Vue3中的pinia使用方法总结(建议收藏版)
作者:紫陌~
1.pinia介绍
pinia 是 Vue 的存储库,它允许您跨组件/页面共享状态。就是和vuex一样的实现数据共享。
依据Pinia官方文档,Pinia是2019年由vue.js官方成员重新设计的新一代状态管理器,更替Vuex4成为Vuex5。
Pinia 目前也已经是 vue 官方正式的状态库。适用于 vue2 和 vue3。可以简单的理解成 Pinia 就是 Vuex5。也就是说, Vue3 项目,建议使用Pinia。
Pinia 的优点
- pinia 符合直觉,易于学习。
- pinia 是轻量级状态管理工具,大小只有1KB.
- pinia 模块化设计,方便拆分。
- pinia 没有 mutations,直接在 actions 中操作 state,通过 this.xxx 访问响应的状态,尽管可 以直接操作 state,但是还是推荐在 actions 中操作,保证状态不被意外的改变。
- store 的 action 被调度为常规的函数调用,而不是使用 dispatch 方法或者是 MapAction 辅助函数,这是在 Vuex 中很常见的。
- 支持多个 store。
- 支持 Vue devtools、SSR、webpack 代码拆分。
更多查看文档…
2.pinia基本使用
1.首先先安装依赖
npm install pinia
2.在main.js中引入pinia并创建容器挂载到根实例上
//引入stores暴露出的pinia的实例
import pinia from './stores'
createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app')
3.创建stores文件夹和index.js文件(这个文件以后基本不用管了)
import { createPinia } from "pinia";
const pinia = createPinia()
export default pinia
4.在stores文件夹下创建counter.js文件。这个文件就是存有关counter相关的数据。(类似vuex的模块化)
defineStore 是需要传参数的,
- 第一个参数是id,就是一个唯一的值,简单点说就可以理解成是一个命名空间.
- 第二个参数就是一个对象,里面有三个模块需要处理,第一个是 state,第二个是 getters,第三个是 actions。
//定义关于counter的store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
/*defineStore 是需要传参数的,其中第一个参数是id,就是一个唯一的值,
简单点说就可以理解成是一个命名空间.
第二个参数就是一个对象,里面有三个模块需要处理,第一个是 state,
第二个是 getters,第三个是 actions。
*/
const useCounter = defineStore("counter",{
state:() => ({
count:66,
}),
getters: {
},
actions: {
}
})
//暴露这个useCounter模块
export default useCounter
注意:返回的函数统一使用useXXX作为命名方案,这是约定的规矩。例如上面的useCounter
5.然后再组件中使用:
<template>
<!-- 在页面中直接使用就可以了 不用 .state-->
<div>展示pinia的counter的count值:{{counterStore.count}}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 首先需要引入一下我们刚刚创建的store
import useCounter from '../stores/counter'
// 因为是个方法,所以我们得调用一下
const counterStore = useCounter()
</script>
注意:在模板使用 ,不用和vuex一样还要.state,直接点state里面的K
运行效果: 可以用vue3的调试工具看pinia
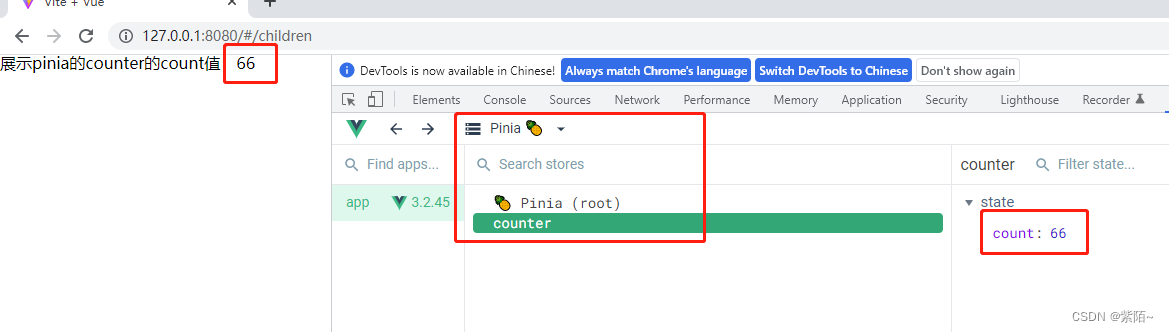
2.1注意Store获取到后不能解构,否则失去响应式
案例需求,点击按钮加一:
一个不解构,一个不解构看看区别。
<template>
<div>展示pinia的counter的count值:{{counterStore.count}}</div>
<div>展示解构出来的pinia的counter的count值:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="addCount">count+1</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import useCounter from '../stores/counter'
const counterStore = useCounter()
const {count} = counterStore
function addCount(){
//这里可以直接操作count,这就是pinia好处,在vuex还要commit在mutaitions修改数据
counterStore.count++
}
<script/>
在 vuex 里面是坚决不允许这样子直接操作 state 数据的,pinia是可以的,看看上面的addCount函数直接操作。
运行结果:
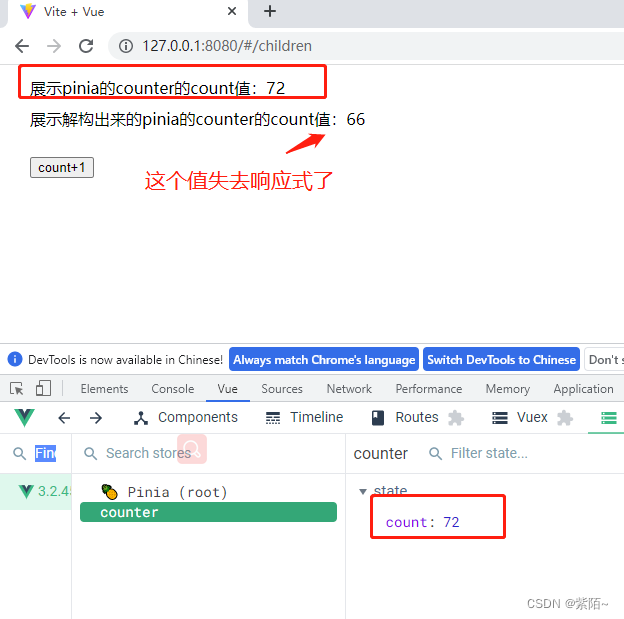
解决方案:
pinia提供了一个函数storeToRefs解决。引用官方API storeToRef 作用就是把结构的数据使用ref做代理
import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'
const counterStore = useCounter()
const {count} = storeToRefs(counterStore)现在数据都是响应式的了
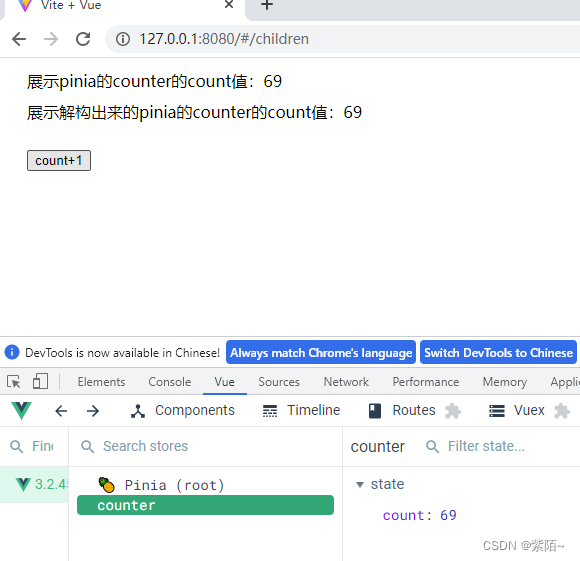
3.修改state的数据
重新新建一个user模块
stores/user.js
//定义一个关于user的store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
const useUser = defineStore("user",{
state:()=>({
name:"紫陌",
age:18
})
})
export default useUser
组件中修改数据:
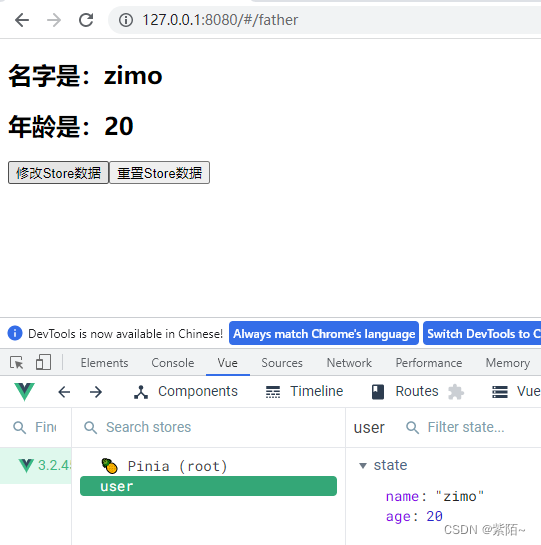
**第一种方法:**点击按钮修改数据,这种方法是最直接的修改数据
<template>
<div>
<h2>名字是:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄是:{{age}}</h2>
<button @click="updateStore">修改Store数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import useUser from '../stores/user'
import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'
const userStore = useUser()
const {name,age} = storeToRefs(userStore)
function updateStore(){
//一个个的修改状态
userStore.name = "zimo"
userStore.age = 20
}效果:点击也修改了
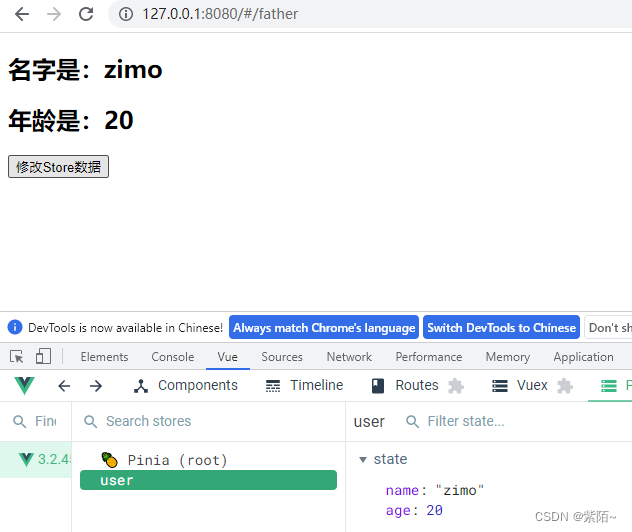
第二种方法:$patch函数修改
function updateStore(){
//一个个的修改状态
// userStore.name = "zimo"
// userStore.age = 20
// 一次性修改多个状态
userStore.$patch({
name:"zimo",
age:20
})
}
这个方式也可以,效果一样。
第三种方法:$state 方式(这个是替换的方式。)这个基本不用,这里就不多说。可以看查阅文档。
第四种方法:$reset()函数是重置state数据的
新增一个重置按钮:
function resetStore(){
userStore.$reset()
}
运行结果:点击了修改数据按钮之后在点重置按钮就恢复原始的数据。
4.getters的使用
getters 类似于 vue 里面的计算属性,可以对已有的数据进行修饰。不管调用多少次,getters中的函数只会执行一次,且都会缓存。
1.最基本的使用
在counter模块演示了,counter模块:
//定义关于counter的store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
const useCounter = defineStore("counter",{
state:() => ({
count:66,
}),
getters:{
//基本使用
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
},
})
//暴露这个useCounter模块
export default useCounter
组件中:
<div>
<h1>getters的使用</h1>
<h2>doubleCount:{{counterStore.doubleCount}}</h2>
</div>
运行效果:
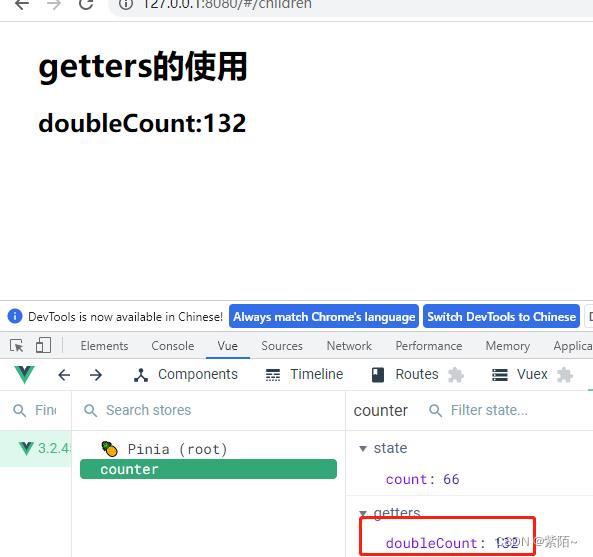
这样就是最基本的使用了。
2.一个getter引入另外一个getter
couter模块:
getters:{
//基本使用
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
//一个getter引入另外一个getter
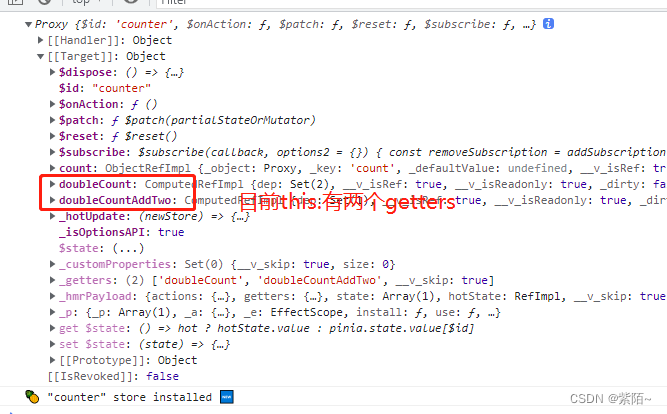
doubleCountAddTwo(){
console.log(this);
//this.是store实例
return this.doubleCount + 2
}
},
组件中使用:
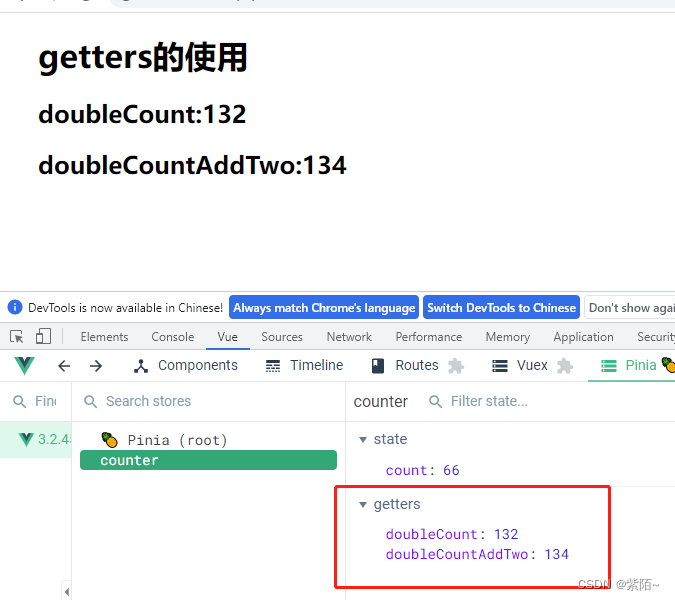
<div>
<h1>getters的使用</h1>
<h2>doubleCount:{{counterStore.doubleCount}}</h2>
<h2>doubleCountAddTwo:{{counterStore.doubleCountAddTwo}}</h2>
</div>
运行效果并且看看打印的this:
3.getters中用别的store中的数据
在counter模块中拿user模块的store数据。
count模块:
//定义关于counter的store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
import useUser from "./user"
const useCounter = defineStore("counter",{
state:() => ({
count:66,
}),
getters:{
//基本使用
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
//一个getter引入另外一个getter
doubleCountAddTwo(){
console.log(this);
//this.是store实例
return this.doubleCount + 2
},
//getters中用别的store中的数据
showMessage(state){
console.log(state);
console.log(this)
//获取user信息,拿到useUser模块
const userStore = useUser()
//拼接信息
return `name:${userStore.name}--count:${state.count}`
}
},
})
//暴露这个useCounter模块
export default useCounter
注意:要引入user模块
组件中:
<div>
<h1>getters的使用</h1>
<h2>doubleCount:{{counterStore.doubleCount}}</h2>
<h2>doubleCountAddTwo:{{counterStore.doubleCountAddTwo}}</h2>
<h2>showMessage:{{counterStore.showMessage}}</h2>
</div>
运行结果:
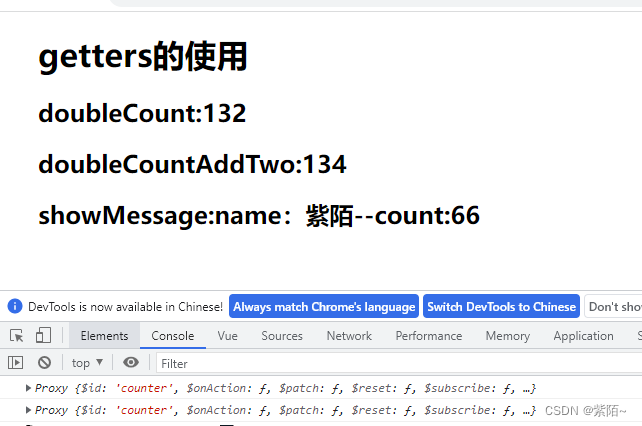
注意:我打印了this和store,他们都是当前这这个模块的实例
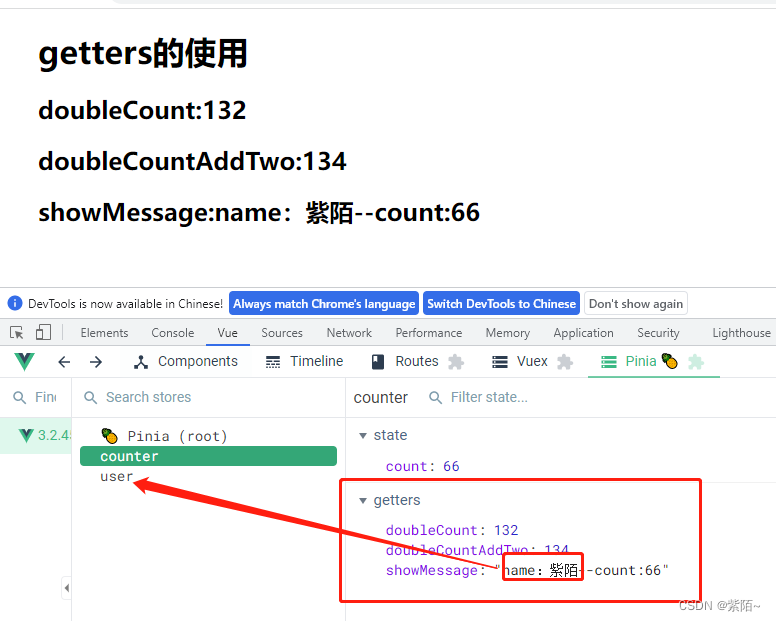
这样就在counter模块拿到了user模块的数据了。
5. actions的使用
actions 是可以处理同步,也可以处理异步,同步的话相对来说简单一点.actions类似methods
1.先看同步使用:
counter模块使用:
在actions定义了两个函数一个加一的函数,一个加20的函数。
//定义关于counter的store
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
const useCounter = defineStore("counter",{
state:() => ({
count:66,
}),
actions:{
increment(state){
//actions没有state,只能通过this拿store,这里打印
console.log(state);
this.count++
},
incrementNum(num){
this.count += num
}
}
})
//暴露这个useCounter模块
export default useCounter
组件中:
actions函数在组件中使用
<div>
<h1>actions的使用</h1>
<h2>count的事值:{{counterStore.count}}</h2>
<button @click="changeState">count+1</button>
<button @click="incrementNum">count+20</button>
</div>
<script setup>
import useCounter from '../stores/counter'
const counterStore = useCounter()
function changeState(){
counterStore.increment()
}
function incrementNum(){
counterStore.incrementNum(20)
}
</script>
运行结果并且看看state是什么
初始值是66,点了一次加1和点了一次加20
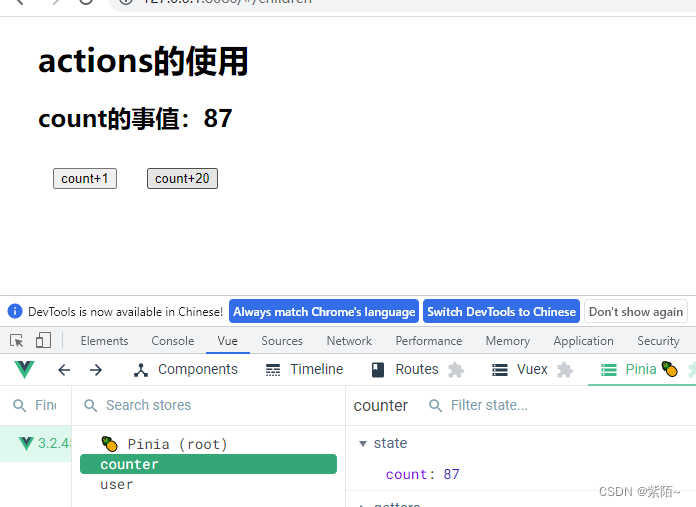
注意:state的结果是undefined 所以actions只能通过this访问store。getter的话state和this都能访问。
2.异步操作使用
在 actions 处理异步的时候呢,我们一般是与 async 和 await 连用。
counter模块: 这里大致演示,具体还看自己怎么使用。
state:() => ({
count:66,
list:[]
}),
actions:{
//大概演示这个异步流程
async axiosData(){
const res = await fetch("http://-----------------")
if(code ==200){
//收到数据保存到store
this.list = res.data.list
return "ok"
}
}
}
组件使用:
<template>
<!-- 遍历store的数据 -->
<div v-for="item in counterStore.list"></div>
</template>
<script setup>
import useCounter from '../stores/counter'
const counterStore = useCounter()
counterStore.axiosData().then(res =>{
console.log("成功",res);
})
</script>
就这样可以啦!!!
是不是比vuex简洁很多。。。
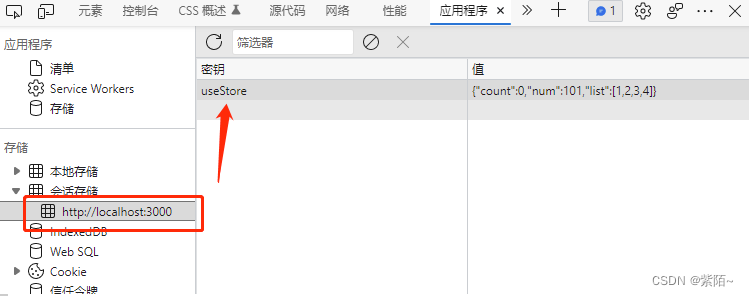
6.数据的持久化
pinia支持扩展插件
我们想实现数据持久化
npm i pinia-plugin-persist
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
state () {
return {
count: 0,
num: 101,
list: [1, 2, 3, 4 ]
}
},
persist: {
enabled: true, // 开启缓存 默认会存储在本地localstorage
storage: sessionStorage, // 缓存使用方式
paths:[] // 需要缓存键
}
})效果:
总结
到此这篇关于Vue3中pinia使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue3中pinia使用内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
