Python基础知识+结构+数据类型
作者:蚂蚁ailing
前言
今天给大家分享一些Python的基础知识,想要盖好大房子,不把地基打扎实打牢怎么行呢?所以,今天咱们就来学习基础知识,
这样后期学习Python的时候才能更容易掌握,更轻松的学会Python的使用。
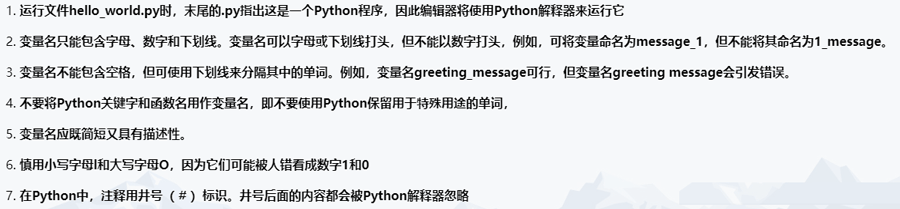
一、编程基础
1.基本的输入输出
print("Hello World");
Name = input('请输入您的姓名:');
print(Name);
D:\工作空间\Python\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/工作空间/Python/main.py
Hello World
请输入您的姓名:Alice
Alice
进程已结束,退出代码02.变量
print("-------------输出语句-------------");
message="Hello Python world";
print(message);
print("-------------首字母大写-------------");
name="ada lovelace";
print(name.title());
print("-------------大小写-------------");
print(name.upper());
print(name.lower());
print("-------------拼接字符串-------------");
first_name = "ada"
last_name = "lovelace"
full_name = first_name + " " + last_name
print(full_name);
print("-------------添加空白-------------");
print("\tPython");
print("Languages:\nPython\nC\nJavaScript");
print("-------------删除空白-------------");
print("Hello ".rstrip());
print("-------------运算-------------");
print(2+3);
print(3-2);
print(2*3);
print(3/2);
print(3**2);
print(3**3);
print(10**6);
print(0.1+0.1);
print(0.2+0.2);
print("------------注释-------------");
# 测试注释-------------输出语句-------------
Hello Python world
-------------首字母大写-------------
Ada Lovelace
-------------大小写-------------
ADA LOVELACE
ada lovelace
-------------拼接字符串-------------
ada lovelace
-------------添加空白-------------
Python
Languages:
Python
C
JavaScript
-------------删除空白-------------
Hello
-------------运算-------------
5
1
6
1.5
9
27
1000000
0.2
0.4
------------注释-------------Process finished with exit code 0
3.基本运算符
print("-----------------算数运算符-----------------");
#+ 加,两个对象相加
#- 减,得到负数或是一个数减去另一个数
#* 乘,两个数相乘或是返回一个被重复若干次的字符串
#x/y 除,x 除以 y
#% 取模,返回除法的余数
#// 取整除,返回商的整数部分
#x**y 幂
print(12+13);
print(12-13);
print(12*13);
print(12/13);
print(12/13);
print(12%13);
print(12//13);
print(12**13);
print("-----------------比较运算符-----------------");
#== 等于,比较对象是否相等 (a == b)返回 False
#!= 不等于,比较两个对象是否不相等 (a != b)返回 True
#<> 不等于,比较两个对象是否不相等 (a <> b)返回 True。这个运算符类似 !=
#x > y 大于,返回 x 是否大于 y (a > b)返回 False
#x < y小于,返回 x 是否小于 y。所有比较运算符返回 1表示真,返回 0 表示假。这分别与特殊的变量 True 和 False 等价。注意这些变量名的大小写(a < b)返回 True
#x >= y 大于等于,返回 x 是否大于等于 y (a >= b)返回 False
#x <= y 小于等于,返回 x 是否小于等于 y (a <= b)返回 True
print(12>13);
print(12>=13);
print(12<13);
print(12<=13);
print(12!=13);
print(12==13);
print("-----------------赋值运算符-----------------");
#= 简单的赋值运算符 c = a + b 将 a + b 的运算结果赋值为 c
#+= 加法赋值运算符 c += a 等效于 c = c + a
#-= 减法赋值运算符 c-= a 等效于 c = c-a
#*= 乘法赋值运算符 c *= a 等效于 c = c * a
#/= 除法赋值运算符 c /= a 等效于 c = c / a
#%= 取模赋值运算符 c %= a 等效于 c = c % a
#**= 幂赋值运算符 c **= a 等效于 c = c ** a
#//= 取整除赋值运算符 c //= a 等效于 c = c // a
a=21;
b=10;
c=0;
c+=a;
print(c);
c*=b;
print(c);
c/=a;
print(c);
c-=b;
print(c);
c=2;
c%=a;
print(c);
c**=a;
print(c);
c//=a;
print(c);
print("-----------------位运算符-----------------");
#& 按位与运算符 (a & b)输出结果 12,二进制解释:0000 1100
#| 按位或运算符 (a | b)输出结果 61,二进制解释:0011 1101
#^ 按位异或运算符 (a ^ b)输出结果 49,二进制解释:0011 0001
#~ 按位取反运算符
#(~a)输出结果−61,二进制解释:1100 0011,
#在一个有符号二进制数的补码形式
#<< 左移动运算符 a << 2 输出结果 240,二进制解释:1111 0000
#>> 右移动运算符 a >> 2 输出结果 15,二进制解释:0000 1111
a=60;
b=13;
c=0;
c=a&b;
print(c);
c=a|b;
print(c);
c=a^b;
print(c);
c=~a;
print(c);
c=a<<2;
print(c);
c=a>>2;
print(c);
print("-----------------逻辑运算符-----------------");
#x and y 布尔“与”,如果 x 为 False,x and y 返回 False,否则它返回 y 的计算值
#x or y 布尔“或”,如果 x 是 True,它返回 True,否则它返回 y 的计算值
#x not y 布尔“非”,如果 x 为 True,返回 False。如果 x 为 False,它返回 True
a=10;
b=20;
print(a and b);
a=0;
print(a and b);D:\工作空间\Python\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/工作空间/Python/main.py
-----------------算数运算符-----------------
25
-1
156
0.9230769230769231
0.9230769230769231
12
0
106993205379072
-----------------比较运算符-----------------
False
False
True
True
True
False
-----------------赋值运算符-----------------
21
210
10.0
0.0
2
2097152
99864
-----------------位运算符-----------------
12
61
49
-61
240
15
进程已结束,退出代码0

二、控制流程
1.选择结构
print("-------------检查是否相等-------------");
car='bmw';
print(car=='bmw');
print(car=='audi');
print(car=='BMW');
print(car.upper()=='BMW');
age=18;
print(age==18);
print(age>=18);
print(age<=18);
print(age>18);
print(age<18);
age_0 = 22;
age_1 = 18;
print(age_0 >= 21 and age_1 >= 21);
print(age_0 >= 21 or age_1 >= 21);
print("-------------if语句-------------");
age = 19
if age >= 18:
print("You are old enough to vote!");
age=17
if age>=18:
print("You are old enough to vote!");
else:
print("Sorry you are too young");
age = 12
if age < 4:
print("Your admission cost is $0.")
elif age < 18:
print("Your admission cost is $5.")
else:
print("Your admission cost is $10.")
age = 12
if age < 4:
price = 0
elif age < 18:
price = 5
elif age < 65:
price = 10
elif age >= 65:
price = 5
print("Your admission cost is $" + str(price) + ".")
-------------检查是否相等-------------
True
False
False
True
True
True
True
False
False
False
True
-------------if语句-------------
You are old enough to vote!
Sorry you are too young
Your admission cost is $5.
Your admission cost is $5.
Process finished with exit code 0
2.循环结构
print("-------------函数input()的工作原理-------------");
message = input("Tell me something, and I will repeat it back to you: ")
print(message)
print("-------------编写清晰的程序-------------");
name=input("Please enter your name:");
print("Hello,"+name+"!");
print("-------------求模运算符-------------");
print(4%3);
print("-------------while循环-------------");
current_number = 1
while current_number <= 5:
print(current_number)
current_number += 1
print("-------------让用户选择何时退出-------------");
prompt = "\nTell me something, and I will repeat it back to you:"
prompt += "\nEnter 'quit' to end the program. "
message = ""
while message != 'quit':
message = input(prompt)
print(message)
print("-------------break语句-------------");
prompt = "\nPlease enter the name of a city you have visited:"
prompt += "\n(Enter 'quit' when you are finished.) "
while True:
city = input(prompt)
if city == 'quit':
break
else:
print("I'd love to go to " + city.title() + "!")
-------------函数input()的工作原理-------------
Tell me something, and I will repeat it back to you: Hello World
Hello World
-------------编写清晰的程序-------------
Please enter your name:Alice
Hello,Alice!
-------------求模运算符-------------
1
-------------while循环-------------
1
2
3
4
5
-------------让用户选择何时退出-------------
Tell me something, and I will repeat it back to you:
Enter 'quit' to end the program. Hello World
Hello World
Tell me something, and I will repeat it back to you:
Enter 'quit' to end the program. quit
quit
-------------break语句-------------
Please enter the name of a city you have visited:
(Enter 'quit' when you are finished.) ShangHai
I'd love to go to Shanghai!
Please enter the name of a city you have visited:
(Enter 'quit' when you are finished.) quit
Process finished with exit code 0
三、数据类型
1.字符串
print("-------------字符串操作-------------");
#coding=utf-8
str = 'Hello World!'
print(str) # 输出完整字符串
print(str[0]) # 输出字符串中的第一个字符
print(str[2:5]) # 输出字符串中第三个至第五个之间的字符串
print(str[2:]) # 输出从第三个字符开始的字符串
print(str * 2) # 输出字符串两次
print(str + "TEST") # 输出连接的字符串
print("-------------格式化输出-------------");
x="欢迎您,%s,当前第%d 次访问! "
y=x%("小明",1)
#y=("欢迎您,%s,当前第%d 次访问! "%("小明",1)),以上两行可以合并为这一行。
print(y)
print("-------------三引号-------------");
hi = '''hi
there'''
print(hi) # str()
D:\工作空间\Python\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/工作空间/Python/main.py
-------------字符串操作-------------
Hello World!
H
llo
llo World!
Hello World!Hello World!
Hello World!TEST
-------------格式化输出-------------
欢迎您,小明,当前第1 次访问!
-------------三引号-------------
hi
there
进程已结束,退出代码0
到此这篇关于Python基础知识+结构+数据类型的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python结构数据类型内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
