dubbo自定义异常的完整步骤与测试
作者:逆风飞翔的小叔
最近在项目上遇到一个有关dubbo的问题,想着给大家总结下,这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于dubbo自定义异常的完整步骤与测试的相关资料,文中通过实例代码介绍的非常详细,需要的朋友可以参考下
前言
在很多公司,使用dubbo做微服务治理也是很常见的一种方式,简单来说,就是服务提供者一方将服务注册并发布到注册中心,消费者订阅服务,然后像调用本地接口一样;
但是在实际实践中,经常有这么一种场景,就是对于服务消费者来说,当调用服务生产者的服务接口时,一旦服务提供者的接口抛出异常,如果消费端不使用 try-catch 捕捉的话,在进行问题排查、故障分析时,将会是个头疼的问题;
对于消费端来说,不可能在所有的调用dubbo接口的地方都用 try-catch进行包裹吧?有没有一种办法,用来统一处理这样的服务接口调用异常方式呢?答案是肯定的,可以使用dubbo自定义过滤器,通过过滤器统一拦截调用异常问题;
操作步骤
一、创建一个公共的用于处理异常的工程
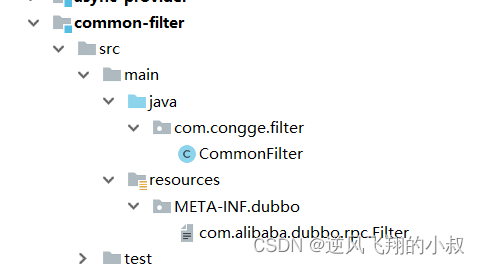
ComnonFilter 类,只需要实现dubbo提供的Filter 接口即可
package com.congge.filter;
import cn.hutool.core.date.DateUtil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.Constants;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Activate;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.*;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.service.GenericService;
import java.util.Date;
@Activate(group = {Constants.PROVIDER,Constants.CONSUMER})
public class CommonFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
try {
result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (result.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
Throwable exception = result.getException();
String data = String.format("\r\n[level]:Error,[createTime]:%s,[serviceName]:%s,[methodName]:%s,[inputParam]:%s",
DateUtil.formatDateTime(new Date()),
invoker.getInterface().getName(),
invocation.getMethodName(),
JSON.toJSONString(invocation.getArguments()));
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println(exception);
}
}catch (RuntimeException e){
String data = String.format("\r\n[level]:Error," +
"[createTime]:%s," +
"[serviceName]:%s," +
"[methodName]:%s," +
"[inputParam]:%s",
DateUtil.formatDateTime(new Date()),
invoker.getInterface().getName(),
invocation.getMethodName(),
JSON.toJSONString(invocation.getArguments()));
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println(e);
}
return result;
}
}在resources目录下创建相关的目录,注意文件路径和文件名称是固定的,文件内容如下

二、生产端配置文件改造
1、pom中导入上面这个公共依赖的maven工程坐标,然后在配置文件中,将过滤器的名称配置进去

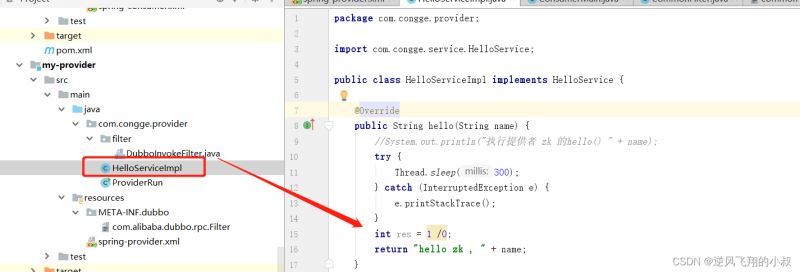
2、生产端提供的服务中手动添加一个异常
三、消费端配置
消费端暂时无需做其他配置
import com.congge.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConsumerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-consumer.xml");
HelloService service = (HelloService) ac.getBean("helloService");
String hello = service.hello("Hello Provider");
System.out.println(hello);
}
}测试
1、启动本地的zk服务
2、启动生产端服务

3、启动消费端服务模拟服务调用
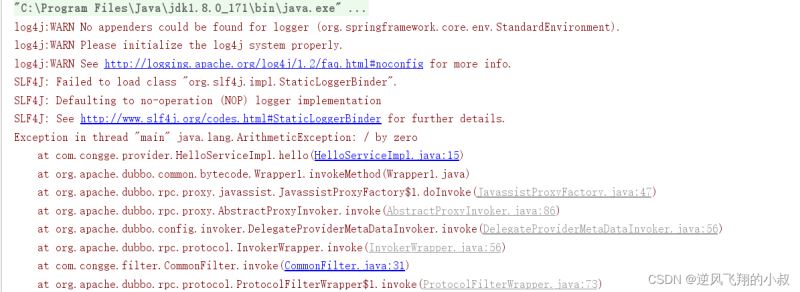
消费端报出的异常信息
由于我们将过滤器配置在生产端了,这时再去观察生产端的控制台,可以看到,调用异常的信息也输出了

使用场景说明
通常来说,在微服务的调用链路比较长的时候,在消费端采用上面的方式进行配置,是有一定意义的,可以较快的定位到调用的服务接口,以及抛出的具体的问题原因,便于服务提供者快速进行问题定位和修复
总结
到此这篇关于dubbo自定义异常的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关dubbo自定义异常内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
