Python机器学习应用之基于天气数据集的XGBoost分类篇解读
作者:柚子味的羊
XGBoost是一个优化的分布式梯度增强库,旨在实现高效,灵活和便携。它在 Gradient Boosting 框架下实现机器学习算法。XGBoost提供并行树提升(也称为GBDT,GBM),可以快速准确地解决许多数据科学问题
一、XGBoost
XGBoost并不是一种模型,而是一个可供用户轻松解决分类、回归或排序问题的软件包。
1 XGBoost的优点
- 简单易用。相对其他机器学习库,用户可以轻松使用XGBoost并获得相当不错的效果。
- 高效可扩展。在处理大规模数据集时速度快效果好,对内存等硬件资源要求不高。
- 鲁棒性强。相对于深度学习模型不需要精细调参便能取得接近的效果。
- XGBoost内部实现提升树模型,可以自动处理缺失值。
2 XGBoost的缺点
- 相对于深度学习模型无法对时空位置建模,不能很好地捕获图像、语音、文本等高维数据。
- 在拥有海量训练数据,并能找到合适的深度学习模型时,深度学习的精度可以遥遥领先XGBoost。
二、实现过程
1 数据集
2 实现
#%%导入基本库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
## 绘图函数库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
#读取数据
data=pd.read_csv('D:\Python\ML\data\XGBtrain.csv')
通过variable explorer查看样本数据

也可以使用head()或tail()函数,查看样本前几行和后几行。不难看出,数据集中含有NAN,代表数据中存在缺失值,可能是在数据采集或者处理过程中产生的一种错误,此处采用-1将缺失值进行填充,还有其他的填充方法:
- 中位数填补
- 平均数填补
注:在数据的前期处理中,一定要注意对缺失值的处理。前期数据处理的结果将会严重影响后面是否可能得到合理的结果
data=data.fillna(-1) #利用value_counts()函数查看训练集标签的数量(Raintomorrow=no) print(pd.Series(data['RainTomorrow']).value_counts()) data_des=data.describe()
填充后:

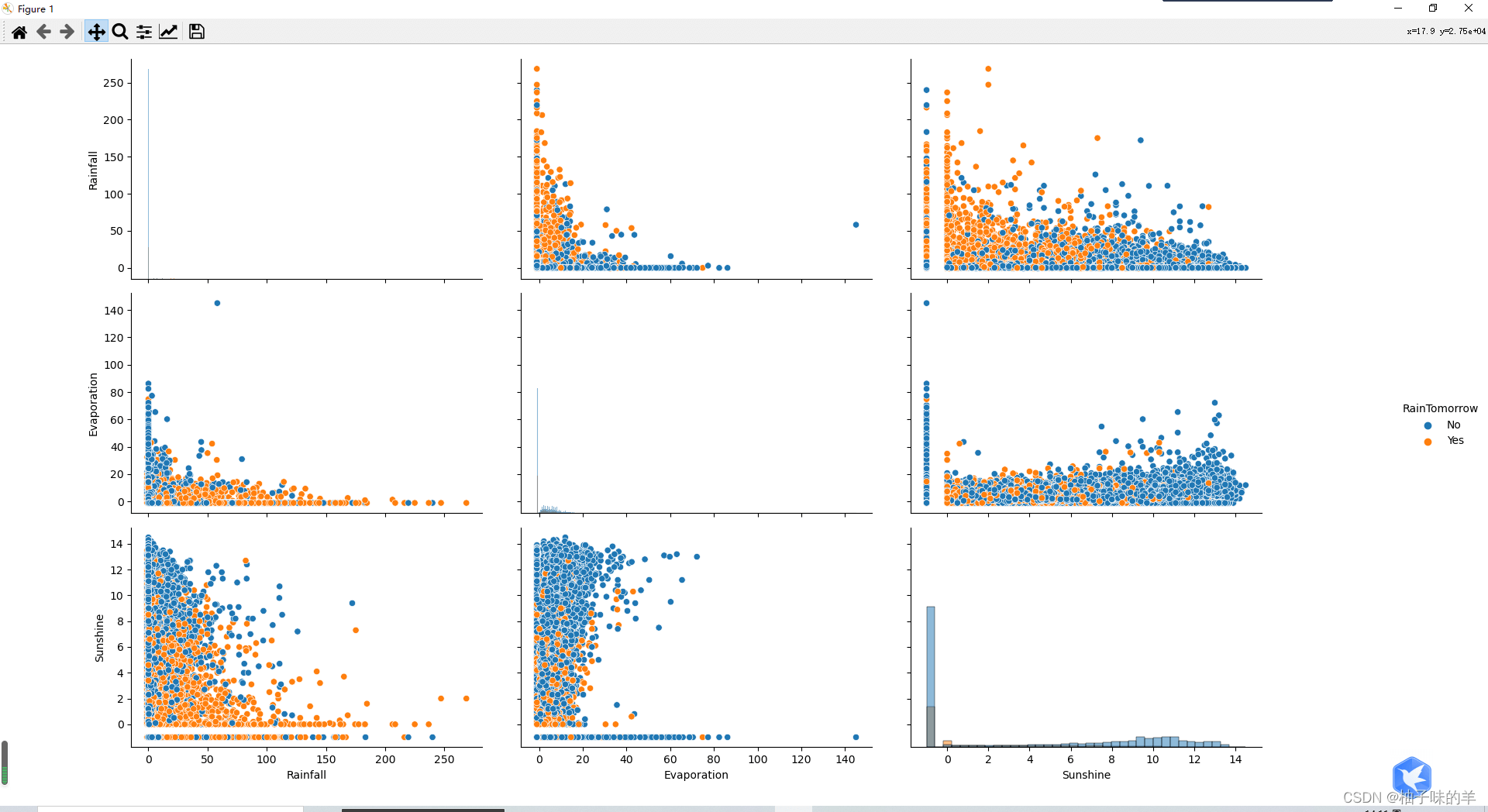
#%%#可视化数据(特征值包括数字特征和非数字特征) numerical_features = [x for x in data.columns if data[x].dtype == np.float] category_features = [x for x in data.columns if data[x].dtype != np.float and x != 'RainTomorrow'] #%% 选取三个特征与标签组合的散点可视化 sns.pairplot(data=data[['Rainfall','Evaporation','Sunshine'] + ['RainTomorrow']], diag_kind='hist', hue= 'RainTomorrow') plt.show()
#%%每个特征的箱图
i=0
for col in data[numerical_features].columns:
if col != 'RainTomorrow':
plt.subplot(2,8,i+1)
sns.boxplot(x='RainTomorrow', y=col, saturation=0.5, palette='pastel', data=data)
plt.title(col)
i=i+1
plt.show()

#%%非数字特征
tlog = {}
for i in category_features:
tlog[i] = data[data['RainTomorrow'] == 'Yes'][i].value_counts()
flog = {}
for i in category_features:
flog[i] = data[data['RainTomorrow'] == 'No'][i].value_counts()
#%%不同地区下雨情况
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('RainTomorrow')
sns.barplot(x = pd.DataFrame(tlog['Location']).sort_index()['Location'], y = pd.DataFrame(tlog['Location']).sort_index().index, color = "red")
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('Not RainTomorrow')
sns.barplot(x = pd.DataFrame(flog['Location']).sort_index()['Location'], y = pd.DataFrame(flog['Location']).sort_index().index, color = "blue")
plt.show()

#%%
plt.figure(figsize=(20,5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('RainTomorrow')
sns.barplot(x = pd.DataFrame(tlog['RainToday'][:2]).sort_index()['RainToday'], y = pd.DataFrame(tlog['RainToday'][:2]).sort_index().index, color = "red")
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('Not RainTomorrow')
sns.barplot(x = pd.DataFrame(flog['RainToday'][:2]).sort_index()['RainToday'], y = pd.DataFrame(flog['RainToday'][:2]).sort_index().index, color = "blue")
plt.show()

XGBoost无法处理字符串类型的数据,需要将字符串数据转化成数值
#%%对离散变量进行编码
## 把所有的相同类别的特征编码为同一个值
def get_mapfunction(x):
mapp = dict(zip(x.unique().tolist(),
range(len(x.unique().tolist()))))
def mapfunction(y):
if y in mapp:
return mapp[y]
else:
return -1
return mapfunction
#将非数字特征离散化
for i in category_features:
data[i] = data[i].apply(get_mapfunction(data[i]))
#%%利用XGBoost进行训练与预测
## 为了正确评估模型性能,将数据划分为训练集和测试集,并在训练集上训练模型,在测试集上验证模型性能。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
## 选择其类别为0和1的样本 (不包括类别为2的样本)
data_target_part = data['RainTomorrow']
data_features_part = data[[x for x in data.columns if x != 'RainTomorrow']]
## 测试集大小为20%, 80%/20%分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data_features_part, data_target_part, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 2020)
#%%导入XGBoost模型
from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier
## 定义 XGBoost模型
clf = XGBClassifier()
# 在训练集上训练XGBoost模型
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
#%% 在训练集和测试集上分布利用训练好的模型进行预测
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
from sklearn import metrics
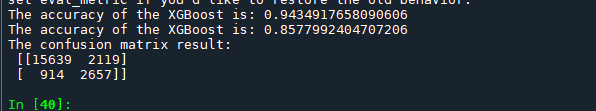
## 利用accuracy(准确度)【预测正确的样本数目占总预测样本数目的比例】评估模型效果
print('The accuracy of the XGBoost is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the XGBoost is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
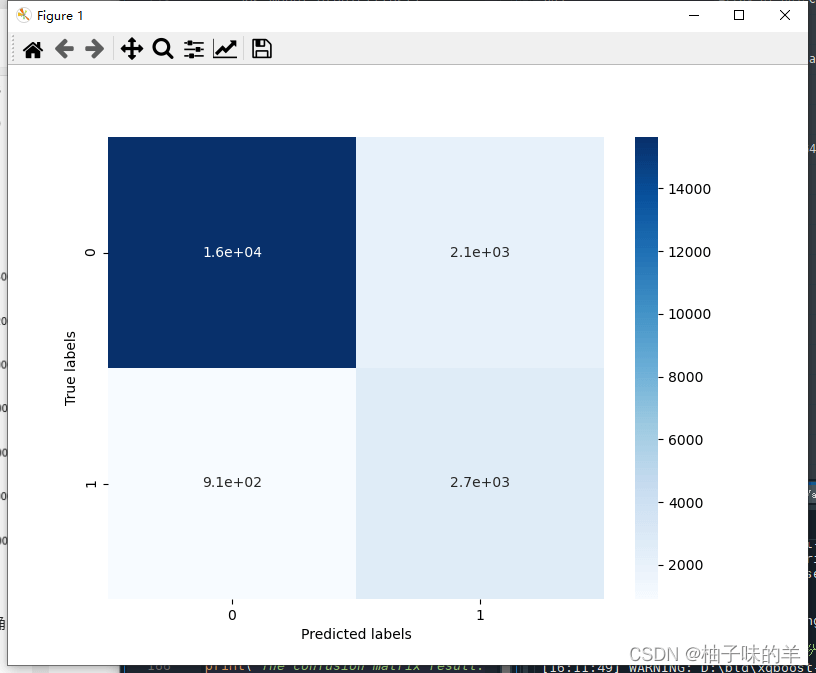
## 查看混淆矩阵 (预测值和真实值的各类情况统计矩阵)
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# 利用热力图对于结果进行可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()

#%%利用XGBoost进行特征选择: #XGboost中可以用属性feature_importances_去查看特征的重要度。 sns.barplot(y=data_features_part.columns,x=clf.feature_importances_)

初次之外,我们还可以使用XGBoost中的下列重要属性来评估特征的重要性:
- weight:是以特征用到的次数来评价
- gain:当利用特征做划分的时候的评价基尼指数
- cover:利用一个覆盖样本的指标二阶导数(具体原理不清楚有待探究)平均值来划分。
- total_gain:总基尼指数
- total_cover:总覆盖
#利用XGBoost的其他重要参数评估特征的重要性
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from xgboost import plot_importance
def estimate(model,data):
#sns.barplot(data.columns,model.feature_importances_)
ax1=plot_importance(model,importance_type="gain")
ax1.set_title('gain')
ax2=plot_importance(model, importance_type="weight")
ax2.set_title('weight')
ax3 = plot_importance(model, importance_type="cover")
ax3.set_title('cover')
plt.show()
def classes(data,label,test):
model=XGBClassifier()
model.fit(data,label)
ans=model.predict(test)
estimate(model, data)
return ans
ans=classes(x_train,y_train,x_test)
pre=accuracy_score(y_test, ans)
print('acc=',accuracy_score(y_test,ans))




XGBoost中包括但不限于下列对模型影响较大的参数:
- learning_rate: 有时也叫作eta,系统默认值为0.3。每一步迭代的步长,很重要。太大了运行准确率不高,太小了运行速度慢。
- subsample:系统默认为1。这个参数控制对于每棵树,随机采样的比例。减小这个参数的值,算法会更加保守,避免过拟合, 取值范围零到一。
- colsample_bytree:系统默认值为1。我们一般设置成0.8左右。用来控制每棵随机采样的列数的占比(每一列是一个特征)。max_depth: 系统默认值为6,我们常用3-10之间的数字。这个值为树的最大深度。这个值是用来控制过拟合的。
- max_depth越大,模型学习的更加具体。
调节模型参数的方法有贪心算法、网格调参、贝叶斯调参等。这里我们采用网格调参,它的基本思想是穷举搜索:在所有候选的参数选择中,通过循环遍历,尝试每一种可能性,表现最好的参数就是最终的结果
#%%通过调参获得更好的效果
## 从sklearn库中导入网格调参函数
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
## 定义参数取值范围
learning_rate = [0.1, 0.3, 0.6]
subsample = [0.8, 0.9]
colsample_bytree = [0.6, 0.8]
max_depth = [3,5,8]
parameters = { 'learning_rate': learning_rate,
'subsample': subsample,
'colsample_bytree':colsample_bytree,
'max_depth': max_depth}
model = XGBClassifier(n_estimators = 50)
## 进行网格搜索
clf = GridSearchCV(model, parameters, cv=3, scoring='accuracy',verbose=1,n_jobs=-1)
clf = clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
#%%网格搜索后的参数
print(clf.best_params_)

#%% 在训练集和测试集上分别利用最好的模型参数进行预测
## 定义带参数的 XGBoost模型
clf = XGBClassifier(colsample_bytree = 0.6, learning_rate = 0.3, max_depth= 8, subsample = 0.9)
# 在训练集上训练XGBoost模型
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
## 利用accuracy(准确度)【预测正确的样本数目占总预测样本数目的比例】评估模型效果
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
## 查看混淆矩阵 (预测值和真实值的各类情况统计矩阵)
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# 利用热力图对于结果进行可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()
三、Keys
XGBoost的重要参数
- eta【默认0.3】:通过为每一颗树增加权重,提高模型的鲁棒性。典型值为0.01-0.2。
- min_child_weight【默认1】:决定最小叶子节点样本权重和。这个参数可以避免过拟合。当它的值较大时,可以避免模型学习到局部的特殊样本。但是如果这个值过高,则会导致模型拟合不充分。
- max_depth【默认6】:这个值也是用来避免过拟合的,max_depth越大,模型会学到更具体更局部的样本。典型值:3-10
- max_leaf_nodes:树上最大的节点或叶子的数量。可以替代max_depth的作用。这个参数的定义会导致忽略max_depth参数。
- gamma【默认0】:在节点分裂时,只有分裂后损失函数的值下降了,才会分裂这个节点。Gamma指定了节点分裂所需的最小损失函数下降值。这个参数的值越大,算法越保守。这个参数的值和损失函数息息相关。
- max_delta_step【默认0】:这个参数限制每棵树权重改变的最大步长。如果这个参数的值为0,那就意味着没有约束。如果它被赋予了某个正值,那么它会让这个算法更加保守。但是当各类别的样本十分不平衡时,它对分类问题是很有帮助的。
- subsample【默认1】:这个参数控制对于每棵树,随机采样的比例。减小这个参数的值,算法会更加保守,避免过拟合。但是,如果这个值设置得过小,它可能会导致欠拟合。典型值:0.5-1
- colsample_bytree【默认1】:用来控制每棵随机采样的列数的占比(每一列是一个特征)。典型值:0.5-1
- colsample_bylevel【默认1】:用来控制树的每一级的每一次分裂,对列数的采样的占比。subsample参数和colsample_bytree参数可以起到相同的作用,一般用不到。
- lambda【默认1】:权重的L2正则化项。(和Ridge regression类似)。这个参数是用来控制XGBoost的正则化部分的。虽然大部分数据科学家很少用到这个参数,但是这个参数在减少过拟合上还是可以挖掘出更多用处的。
- alpha【默认1】:权重的L1正则化项。(和Lasso regression类似)。可以应用在很高维度的情况下,使得算法的速度更快。
- scale_pos_weight【默认1】:在各类别样本十分不平衡时,把这个参数设定为一个正值,可以使算法更快收敛。
886~~
到此这篇关于Python机器学习应用之基于天气数据集的XGBoost分类篇解读的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python XGBoost内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
