基于线程的wait和notify使用,生产消费案例
作者:strive_day
这篇文章主要介绍了基于线程的wait和notify使用,生产消费案例,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教
多个线程可以相互竞争,也可以互相协作完成一件事情。
Object的相关方法
| Object相关方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void wait() | 让当前线程等待,如果没有被唤醒,就一直等待 |
| void wait(long timeout) | 让当前线程等待指定毫秒值,如果到了指定的毫秒值自动唤醒 |
| void notify() | 唤醒一个线程,唤醒的是当前对象锁下的一个线程 |
| void notifyAll() | 唤醒所有线程,唤醒的是当前对象锁下面的所有线程 |
这些方法一定要放在同步代码块中去使用,并且这些方法要通过锁对象去调用【***】
案例:
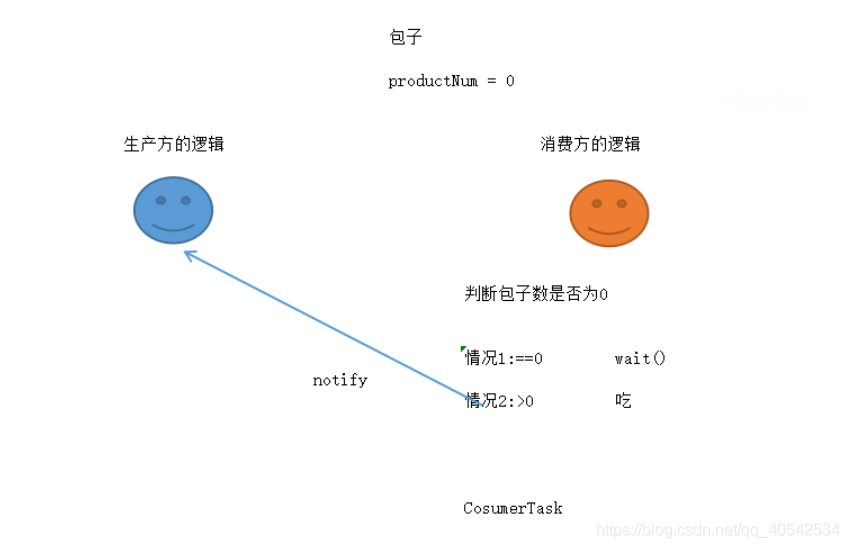
生产方每生产一个产品就需要等待(通知)消费方消费完产品后才能继续生产
消费方每消费一个产品就需要等待(通知)生产方去生产产品后才能继续消费。
案例图解
生产方逻辑图
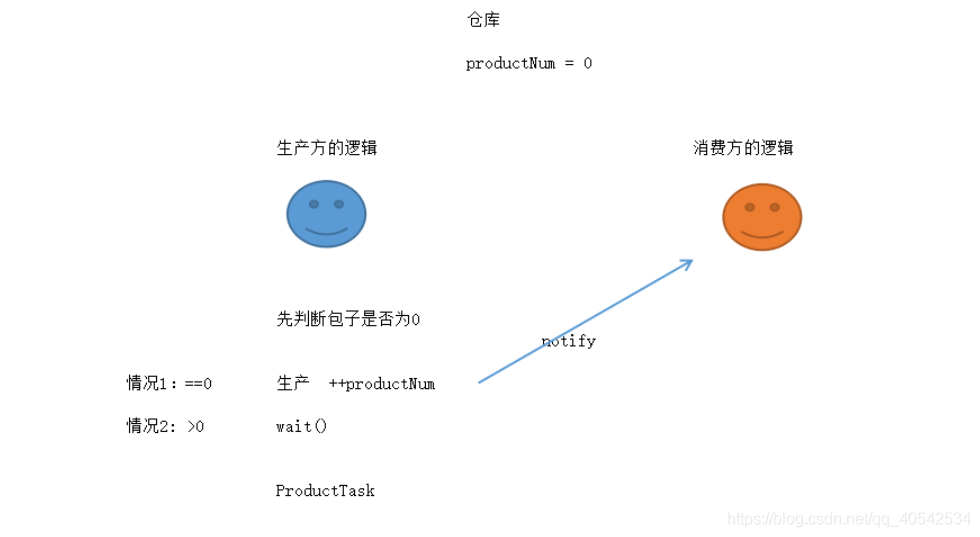
消费方逻辑图
代码实现
【注意】
notify、wait写在同步代码块中,并且使用同一个对象(共有对象:仓库)进行操作。
this.cangku.wait() 和this.wait() 前一个使用的是仓库对象 ,后一个使用的是当前任务对象(使用后一个会造成死锁)
//仓库 - 唯一(锁对象,任何对象都可以,用共有对象做锁对象)
class CangKu { //当作 锁对象
//定义一个变量体现数量
public int productNum = 0;
}
//生产方和消费方共用一个仓库
//生产方
class ProductTask implements Runnable {
private CangKu cangKu; //共用一个仓库不能自己创建,由外部传入
public ProductTask(CangKu cangKu) { //通过构造函数初始化
this.cangKu = cangKu;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//通知notify与等待wait必须写在同步代码块中
synchronized (this.cangKu) {//判断是否有锁可用,有就进入
if (this.cangKu.productNum == 0) {
++this.cangKu.productNum; //生产数目+1
System.out.println("生产了一个产品,当前产品数目:" + this.cangKu.productNum);
//通知消费者,必须用同一个锁对象,不然会造成死锁
this.cangKu.notify();
} else {
//当前还有存货不用生产,等待通知
try {
System.out.println("生产方等待中...");
this.cangKu.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}//end if
}//end synchronized 出房间释放锁
}
}
}
//消费方
class ConsumerTask implements Runnable {
private CangKu cangKu;
public ConsumerTask(CangKu cangKu) { //构造方法
this.cangKu = cangKu;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this.cangKu) {
//判断,仓库是否为0
if (this.cangKu.productNum == 0) {
try {
System.out.println("消费方等待中...");
this.cangKu.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
//有货可以吃
-- this.cangKu.productNum ;
System.out.println("消费了一个产品,当前产品数目:" + this.cangKu.productNum);
//通知生产方生产产品
this.cangKu.notify();
}//end if
}//end synchronized
}
}
}
public class Wait_Notify_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任务对象(生产方和消费方共用一个仓库)
CangKu cangKu = new CangKu();
ProductTask productTask = new ProductTask(cangKu);
ConsumerTask consumerTask = new ConsumerTask(cangKu);
//定义线程(用Executors线程池)
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.submit(productTask); //生产
pool.submit(consumerTask); //消费
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
