python实现线性回归的示例代码
作者:von Libniz
线性回归就是通过多次取点,找出符合函数的曲线,那么就可以完成一维线性回归,本文通过实例代码给大家介绍python实现线性回归的相关知识,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧
1线性回归
1.1简单线性回归

在简单线性回归中,通过调整a和b的参数值,来拟合从x到y的线性关系。下图为进行拟合所需要优化的目标,也即是MES(Mean Squared Error),只不过省略了平均的部分(除以m)。
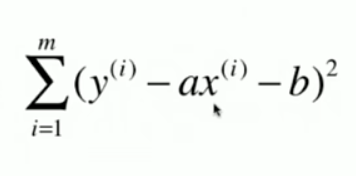
对于简单线性回归,只有两个参数a和b,通过对MSE优化目标求极值(最小二乘法),即可求得最优a和b如下,所以在训练简单线性回归模型时,也只需要根据数据求解这两个参数值即可。

下面使用波士顿房价数据集中,索引为5的特征RM (average number of rooms per dwelling)来进行简单线性回归。其中使用的评价指标为:





# 以sklearn的形式对simple linear regression 算法进行封装
import numpy as np
import sklearn.datasets as datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error,mean_absolute_error
np.random.seed(123)
class SimpleLinearRegression():
def __init__(self):
"""
initialize model parameters
self.a_=None
self.b_=None
def fit(self,x_train,y_train):
training model parameters
Parameters
----------
x_train:train x ,shape:data [N,]
y_train:train y ,shape:data [N,]
assert (x_train.ndim==1 and y_train.ndim==1),\
"""Simple Linear Regression model can only solve single feature training data"""
assert len(x_train)==len(y_train),\
"""the size of x_train must be equal to y_train"""
x_mean=np.mean(x_train)
y_mean=np.mean(y_train)
self.a_=np.vdot((x_train-x_mean),(y_train-y_mean))/np.vdot((x_train-x_mean),(x_train-x_mean))
self.b_=y_mean-self.a_*x_mean
def predict(self,input_x):
make predictions based on a batch of data
input_x:shape->[N,]
assert input_x.ndim==1 ,\
"""Simple Linear Regression model can only solve single feature data"""
return np.array([self.pred_(x) for x in input_x])
def pred_(self,x):
give a prediction based on single input x
return self.a_*x+self.b_
def __repr__(self):
return "SimpleLinearRegressionModel"
if __name__ == '__main__':
boston_data = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston_data['data'][:, 5] # total x data (506,)
y = boston_data['target'] # total y data (506,)
# keep data with target value less than 50.
x = x[y < 50] # total x data (490,)
y = y[y < 50] # total x data (490,)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
# train size:(343,) test size:(147,)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3)
regs = SimpleLinearRegression()
regs.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_hat = regs.predict(x_test)
rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((y_hat - y_test) ** 2) / len(x_test))
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_hat)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_hat)
# notice
R_squared_Error = 1 - mse / np.var(y_test)
print('mean squared error:%.2f' % (mse))
print('root mean squared error:%.2f' % (rmse))
print('mean absolute error:%.2f' % (mae))
print('R squared Error:%.2f' % (R_squared_Error))输出结果:
mean squared error:26.74
root mean squared error:5.17
mean absolute error:3.85
R squared Error:0.50
数据的可视化:

1.2 多元线性回归

多元线性回归中,单个x的样本拥有了多个特征,也就是上图中带下标的x。
其结构可以用向量乘法表示出来:
为了便于计算,一般会将x增加一个为1的特征,方便与截距bias计算。


而多元线性回归的优化目标与简单线性回归一致。

通过矩阵求导计算,可以得到方程解,但求解的时间复杂度很高。

下面使用正规方程解的形式,来对波士顿房价的所有特征做多元线性回归。
import numpy as np
from PlayML.metrics import r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import sklearn.datasets as datasets
from PlayML.metrics import root_mean_squared_error
np.random.seed(123)
class LinearRegression():
def __init__(self):
self.coef_=None # coeffient
self.intercept_=None # interception
self.theta_=None
def fit_normal(self, x_train, y_train):
"""
use normal equation solution for multiple linear regresion as model parameters
Parameters
----------
theta=(X^T * X)^-1 * X^T * y
assert x_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0],\
"""size of the x_train must be equal to y_train """
X_b=np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_train), 1)), x_train])
self.theta_=np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train) # (featere,1)
self.coef_=self.theta_[1:]
self.intercept_=self.theta_[0]
def predict(self,x_pred):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert x_pred.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b=np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_pred),1)),x_pred])
return X_b.dot(self.theta_)
def score(self,x_test,y_test):
Calculate evaluating indicator socre
---------
x_test:x test data
y_test:true label y for x test data
y_pred=self.predict(x_test)
return r2_score(y_test,y_pred)
def __repr__(self):
return "LinearRegression"
if __name__ == '__main__':
# use boston house price dataset for test
boston_data = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston_data['data'] # total x data (506,)
y = boston_data['target'] # total y data (506,)
# keep data with target value less than 50.
x = x[y < 50] # total x data (490,)
y = y[y < 50] # total x data (490,)
# train size:(343,) test size:(147,)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3,random_state=123)
regs = LinearRegression()
regs.fit_normal(x_train, y_train)
# calc error
score=regs.score(x_test,y_test)
rmse=root_mean_squared_error(y_test,regs.predict(x_test))
print('R squared error:%.2f' % (score))
print('Root mean squared error:%.2f' % (rmse))输出结果:
R squared error:0.79
Root mean squared error:3.36
1.3 使用sklearn中的线性回归模型
import sklearn.datasets as datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from PlayML.metrics import root_mean_squared_error
np.random.seed(123)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# use boston house price dataset
boston_data = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston_data['data'] # total x size (506,)
y = boston_data['target'] # total y size (506,)
# keep data with target value less than 50.
x = x[y < 50] # total x size (490,)
y = y[y < 50] # total x size (490,)
# train size:(343,) test size:(147,)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=123)
regs = LinearRegression()
regs.fit(x_train, y_train)
# calc error
score = regs.score(x_test, y_test)
rmse = root_mean_squared_error(y_test, regs.predict(x_test))
print('R squared error:%.2f' % (score))
print('Root mean squared error:%.2f' % (rmse))
print('coeffient:',regs.coef_.shape)
print('interception:',regs.intercept_.shape)R squared error:0.79 Root mean squared error:3.36 coeffient: (13,) interception: ()
到此这篇关于python实现线性回归的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python线性回归内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
