详解Spring中的Environment外部化配置管理
作者:跟着Mic学架构
Environment的中文意思是环境,它表示整个spring应用运行时的环境信息,它包含两个关键因素
- profiles
- properties
profiles
profiles这个概念相信大家都已经理解了,最常见的就是不同环境下,决定当前spring容器中的不同配置上下文的解决方案。比如针对开发环境、测试环境、生产环境,构建不同的application.properties配置项,这个时候我们可以通过profiles这个属性来决定当前spring应用上下文中生效的配置项。
实际上,通过profiles可以针对bean的配置进行逻辑分组。 简单来说,我们可以通过profiles来针对不同的bean进行逻辑分组,这个分组和bean本身的定义没有任何关系,无论是xml还是注解方式,都可以配置bean属于哪一个profile分组。
当存在多个profile分组时,我们可以指定哪一个profile生效,当然如果不指定,spring会根据默认的profile去执行。我们来通过一个代码演示一下。
ProfileService
创建一个普通的类,代码如下
public class ProfileService {
private String profile;
public ProfileService(String profile) {
this.profile = profile;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ProfileService{" +
"profile='" + profile + '\'' +
'}';
}
}声明一个配置类
在配置类中,构建两个bean,配置不同的profile。
@Configuration
public class ProfileConfiguration {
@Bean
@Profile("dev")
public ProfileService profileServiceDev(){
return new ProfileService("dev");
}
@Bean
@Profile("prod")
public ProfileService profileServiceProd(){
return new ProfileService("prod");
}
}定义测试方法
public class ProfileMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod");
applicationContext.register(ProfileConfiguration.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(ProfileService.class));
}
}可以通过很多种方式来激活配置,默认情况下不添加applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod");时,会发现bean没有被装载。添加了之后,会根据当前激活的profiles来决定装载哪个bean。
除此之外,我们还可以在启动参数中增加-Dspring.profiles.active=prod来决定当前激活哪个profile。该属性可以配置在系统环境变量、JVM系统属性、等。
注意配置文件不是单选;可能会同时激活多个配置文件,编程式的使用方法setActiveProfiles(),该方法接收String数组参数,也就是多个配置文件名
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod","dev");如果没有任何profile配置被激活,默认的profile将会激活。 默认profile配置文件可以更改,通过环境变量的setDefaultProfiles方法,或者是声明的spring.profiles.default属性值
profiles总结
简单总结一下profiles,通过profiles可以最一组bean进行逻辑分组,这些逻辑分组的bean会根据Environment上下文中配置的激活的profile来进行加载,也就是Environment对于profiles配置来说,它能决定当前激活的是哪个profile配置。
- 一个profile就是一组Bean定义的逻辑分组。
- 这个分组,也就 这个profile,被赋予一个命名,就是这个profile名字。
- 只有当一个profile处于active状态时,它对应的逻辑上组织在一起的这些Bean定义才会被注册到容器中。
- Bean添加到profile可以通过XML定义方式或者annotation注解方式。
- Environment对于profile所扮演的角色是用来指定哪些profile是当前活跃的缺省。
Properties
properties的作用就是用来存放属性的,它可以帮我们管理各种配置信息。这个配置的来源可以是properties文件、JVM properties、系统环境变量、或者专门的Properties对象等。
我们来看一下Environment这个接口,它继承了PropertyResolver,这个接口和属性的操作有关,也就是我们可以通过Environment来设置和获得相关属性。
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
String[] getActiveProfiles();
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... var1);
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles var1);
}至此,我们可以可以简单的总结Environment的作用,Environment提供了不同的profile配置,而PropertyResolver提供了配置的操作,由此我们可以知道,Spring 容器可以根据不同的profile来获取不同的配置信息,从而实现Spring容器中运行时环境的处理。
environment的应用
在spring boot应用中,修改application.properties配置
env=default
创建一个Controller进行测试
@RestController
public class EnvironementController {
@Autowired
Environment environment;
@GetMapping("/env")
public String env(){
return environment.getProperty("env");
}
}指定profile属性
在前面的内容中我们介绍了profile和property这两个概念,现在我们来结合使用加深对这两者的理解。
在spring boot应用中,默认的外部化配置是application.properties文件,事实上,除了这个默认的配置文件之外,我们还可以使用springboot中的约定命名格式来实现不同环境的配置
application-profile.properties
当前spring boot应用选择使用哪个properties文件作为上下文环境配置,取决与当前激活的profile。同样,我们可以通过很多种方式来激活,比如在application.properties中增加spring.profiles.active=dev这种方式,也可以在JVM参数中增加该配置来指定生效的配置。
在不指定的情况下,则使用默认的配置文件,简单来说,如果没有显式激活某一个配置文件,那么应用程序就将加载application-default.properties中的属性。
这个功能非常实用,一般的公司里面都会有几套运行环境,比如开发、测试、生产环境,这些环境中会有一些配置信息是不同的,比如服务器地址。那我们需要针对不同的环境使用指定的配置信息,通过这种方式就可以很方便的去解决。
@Value注解的使用
在properties文件中定义的属性,除了可以通过environment的getProperty方法获取之外,spring还提供了@Value注解,
@RestController
public class EnvironementController {
@Value("${env}")
private String env;
@GetMapping("/env")
public String env(){
return env;
}
}spring容器在加载一个bean时,当发现这个Bean中有@Value注解时,那么它可以从Environment中将属性值进行注入,如果Environment中没有这个属性,则会报错。
Spring Environment原理设计
结合前面咱们讲过的内容,我们来推测一下Environment的实现原理。
简单演示一下Environment中的配置来源
- @Value("${java.version}") 获取System.getProperties , 获取系统属性
- 配置command的jvm参数,
-Denvtest=command
基于现有的内容的推导,我们可以画出下面这样一个图。
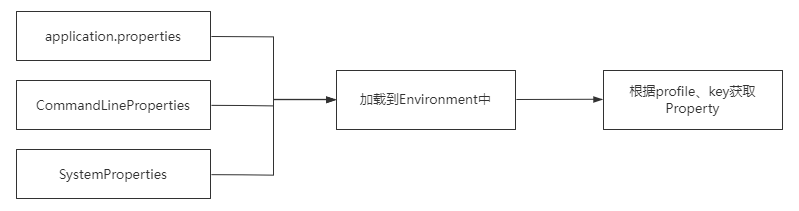
- 第一部分是属性定义,这个属性定义可以来自于很多地方,比如application.properties、或者系统环境变量等。
- 然后根据约定的方式去指定路径或者指定范围去加载这些配置,保存到内存中。
- 最后,我们可以根据指定的key从缓存中去查找这个值。
下面这个是表示Environment的类关系图,这个类关系图还是非常清晰的体现了Environment的原理。
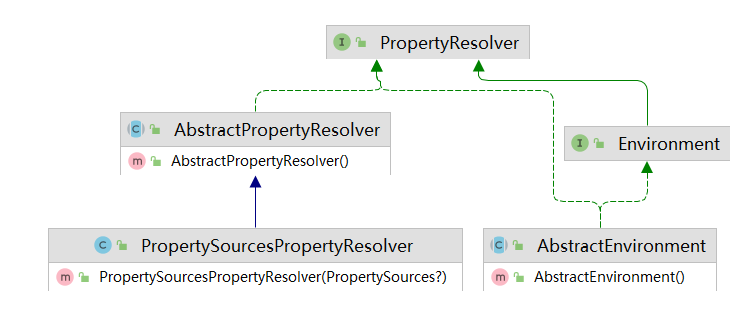
上述类图的核心API说明如下
Environment接口,继承了PropertyResolver。 PropertyResolver,它主要有两个作用。
- 通过
propertyName属性名获取与之对应的propertValue属性值(getProperty)。 - 把
${propertyName:defaultValue}格式的属性占位符,替换为实际的值(resolvePlaceholders)。
PropertyResolver的具体实现类是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver,属性源的解决方案。该类是体系中唯一的完整实现类。它以PropertySources属性源集合(内部持有属性源列表List )为属性值的来源,按序遍历每个PropertySource,获取到一个非null的属性值则返回。
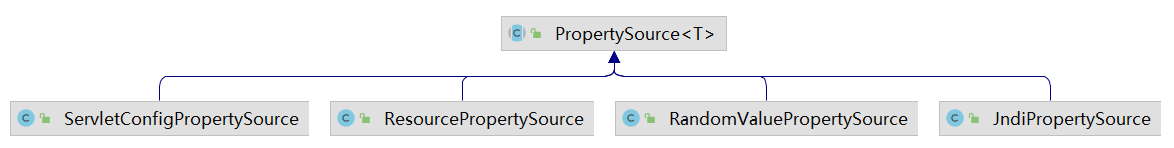
其中,PropertySourcesPropertyResolver中的List ,表示不同属性源的来源,它的类关系图如下,表示针对不同数据源的存储。
到此这篇关于详解Spring中的Environment外部化配置管理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Environment外部化配置内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- SpringBoot Test的webEnvironment源码解读
- springboot的EnvironmentPostProcessor接口方法源码解析
- Spring运行环境Environment的解析
- Spring Boot读取配置文件内容的3种方式(@Value、Environment和@ConfigurationProperties)
- Spring之底层架构核心概念Environment及用法详解
- SpringBoot扩展点EnvironmentPostProcessor实例详解
- 基于Spring Boot的Environment源码理解实现分散配置详解
- Spring之Environment类的使用方式
