详解Java SpringAOP切面类
投稿:BJT
切面类是什么
简单的来说,就是动态的在方法的指定位置添加指定的代码。
为什么需要切面类?
在软件开发的过程中,有很多业务,特别是在编写核心业务的时候,往往需要很多其他的辅助业务,比如说身份验证(银行转账需要身份验证)、数据缓存、日志输出。这些往往在某个核心业务中处于辅助的部分。这些辅助的任务都有个特点,就是这些业务都处在核心业务的同一个切面上?
什么意思呢?
假如有加减乘除四个方法,方法开始位置和方法结束位置只是一个标志,方法执行位置处是核心业务,我们想在这四个方法的核心代码前执行一些准备操作,那么我们可以在方法开始位置和方法执行位置之间加入一段代码,那么这些准备操作实际上就是在同一个切面上的。同理,在四个方法的任意处切一刀,都是一个切面。
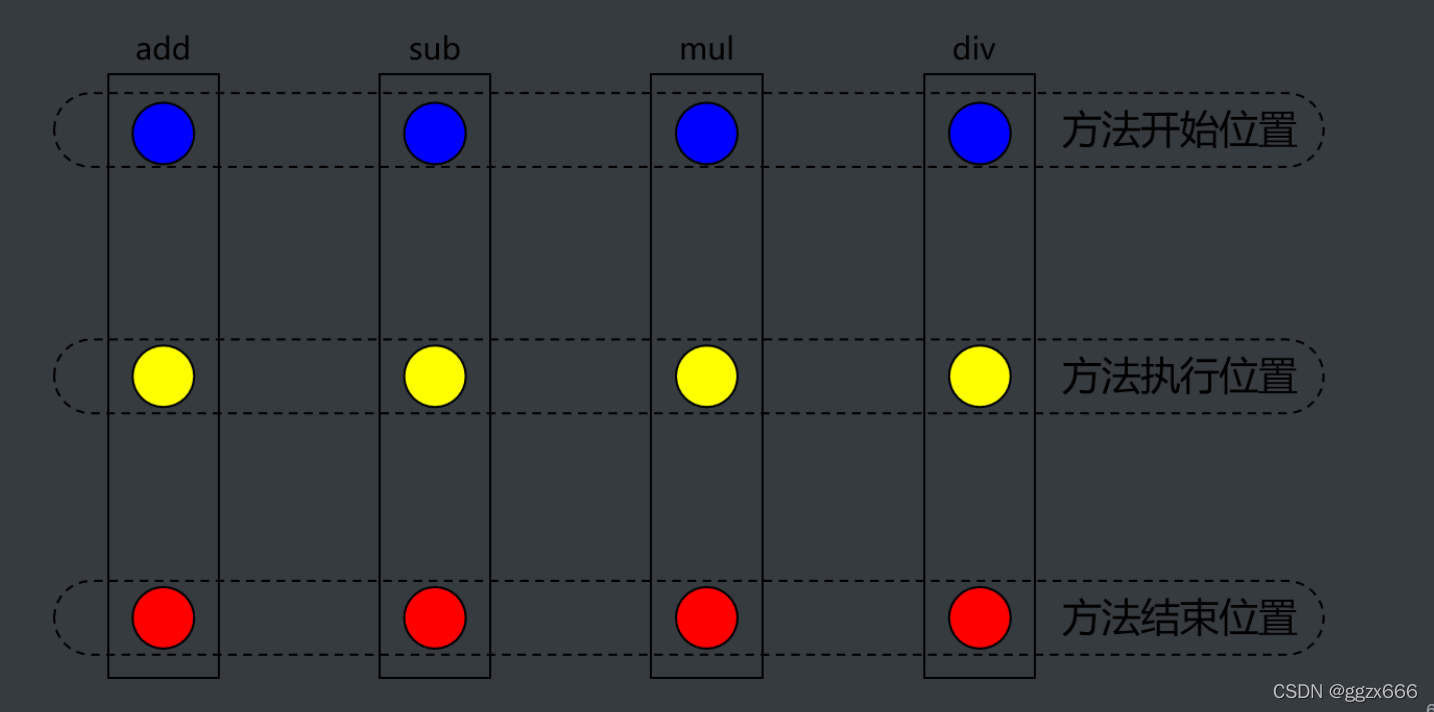
什么时候需要用切面类?
对于一些方法,抽取出来同一类非核心业务,然后可以将提取出来的业务编写成一个切面类,切面类可以;例如加减乘除,加入日志功能,那么日志功能就是非核心业务。
切面类有什么用?
解决代码混乱问题,非核心业务和核心业务代码处于同一个方法中会影响代码的质量,甚至可能会影响到核心业务
下面用日志功能来讲解切面类怎么创建
日志的作用
- 在数据处理之前显示我们传入的数据
- 遇到异常返回
- 处理结束显示处理完成
日志如何实现
最简单的方法,在数据处理之前手动输出。
public void receiveMoney(int receiveMoney) throws ReceiveMoneyException {
System.out.println("[收钱]:参数为"+receiveMoney);
System.out.println("[收钱]数据处理中。。。。");
checkAmount(receiveMoney);
System.out.println("[收钱]数据处理事务完成完成");
}
这样我们的日志功能就可以实现了,但是,这只是其中一个辅助业务,一个项目中有很多业务,各种繁琐的功能和日志都实现在一个方法中,代码结构会无比的混乱,特别是一个日志功能和核心功能放在一起,很容易发生问题,并且一个业务中往往还要很多其他非核心的业务需要处理,比如说在接受钱之前,需要验明身份,来路不明的钱银行不能直接接收,若身份核验正确,那么接收到钱后还得进行数据缓存。
身份验证、数据缓存、异常处理等非核心业务如果处理不好往往会导致核心业务代码结构混乱。
那么怎样能将日志功能、身份验证加入到核心业务方法之中,但是不影响核心业务 的代码
切面类能完成这些任务
- 切面类能动态的在指定位置添加指定代码
AOP的五大通知
AspectJ 支持 5 种类型的通知注解:
@Before:前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行@After:后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行@AfterRunning:返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行@AfterThrowing: 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后@Around:环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
通知是啥?简单理解就是上面说到的辅助业务,我们在划分切面的提取辅助业务代码时候,会有以下情况
- 需要在核心业务前执行该辅助业务
- 需要在核心业务执行之后执行该辅助业务
- 需要在报错时候执行该辅助业务
- 需要在返回结果是执行该辅助业务
- 需要在方法执行之前之后异常时执行该辅助业务
上面需要搞清的时后置通知和返回通知
返回通知(after-returning):当核心业务代码执行完成后执行,发生异常不执行
后置通知(after):不论目标方法是否发生异常都会执行,若无异常,则执行顺序在返回通知之后
Spring AOP类的实现技术
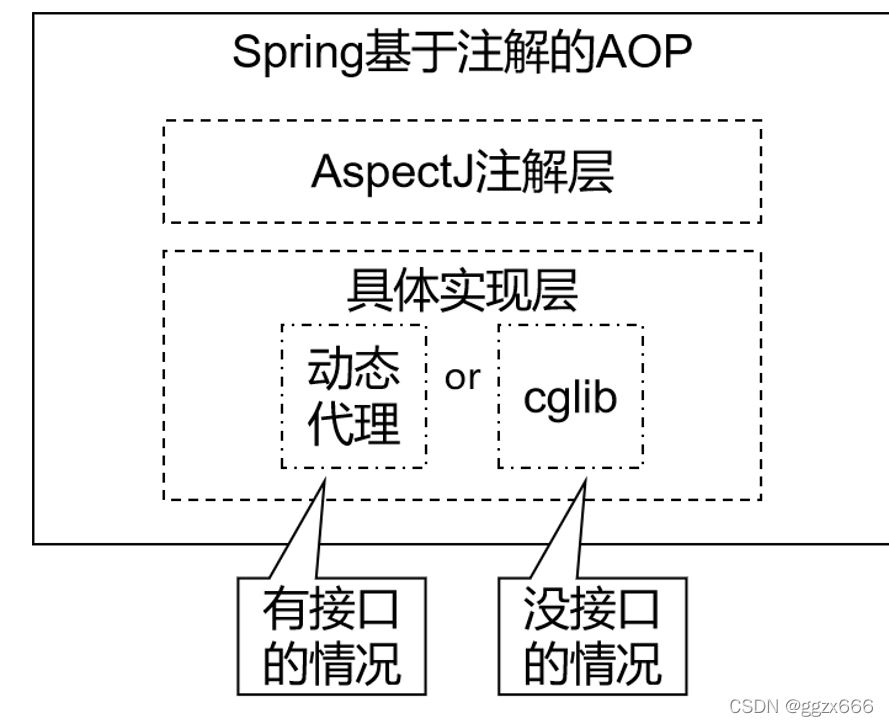
- 动态代理(
InvocationHandler):JDK原生的实现方式,需要被代理的目标类必须实现接口。因为这个技术要求代理对象和目标对象实现同样的接口(兄弟两个拜把子模式)。 cglib:通过继承被代理的目标类(认干爹模式)实现代理,所以不需要目标类实现接口。AspectJ:本质上是静态代理,将代理逻辑“织入”被代理的目标类编译得到的字节码文件,所以最终效果是动态的。weaver就是织入器。Spring只是借用了AspectJ中的注解。
一、准备工作
在maven的pom.xml中加入如下代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-AOP</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.14</version>
</dependency>
<!--在使用这个代码的时候,我用IDEA没有代码提示,并且写完会爆红色,直接同步即可,不-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
因为我们要使用的是AspectJ中的注解,所以需要导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
springconfig
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
</beans>
测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//这个需要spring-test依赖,使用后不需要创建IOC容器
@ContextConfiguration(value = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class AOPTEST {
@Autowired
private Calc calc;
@Test
public void testAnnotationAOP(){
int add=calc.add(10,0);
System.out.println("外部 add"+add);
}
}
这篇文章我们先用有接口的形式来写切面类
文件结构
切面类中有什么?
- 前置通知(
Before):在目标方法执行之前执行某段代码 - 后置通知(
AfterReturning):在目标方执行完成后执行,如果目标方法异常,则后置通知不再执行某段代码 - 异常通知(
Afterthrowing):目标方法抛出异常的时候执行某段代码 - 最终通知(
After);不管目标方法是否有异常都会执行,相当于try…catch…finally中的finally。 - 环绕通知(
Around):可以控制目标方法是否执行
这些通知有什么用?
- 不需要再核心代码内部添加多余的代码,而是在调用核心代码前、后、抛异常、结束时调用某部分代码。
- 这里涉及到了反射的知识,因为这些通知的实现底层就是动态代理或cglib。简单来说,就是在调用核心代码前,调用的方法会被拦截下来,然后执行切面类中的某段代码。
为什么命名为切面类?
首先要知道一点,切面类可以对很多方法或者很多类切面,主要看你想实现怎么样的功能。比如说我们想在方法执行之前调用日志功能,那么我们要把这些方法在执行之前“切开”,然后在方法内“加入”日志输出。因为这些事情都是切面类做的,所以才有这样的名称。

下面来看代码
切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
//前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(public int com.Calc.add(int ,int ))")
public void printLogBefore(){
System.out.println("[AOP前置通知]方法开始了");
}
//后置通知
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int com.Calc.add(int ,int ))")
//在返回通知中获取目标方法返回值分为两步,给returning设置一个名称,然后使用该名称在通知方法中声明一个对应的形参
public void printLogAfterSuccess(){
System.out.println("[AOP返回通知]方法成功返回了");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value ="execution(public int com.Calc.add(int ,int ))")
public void printLogAfterException(){
System.out.println("[AOP异常通知]方法抛出异常");
}
//结束通知
@After("execution(public int com.Calc.add(int ,int ))")
public void printLogFinish(){
System.out.println("[AOP结束通知]方法结束了");
}
}
再来看看测试方法
@Test
public void testAnnotationAOP(){
int add=calc.add(10,0);//调用
System.out.println("外部 add"+add);
}
结果:
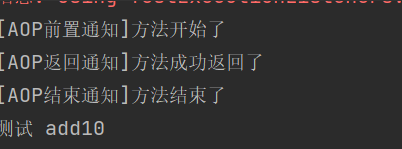
可以看见,切面类成功在Calculator中实现了日志功能
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注脚本之家的更多内容!
