MySQL存储过程和存储函数的用法解读
作者:緑水長流*z
MySQL存储过程和存储函数
MySQL中提供存储过程与存储函数机制,我们先将其统称为存储程序,一般的SQL语句需要先编译然后执行,存储程序是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集,经编译后存储在数据库中,当用户通过指定存储程序的名字并给定参数(如果该存储程序带有参数)来调用才会执行。
1.1 存储程序优缺点
- 优点:
通常存储过程有助于提高应用程序的性能。当创建,存储过程被编译之后,就存储在数据库中。 但是,MySQL实现的存储过程略有不同。 MySQL存储过程按需编译。 在编译存储过程之后,MySQL将其放入缓存中。 MySQL为每个连接维护自己的存储过程高速缓存。 如果应用程序在单个连接中多次使用存储过程,则使用编译版本,否则存储过程的工作方式类似于查询。
1)性能:存储过程有助于减少应用程序和数据库服务器之间的流量,因为应用程序不必发送多个冗长的SQL语句,而只能发送存储过程的名称和参数。
2)复用:存储的程序对任何应用程序都是可重用的和透明的。 存储过程将数据库接口暴露给所有应用程序,以便开发人员不必开发存储过程中已支持的功能。
3)安全:存储的程序是安全的。 数据库管理员可以向访问数据库中存储过程的应用程序授予适当的权限,而不向基础数据库表提供任何权限。
- 缺点:
1)如果使用大量存储过程,那么使用这些存储过程的每个连接的内存使用量将会大大增加。 此外,如果在存储过程中过度使用大量逻辑操作,则CPU使用率也会增加,因为数据库服务器的设计不偏于逻辑运算。
2)很难调试存储过程。只有少数数据库管理系统允许调试存储过程。不幸的是,MySQL不提供调试存储过程的功能。
1.2 数据准备
- 创建数据库:
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8; use test;
这里记得设置编码!
- 创建测试表:
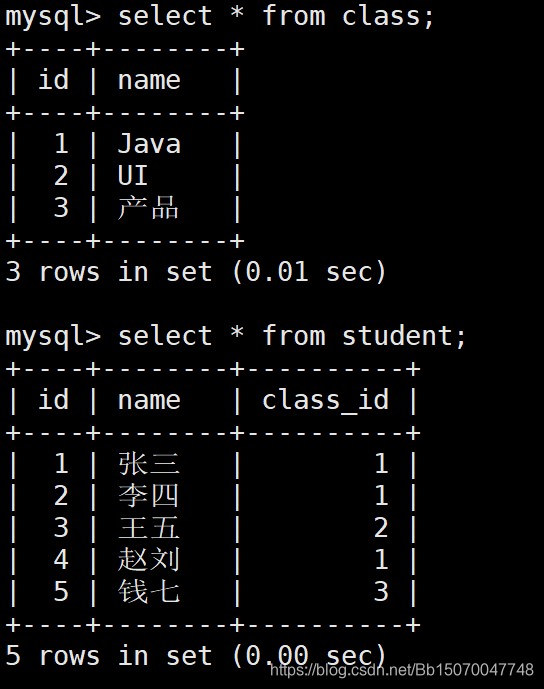
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `class`; CREATE TABLE `class` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; insert into `class`(`id`,`name`) values (1,'Java'), (2,'UI'), (3,'产品'); DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`; CREATE TABLE `student` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `class_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; /*Data for the table `student` */ insert into `student`(`id`,`name`,`class_id`) values (1,'张三',1), (2,'李四',1), (3,'王五',2), (4,'赵刘',1), (5,'钱七',3);
- 查询数据:
select * from class; select * from student;
1.3 存储过程的使用
- 语法
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name ([parameters[,...]]) begin -- SQL语句 end ;
- 示例
create procedure test1() begin select 'Hello'; end;
- 调用存储过程
call test1();

- 查看存储过程
-- 查看db01数据库中的所有存储过程 select name from mysql.proc where db='test'; -- 查看存储过程的状态信息 show procedure status; -- 查看存储过程的创建语句 show create procedure test1;
- 删除存储过程
drop procedure test1;
1.2 存储过程的语法
1.2.1 变量
- declare:声明变量
CREATE PROCEDURE test2 () begin declare num int default 0; -- 声明变量,赋默认值为0 select num+10; end ; call test2(); -- 调用存储过程

- set:赋值操作
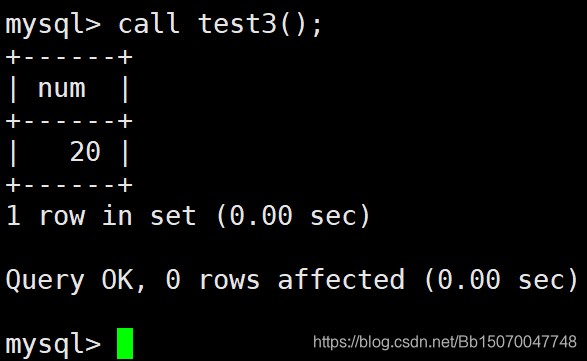
CREATE PROCEDURE test3 () begin declare num int default 0; set num =20; -- 给num变量赋值 select num; end ; call test3();
- into:赋值
CREATE PROCEDURE test4 () begin declare num int default 0; select count(1) into num from student; select num; end ; call test4();

1.2.2 if语句
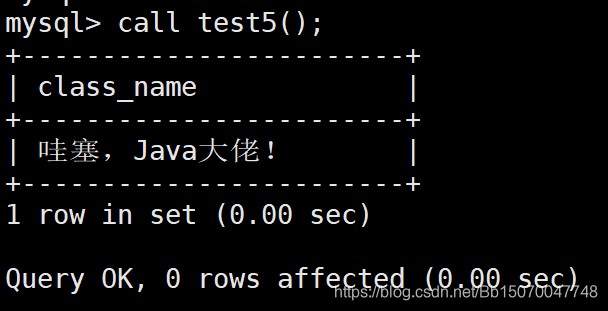
- 需求:根据class_id判断是Java还是UI还是产品
CREATE PROCEDURE test5 () begin declare id int default 1; declare class_name varchar(30); if id=1 then set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!'; elseif id=2 then set class_name='原来是UI的啊'; else set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样'; end if; select class_name; end ; call test5();
1.2.3 传递参数
- 语法:
create procedure procedure_name([in/out/inout] 参数名 参数类型)
- in:该参数可以作为输入,也就是需要调用方传入值 , 默认
- out:该参数作为输出,也就是该参数可以作为返回值
- inout:既可以作为输入参数,也可以作为输出参数
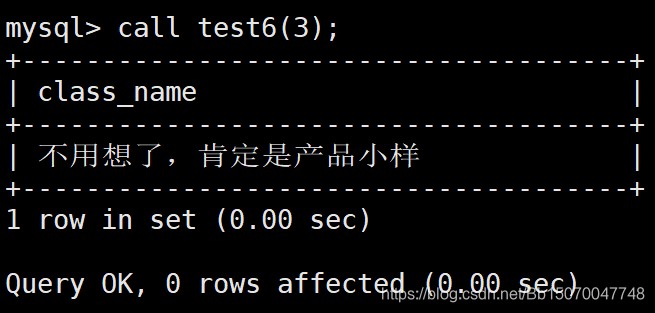
1.2.3.1 in-输入参数
-- 定义一个输入参数 CREATE PROCEDURE test6 (in id int) begin declare class_name varchar(30); if id=1 then set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!'; elseif id=2 then set class_name='原来是UI的啊'; else set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样'; end if; select class_name; end ; call test6(3);
1.2.3.2 out-输出参数
-- 定义一个输入参数和一个输出参数 CREATE PROCEDURE test7 (in id int,out class_name varchar(100)) begin if id=1 then set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!'; elseif id=2 then set class_name='原来是UI的啊'; else set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样'; end if; end ; call test7(1,@class_name); -- 创建会话变量 select @class_name; -- 引用会话变量

- @xxx:代表定义一个会话变量,整个会话都可以使用,当会话关闭(连接断开)时销毁
- @@xxx:代表定义一个系统变量,永久生效。
1.2.4 case语句
- 需求:传递一个月份值,返回所在的季节。
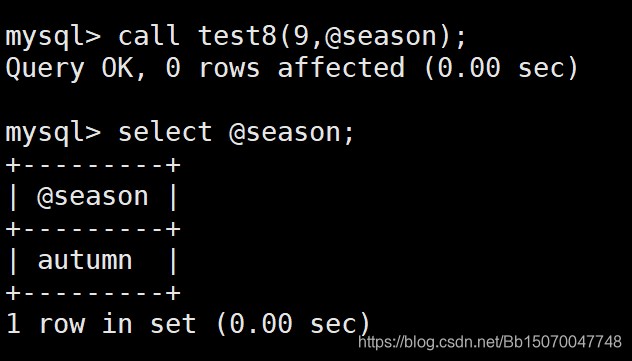
CREATE PROCEDURE test8 (in month int,out season varchar(10)) begin case when month >=1 and month<=3 then set season='spring'; when month >=4 and month<=6 then set season='summer'; when month >=7 and month<=9 then set season='autumn'; when month >=10 and month<=12 then set season='winter'; end case; end ; call test8(9,@season); -- 定义会话变量来接收test8存储过程返回的值 select @season;
1.3.5 while循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
CREATE PROCEDURE test10 (in count int) begin declare total int default 0; declare i int default 1; while i<=count do set total=total+i; set i=i+1; end while; select total; end ; call test10(10);

1.3.6 repeat循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
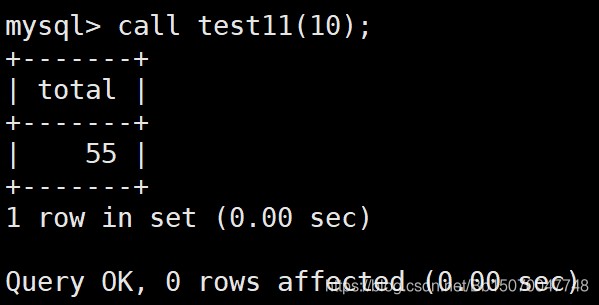
CREATE PROCEDURE test11 (count int) -- 默认是输入(in)参数 begin declare total int default 0; repeat set total=total+count; set count=count-1; until count=0 -- 结束条件,注意不要打分号 end repeat; select total; end ; call test11(10);
1.3.7 loop循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
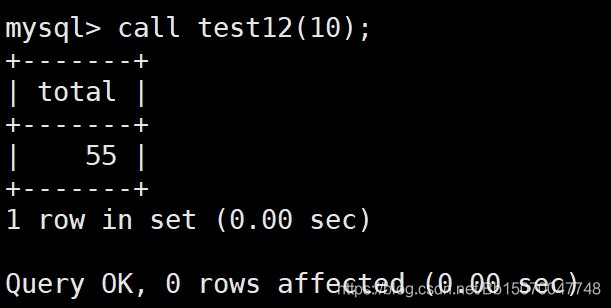
CREATE PROCEDURE test12 (count int) -- 默认是输入(in)参数 begin declare total int default 0; sum:loop -- 定义循环标识 set total=total+count; set count=count-1; if count < 1 then leave sum; -- 跳出循环 end if; end loop sum; -- 标识循环结束 select total; end ; call test12(10);
1.3.8 游标
游标是用来存储查询结果集的数据类型,可以帮我们保存多条行记录结果,我们要做的操作就是读取游标中的数据获取每一行的数据。
- 声明游标
declare cursor_name cursor for statement;
- 打开游标
open cursor_name;
- 关闭游标
close cursor_name;
- 案例:
CREATE PROCEDURE test13 () -- 默认是输入(in)参数
begin
declare id int(11);
declare `name` varchar(20);
declare class_id int(11);
-- 定义游标结束标识符
declare has_data int default 1;
declare stu_result cursor for select * from student;
-- 监测游标结束
declare exit handler for not FOUND set has_data=0;
-- 打开游标
open stu_result;
repeat
fetch stu_result into id,`name`,class_id;
select concat('id: ',id,';name: ',`name`,';class_id',class_id);
until has_data=0 -- 退出条件,注意不要打分号
end repeat;
-- 关闭游标
close stu_result;
end ;
call test13();

1.3 存储过程和存储函数的区别
存储函数的限制比较多,例如不能用临时表,只能用表变量,而存储过程的限制较少,存储过程的实现功能要复杂些,而函数的实现功能针对性比较强。
返回值不同。存储函数必须有返回值,且仅返回一个结果值;存储过程可以没有返回值,但是能返回结果集(out,inout)。
调用时的不同。存储函数嵌入在SQL中使用,可以在select 存储函数名(变量值);存储过程通过call语句调用 call 存储过程名。
参数的不同。存储函数的参数类型类似于IN参数,没有类似于OUT和INOUT的参数。存储过程的参数类型有三种,in、out和inout:
- in:数据只是从外部传入内部使用(值传递),可以是数值也可以是变量
- out:只允许过程内部使用(不用外部数据),给外部使用的(引用传递:外部的数据会被先清空才会进入到内部),只能是变量
- inout:外部可以在内部使用,内部修改的也可以给外部使用,典型的引用 传递,只能传递变量。
1.3.1 临时表
临时表顾名思义就是临时要用创建的表,临时表的作用仅限于本次会话,等连接关闭后重新打开连接临时表将不存在
- 创建一张临时表:
create temporary table temp_table( id int, name varchar(10) ); insert into temp_table values (1,'1'); select * from temp_table ;
temporary:代表创建的表是一张临时表;
- 注意:临时表示查询不到的
show tables; -- 不会显示临时表的存在
- 测试存储过程创建临时表:
create procedure pro1() begin create temporary table temp_table( id int ); insert into temp_table values(1); select * from temp_table; end; call pro1();
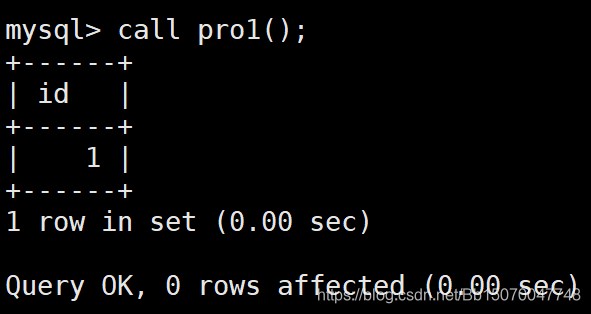
运行没有任何问题
- 测试存储函数创建临时表
create function fun2() returns int begin declare id int ; create table temp_table( id int ); insert into temp_table values(1); select id from into id temp_table; return id; end;
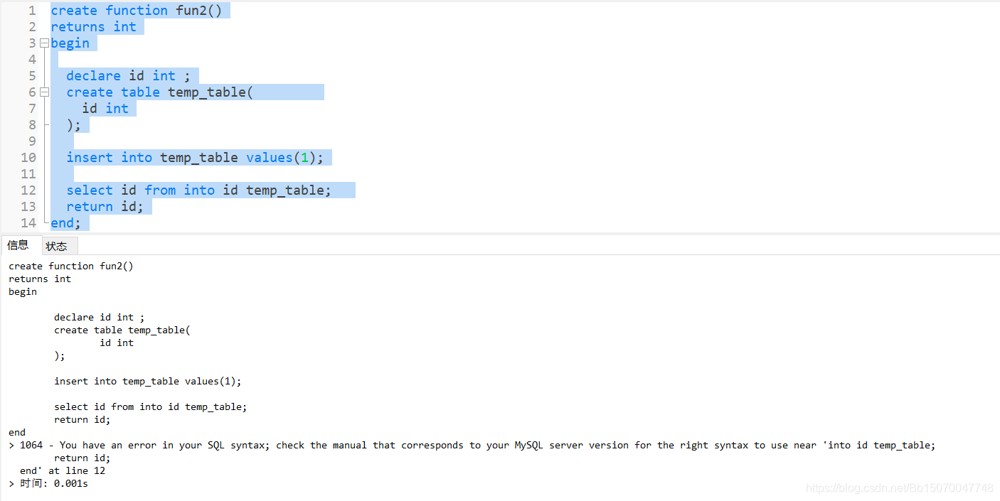
发现报错。
1.4 谈谈为什么大部分公司为什么不用存储过程(函数)?
1.4.1 原因一
参考1.1小结说的存储过程缺点
1.4.2 原因二
咱们分析三层架构就知道了,咱们的业务逻辑应该放到咱们的业务层,也就Tomcat,而不是把业务滞留到数据库来处理,将业务和数据库严重耦合在一起了!
这是导致公司开发不使用存储过程的一个重要原因
1.4.3 原因三
咱们平时对业务性能进行扩容非常好,搭建集群、使用缓存提高响应速度等等。
总之,大多数情况下并不是业务层是整个项目性能的瓶颈,而是数据库!我们应该尽可能的优化数据库方面的性能,而且业务层性能扩容相对于数据库性能扩容要方便的多。
因此我们应该尽可能的优化数据库方面的性能,降低数据层的压力,把所有压力能分单到其他地方就分担,而不是让数据库增加压力!
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
