添加新属性,Vue2 是无法检测到的。
- 数组操作的支持有限:对于数组的操作(如
push、pop等),需要额外处理。 - 性能问题:当对象层级较深时,递归遍历所有属性会带来较大的性能开销。
为了解决这些问题,Vue3 引入了 Proxy 对象来实现数据响应式。Proxy 提供了更强大的功能,可以拦截对目标对象的各种操作,包括属性读取、赋值、删除、数组索引访问等。
Proxy 的优势:
- 全面性:可以监听对象的新增属性和删除属性。
- 高效性:无需递归遍历整个对象树,只有在访问某个属性时才会触发代理。
- 支持数组操作:可以直接监听数组的变化,例如
push、splice等方法。
以下是一个简单的 Proxy 示例,展示了如何监听对象的变化:
const target = {
name: 'Vue3',
features: ['Composition API', 'Teleport', 'Fragments']
};
const handler = {
get(target, key, receiver) {
console.log(`获取属性: ${key}`);
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver);
},
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
console.log(`设置属性: ${key} -> ${value}`);
return Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
}
};
const proxy = new Proxy(target, handler);
proxy.name; // 输出: 获取属性: name
proxy.features.push('Custom Renderer'); // 输出: 获取属性: features通过 Proxy,我们可以轻松地实现对对象的深度监听,从而为 Vue3 的响应式系统奠定了坚实的基础。
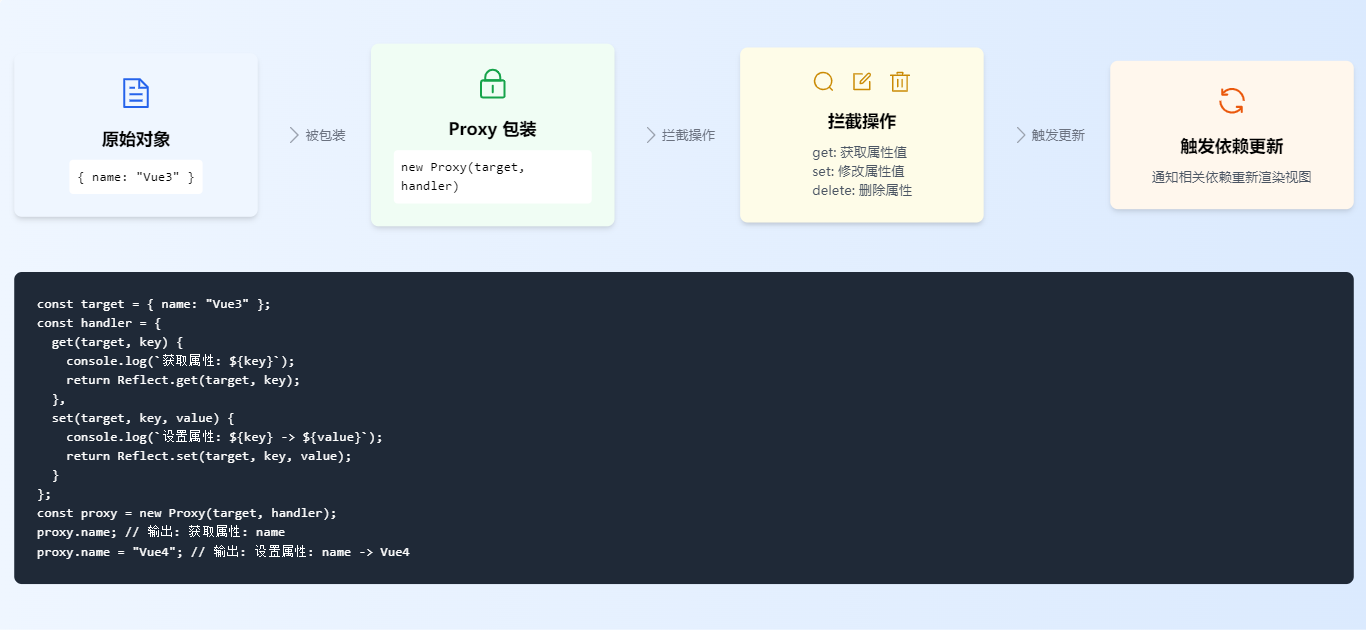
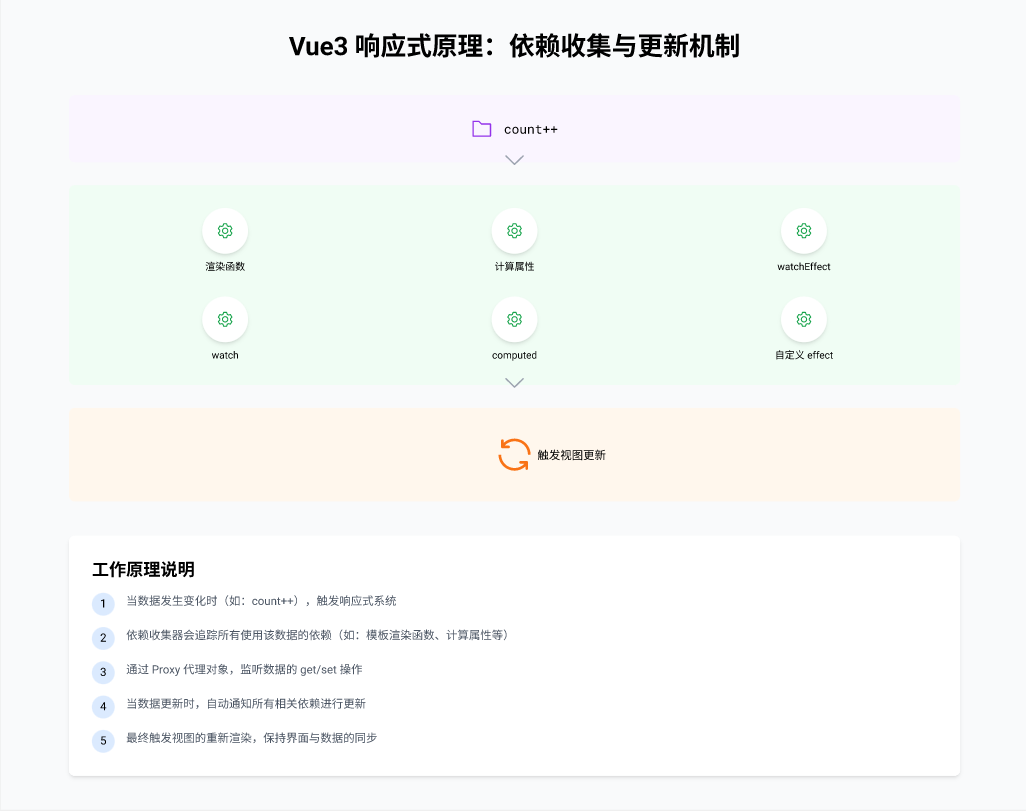
(二)依赖收集与更新机制
Vue3 的响应式系统不仅能够监听数据的变化,还能智能地收集依赖并触发更新。以下是其工作流程的简要说明:
- 依赖收集:当组件渲染时,Vue3 会自动追踪模板中使用的响应式数据,并将其与对应的渲染函数建立关联。
- 触发更新:当响应式数据发生变化时,Vue3 会通知所有相关的依赖(如计算属性、渲染函数等),并重新执行这些依赖以更新视图。
为了更好地理解这一过程,我们可以通过以下图示来展示依赖收集与更新的机制:
二、数据操作方法与实战技巧
(一)ref 与 reactive
1. ref:处理基本类型
- 通过
.value访问和修改数据。 - 适用场景:基本类型(数字、字符串)、需要保持引用稳定的对象。
import { ref } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0); // 创建一个初始值为 0 的响应式数据
console.log(count.value); // 输出: 0
count.value++; // 修改值
console.log(count.value); // 输出: 12. reactive:处理复杂对象
reactive则用于创建复杂对象(如普通对象、数组等)的响应式数据。与 ref 不同,reactive返回的是一个直接可操作的代理对象。
注意:解构会丢失响应性,需使用 toRefs 转换。
import { reactive } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({
name: 'Vue3',
features: ['Composition API', 'Teleport']
});
state.features.push('Fragments'); // 直接修改数组
console.log(state.features); // 输出: ['Composition API', 'Teleport', 'Fragments']对比图:
| 特性 | ref | reactive |
|---|---|---|
| 数据类型 | 基本类型/对象引用 | 对象/数组 |
| 访问方式 | .value | 直接访问属性 |
| 解构响应性 | 需手动处理 | 需使用 toRefs |
(二)计算属性(Computed)
- 缓存机制:只有当依赖项变化时,才会重新计算。
- 链式依赖:计算属性可以依赖其他计算属性。
import { reactive, computed } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({
count: 0
});
const doubleCount = computed(() => state.count * 2);
console.log(doubleCount.value); // 输出: 0
state.count++;
console.log(doubleCount.value); // 输出: 2通过计算属性,我们可以避免重复计算,从而提高应用的性能。
(三)侦听器(Watch)
- 深度监听:设置
{ deep: true }监听嵌套对象变化。 - 立即执行:设置
{ immediate: true }初始化时立即触发回调。
import { ref, watch } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0);
watch(count, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(`count 从 ${oldValue} 变为 ${newValue}`);
});
count.value++; // 输出: count 从 0 变为 1侦听器在处理异步逻辑或副作用时非常有用,例如发送网络请求、更新 DOM 等。
三、实战示例:响应式计数器
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {{ count }}</p>
<p>Double Count: {{ doubleCount }}</p>
<button @click="increment">Increment</button>
<input v-model="state.name" placeholder="Enter name" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive, computed, watch } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0);
const state = reactive({ name: 'Vue3' });
// 计算属性
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2);
// 监听多个数据源
watch([count, () => state.name], ([newCount, newName]) => {
console.log(`Count: ${newCount}, Name: ${newName}`);
});
function increment() {
count.value++;
}
</script>代码解析:
- 使用
ref管理计数器,reactive管理对象状态。 - 计算属性
doubleCount自动追踪count的变化。 watch监听多个数据源,并在控制台输出变化。
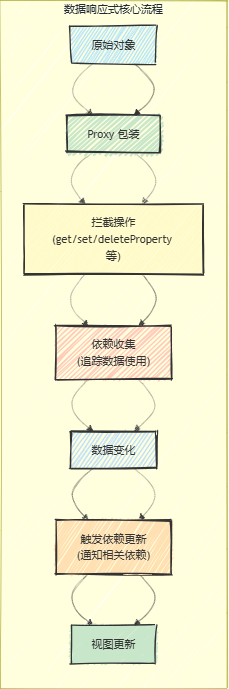
四、响应式系统流程图解
五、总结
- 优先使用 reactive:处理对象和数组时,
reactive更简洁。 - 避免直接解构:使用
toRefs保持响应性。 - 合理使用计算属性:减少重复计算,提升性能。
- 谨慎使用深度监听:
deep: true可能带来性能开销。
希望通过本篇文章的讲解,你能够对 Vue3 的数据响应式原理和操作方法有更深入的理解。在后续的阶段中,我们将结合更多实际案例,探索 Vue3 的更多高级特性。
以上就是Vue3中数据响应式原理与高效数据操作全解析 的详细内容,更多关于Vue3数据响应式的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
