关于BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target)的使用
作者:自由的bug
BeanUtils.copyProperties
首先,使用的是org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
source 来源, target 目标
顾名思义, BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target); 第一个参数是需要拷贝的目标,第二个参数是拷贝后的目标。
因为这个方法有很多种情况,容易分不清,所以今天测了一下不同情况下的结果如何。
1.target里面有source里没有的属性
并且此属性有值时
2.target和source相同属性的值不一样时
下面是没有拷贝之前的值
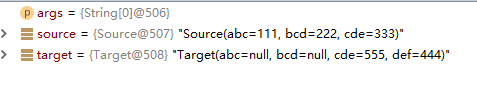
拷贝之后

可以看到,target里面不同值并没有清空,而是保留了下来。而相中属性本身存在的值被覆盖。
3.当target和source里面的属性名相同而类型不同时
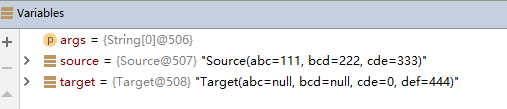
拷贝之后
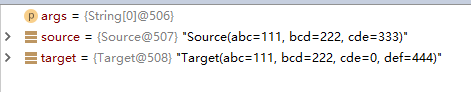
类型不同的属性无法拷贝。
Spring自带BeanUtils.copyProperties(Object source, Object target)之坑
在java服务化项目中,客户端和服务端之间交互经常用到BeanCopy,其目的是为了方便类之间的赋值,简单方便,但是经常会遇到复合对象赋值不上去的情况,究其原因是对BeanUtils.copyProperties(Object source, Object target)方法底层源码的不了解导致的,下面我来一步一步解释其原因。
先看一个例子:
@Data
public class BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopResult implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3251482519506276368L;
/**
* 排名列表
*/
private List<BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopInfo> topInfoList;
/**
* 我的排名信息
*/
private BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo myTopInfo;
@Override
public String toString() {
return ReflectionToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(this,
ToStringStyle.SHORT_PREFIX_STYLE);
}
}
@Data
public class MonthNewStoreTopInfoResponse implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4483822161951780674L;
/**
* 排名信息列表
*/
private List<MonthNewStoreTopInfo> topInfoList;
/**
* 我的排名信息
*/
private MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo myTopInfo;
@Override
public String toString() {
return ReflectionToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(this,
ToStringStyle.SHORT_PREFIX_STYLE);
}
}
当我们用BeanUtils.copyProperties(monthNewStoreTopResponse , bdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopResult )时会发现myTopInfo这个对象赋值为null,这是为什么呢?让我们来看一看源码:
//这是点进源码的第一段代码
public static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target) throws BeansException {
copyProperties(source, target, null, (String[]) null);
}
//这个才是copy的主代码
private static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target, @Nullable Class<?> editable,
@Nullable String... ignoreProperties) throws BeansException {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null");
Class<?> actualEditable = target.getClass();
if (editable != null) {
if (!editable.isInstance(target)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target class [" + target.getClass().getName() +
"] not assignable to Editable class [" + editable.getName() + "]");
}
actualEditable = editable;
}
PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);
List<String> ignoreList = (ignoreProperties != null ? Arrays.asList(ignoreProperties) : null);
for (PropertyDescriptor targetPd : targetPds) {
Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) {
PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName());
if (sourcePd != null) {
Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod();
if (readMethod != null &&
ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())) {
try {
if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
readMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
Object value = readMethod.invoke(source);
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
writeMethod.invoke(target, value);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new FatalBeanException(
"Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
}
其中ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())这个校验起到了关键的作用,我们再进入这段代码的源码看一眼,源码如下:
public static boolean isAssignable(Class<?> lhsType, Class<?> rhsType) {
Assert.notNull(lhsType, "Left-hand side type must not be null");
Assert.notNull(rhsType, "Right-hand side type must not be null");
if (lhsType.isAssignableFrom(rhsType)) {
return true;
}
if (lhsType.isPrimitive()) {
Class<?> resolvedPrimitive = primitiveWrapperTypeMap.get(rhsType);
if (lhsType == resolvedPrimitive) {
return true;
}
}
else {
Class<?> resolvedWrapper = primitiveTypeToWrapperMap.get(rhsType);
if (resolvedWrapper != null && lhsType.isAssignableFrom(resolvedWrapper)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
其中lhsType.isAssignableFrom(rhsType)判定此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口与指定的 Class 参数所表示的类或接口是否相同,或是否是其超类或超接口。
如果是则返回 true;否则返回 false。
如果该 Class表示一个基本类型,且指定的 Class 参数正是该 Class 对象,则该方法返回 true;否则返回 false。
意思其实就是说lhsType是不是rhsType的子类,如果是,则返回true,否则返回false。
这也就是说我们上面的例子MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo 对象和我们将要赋值的对象BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo 是同一个对象或者是它的子类才可以copy赋值成功,否则直接跳过返回了,不进行writeMethod.invoke(target, value)赋值;
哪为什么topInfoList却能赋值成功呢?
因为在lhsType.isAssignableFrom(rhsType)校验的时候是判断的是List类型的子类而不是List<BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo>中的BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo的子类。
所以我们在用Spring自带BeanUtils.copyProperties(Object source, Object target)进行对象copy时候需要特别注意,如果变量为非java自带的对象类型,则需要注意复合对象中的变量对象和被拷贝变量对象是同类型才可以。
如果MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo 和BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo不是同一个类型,可以通过先获得MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo 这个对象再和需要赋值的对象BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo进行变量级别的调用BeanUtils.copyProperties(MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo , BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo),最后再把复制后的结果set进结果集。
最好的解决办法是创建一个公共的model对象,替换MonthNewStoreTopMyInfo和BdmTeamMonthNewStoreTopMyInfo,这样也少创建了一个类,同时也减少了代码量,维护一份model,当有新增需求变化时,只需要修改公共的model对象即可,简单方便。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
