springboot 加载 META-INF/spring.factories方式
作者:kong-kong
springboot 加载 META-INF/spring.factories
用户应用程序Application
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(NacosSpringBootYamlApplication.class, args);
SpringApplication类
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
// 这里Class是数组
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); // 这里就是SpringMvcApplication的实例
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();// deduce(推断)web类型(servlet、reactive、NoWeb)
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));// 这里会处理加载所有的spring.factories文件的内容到缓存 找到*META-INF/spring.factories*中声明的所有ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类并将其实例化
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); //找到*META-INF/spring.factories*中声明的所有ApplicationListener的实现类并将其实例化
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); //获得当前执行main方法的类对象,这里就是SpringMvcApplication的实例
}
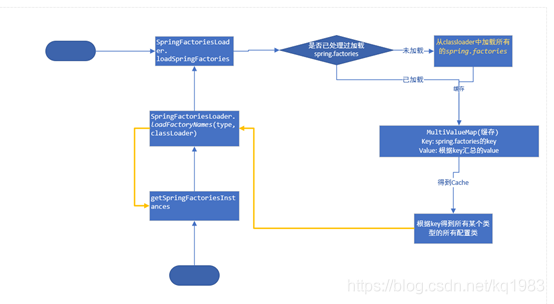
具体加载该classLoader下的所有spring.factories到缓存
如果缓存已经存在,则直接根据key,返回数据
/** key:是spring.factories的key value:是根据key分组,把同个key的不同value放到list里面 */
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) { //已经处理过了 直接返回
return result;
}
//url: // file:/C:/Users/kongqi/.m2/repository/org/springframework/spring-beans/5.1.9.RELEASE/spring-beans-5.1.9.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
try { //得到classloader下的所有jar包中的spring.factories的文件
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); // 得到spring.factories的内容
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { // key: spring.factories的key value: spring.factories的value
String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); // spring.factories的key
for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {//value根据逗号,分隔
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); //factoryClassName其实就是spring.factories的key 由于value是List类型 MultiValueMap value有多个
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
流程图
建立META-INF/spring.factories文件的意义何在
平常我们如何将Bean注入到容器当中
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService() {
HelloService service = new HelloService();
service.setHelloProperties( helloProperties );
return service;
}
}
一般就建立配置文件使用@Configuration,里面通过@Bean进行加载bean
或者使用@Compont注解在类上进行类的注入
注意:
在我们主程序入口的时候:
@SpringBootApplication这个注解里面的东西
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
里面注解@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan注解指扫描@SpringBootApplication注解的入口程序类所在的basepackage下的
所有带有@Component注解的bean,从而注入到容器当中。
但是
如果是加入maven坐标依赖的jar包,就是项目根目录以外的Bean是怎么添加的??
这个时候注解@EnableAutoConfiguration的作用就来了
导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector这个类:
这个类里面有一个方法
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解来注册项目包外的bean。而spring.factories文件,则是用来记录项目包外需要注册的bean类名
为什么需要spring.factories文件,
因为我们整个项目里面的入口文件只会扫描整个项目里面下的@Compont @Configuration等注解
但是如果我们是引用了其他jar包,而其他jar包只有@Bean或者@Compont等注解,是不会扫描到的。
除非你引入的jar包没有Bean加载到容器当中
所以我们是通过写/META-INF/spring.factories文件去进行加载的。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
