Java web.xml之contextConfigLocation作用案例详解
作者:elice_
这篇文章主要介绍了Java web.xml之contextConfigLocation作用案例详解,本篇文章通过简要的案例,讲解了该项技术的了解与使用,以下就是详细内容,需要的朋友可以参考下
在web.xml中通过contextConfigLocation配置spring,contextConfigLocation参数定义了要装入的 Spring 配置文件。
部署applicationContext.xml文件
如果不写任何参数配置,默认的是在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
如果指定了要加载的文件,则会去加载相应的xml,而不会去加载/WEB-INF/下的applicationContext.xml。如果没有指定的话,默认会去/WEB-INF/下加载applicationContext.xml。
如果想要自定义文件名,需要在web.xml中加入contextConfigLocation这个context参数
springmvc的默认配置文件是放在WEB-INF下的,并且要命名为*-servlet.xml,*为servlet—name,即下文中的"Springmvc"。
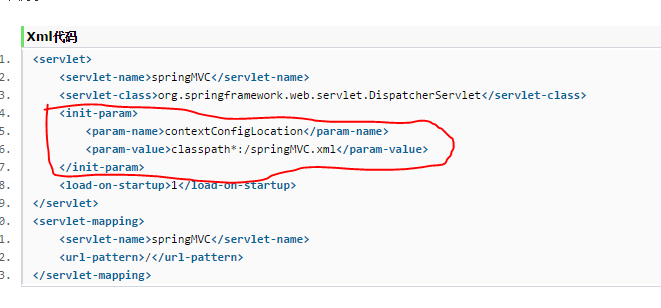
我们可以在web.xml中配置<init-param>来自定义文件名称和位置。如下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 通过初始化参数,指定xml文件的位置 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
classpath:只会到你的class路径中查找找文件;
classpath*:不仅包含class路径,还包括jar文件中(class路径)进行查找.
到此这篇关于Java web.xml之contextConfigLocation作用案例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java web.xml之contextConfigLocation作用内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
