python实现马丁策略的实例详解
作者:达科索斯
这篇文章主要介绍了python实现马丁策略的实例详解,本文给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
马丁策略本来是一种赌博方法,但在投资界应用也很广泛,不过对于投资者来说马丁策略过于简单,所以本文将其改进并使得其在震荡市中获利,以下说明如何实现马丁策略。
策略
逢跌加仓,间隔由自己决定,每次加仓是当前仓位的一倍。
连续跌两次卖出,且卖出一半仓位。
如果爆仓则全仓卖出止损。
初始持仓设置为10%~25%,则可进行2到3次补仓。
初始化马丁策略类属性
def __init__(self,startcash, start, end): self.cash = startcash #初始化现金 self.hold = 0 #初始化持仓金额 self.holdper = self.hold /startcash #初始化仓位 self.log = [] #初始化日志 self.cost = 0 #成本价 self.stock_num = 0 #股票数量 self.starttime = start #起始时间 self.endtime = end #终止时间 self.quantlog = [] #交易量记录 self.earn = [] #总资产记录 self.num_log = [] self.droplog = [0]
为了记录每次买卖仓位的变化初始化了各种列表。
交易函数
首先导入需要的模块
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import tushare as ts import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def buy(self, currentprice, count):
self.cash -= currentprice*count
self.log.append('buy')
self.hold += currentprice*count
self.holdper = self.hold / (self.cash+ self.hold)
self.stock_num += count
self.cost = self.hold / self.stock_num
self.quantlog.append(count//100)
print('买入价:%.2f,手数:%d,现在成本价:%.2f,现在持仓:%.2f,现在筹码:%d' %(currentprice ,count//100, self.cost, self.holdper, self.stock_num//100))
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
self.droplog = [0]
def sell(self, currentprice, count):
self.cash += currentprice*count
self.stock_num -= count
self.log.append('sell')
self.hold = self.stock_num*self.cost
self.holdper = self.hold / (self.cash + self.hold)
#self.cost = self.hold / self.stock_num
print('卖出价:%.2f,手数:%d,现在成本价:%.2f,现在持仓:%.2f,现在筹码:%d' %(currentprice ,count//100, self.cost, self.holdper, self.stock_num//100))
self.quantlog.append(count//100)
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
def holdstock(self,currentprice):
self.log.append('hold')
#print('持有,现在仓位为:%.2f。现在成本:%.2f' %(self.holdper,self.cost))
self.quantlog.append(0)
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
持仓成本的计算方式是利用总持仓金额除以总手数,卖出时不改变持仓成本。持有则是不做任何操作只记录日志
数据接口
def get_stock(self, code): df=ts.get_k_data(code,autype='qfq',start= self.starttime ,end= self.endtime) df.index=pd.to_datetime(df.date) df=df[['open','high','low','close','volume']] return df
数据接口使用tushare,也可使用pro接口,到官网注册领取token。
token = '输入你的token' pro = ts.pro_api() ts.set_token(token) def get_stock_pro(self, code): code = code + '.SH' df = pro.daily(ts_code= code, start_date = self.starttime, end_date= self.endtime) return df
数据结构:

回测函数
def startback(self, data, everyChange, accDropday):
"""
回测函数
"""
for i in range(len(data)):
if i < 1:
continue
if i < accDropday:
drop = backtesting.accumulateVar(everyChange, i, i)
#print('现在累计涨跌幅度为:%.2f'%(drop))
self.martin(data[i], data[i-1], drop, everyChange,i)
elif i < len(data)-2:
drop = backtesting.accumulateVar(everyChange, i, accDropday)
#print('现在累计涨跌幅度为:%.2f'%(drop))
self.martin(data[i],data[i-1], drop, everyChange,i)
else:
if self.stock_num > 0:
self.sell(data[-1],self.stock_num)
else: self.holdstock(data[i])
因为要计算每日涨跌幅,要计算差分,所以第一天的数据不能计算在for循环中跳过,accDropday是累计跌幅的最大计算天数,用来控制入场,当累计跌幅大于某个数值且仓位为0%时可再次入场。以下是入场函数:
def enter(self, currentprice,ex_price,accuDrop):
if accuDrop < -0.01:#and ex_price > currentprice:
count = (self.cash+self.hold) *0.24 // currentprice //100 * 100
print('再次入场')
self.buy(currentprice, count)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
入场仓位选择0.24则可进行两次抄底,如果抄底间隔为7%可承受最大跌幅为14%。
策略函数
def martin(self, currentprice, ex_price, accuDrop,everyChange,i):
diff = (ex_price - currentprice)/ex_price
self.droplog.append(diff)
if sum(self.droplog) <= 0:
self.droplog = [0]
if self.stock_num//100 > 1:
if sum(self.droplog) >= 0.04:
if self.holdper*2 < 0.24:
count =(self.cash+self.hold) *(0.25-self.holdper) // currentprice //100 * 100
self.buy(currentprice, count)
elif self.holdper*2 < 1 and (self.hold/currentprice)//100 *100 > 0 and backtesting.computeCon(self.log) < 5:
self.buy(currentprice, (self.hold/currentprice)//100 *100)
else: self.sell(currentprice, self.stock_num//100 *100);print('及时止损')
elif (everyChange[i-2] < 0 and everyChange[i-1] <0 and self.cost < currentprice):# or (everyChange[i-1] < -0.04 and self.cost < currentprice):
if (self.stock_num > 0) and ((self.stock_num*(1/2)//100*100) > 0):
self.sell(currentprice, self.stock_num*(1/2)//100*100 )
#print("现在累计涨跌幅为: %.3f" %(accuDrop))
elif self.stock_num == 100: self.sell(currentprice, 100)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
else: self.enter(currentprice,ex_price,accuDrop)
首先构建了droplog专门用于计算累计涨跌幅,当其大于0时重置为0,每次购买后也将其重置为0。当跌幅大于0.04则买入,一下为流程图(因为作图软件Visustin为试用版所以有水印,两个图可以结合来看):

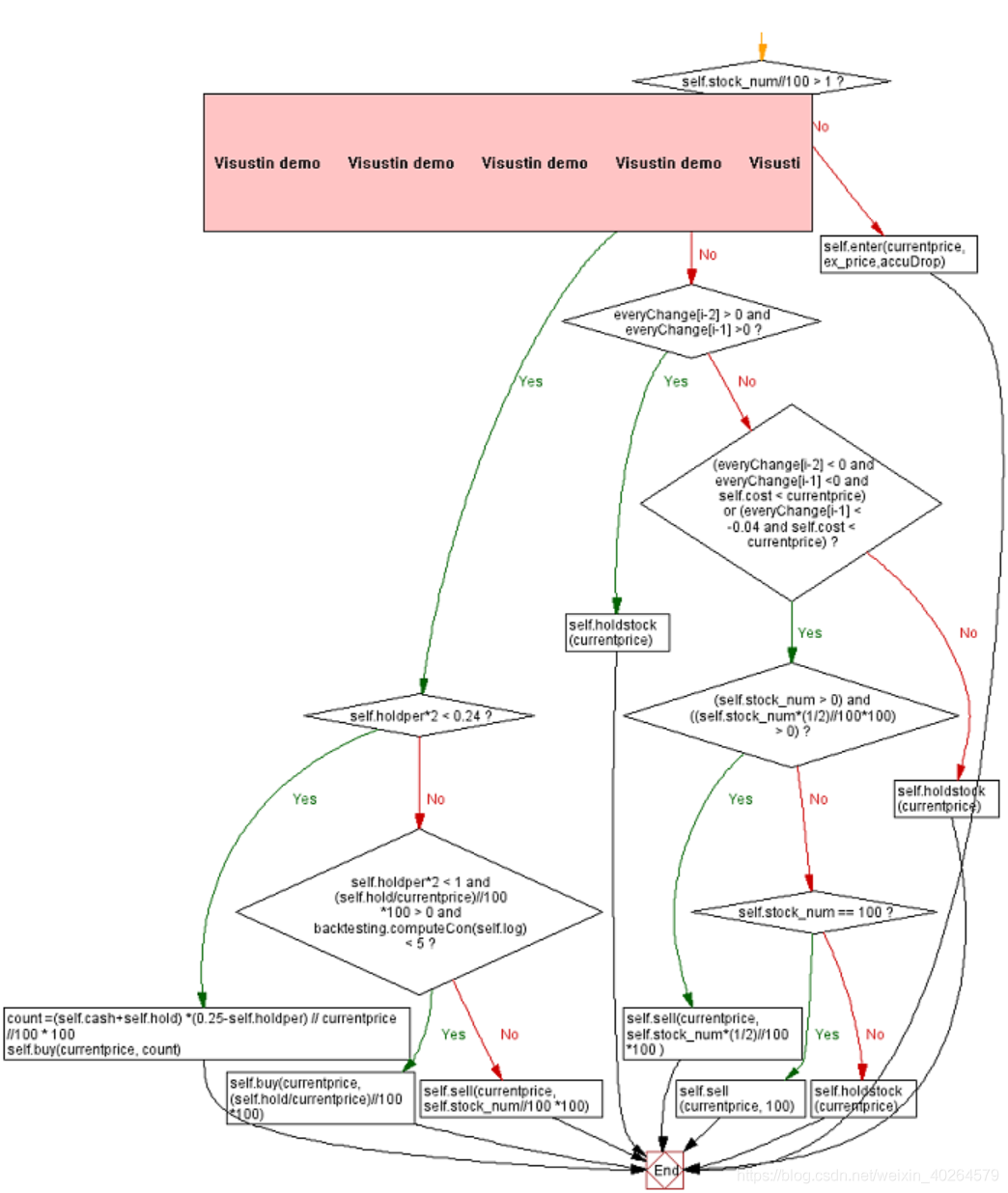
此策略函数可以改成其他策略甚至是反马丁,因为交易函数可以通用。
作图和输出结果
buylog = pd.Series(broker.log)
close = data.copy()
buy = np.zeros(len(close))
sell = np.zeros(len(close))
for i in range(len(buylog)):
if buylog[i] == 'buy':
buy[i] = close[i]
elif buylog[i] == 'sell':
sell[i] = close[i]
buy = pd.Series(buy)
sell = pd.Series(sell)
buy.index = close.index
sell.index = close.index
quantlog = pd.Series(broker.quantlog)
quantlog.index = close.index
earn = pd.Series(broker.earn)
earn.index = close.index
buy = buy.loc[buy > 0]
sell = sell.loc[sell>0]
plt.plot(close)
plt.scatter(buy.index,buy,label = 'buy')
plt.scatter(sell.index,sell, label = 'sell')
plt.title('马丁策略')
plt.legend()
#画图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3,figsize=(15,8))
ax1.plot(close)
ax1.scatter(buy.index,buy,label = 'buy',color = 'red')
ax1.scatter(sell.index,sell, label = 'sell',color = 'green')
ax1.set_ylabel('Price')
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.legend()
ax1.xaxis_date()
ax2.bar(quantlog.index, quantlog, width = 5)
ax2.set_ylabel('Volume')
ax2.xaxis_date()
ax2.grid(True)
ax3.xaxis_date()
ax3.plot(earn)
ax3.set_ylabel('总资产包括浮盈')
plt.show()


交易日志
到此这篇关于python实现马丁策略的实例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python马丁策略内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
