springboot整合sentinel的方法教程
作者:DeyouKong
这篇文章主要介绍了springboot整合sentinel的方法,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
用到的依赖及配置
<!-- Sentinel核心服务 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Sentinel核心服务 -->
<!-- Sentinel本地应用接入控制台 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Sentinel本地应用接入控制台 -->
<!-- Sentinel提供注解无侵入定义资源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-annotation-aspectj</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Sentinel提供注解无侵入定义资源 -->
配置
spring:
application:
name: sentinel
1、搭建项目
1.1、 Maven 依赖
<!-- 版本与控制台保持一致即可 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 版本与控制台保持一致即可 -->
1.2、Controller 层
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/add")
public String create(){
try {
// 设置一个资源名称为 Hello
Entry ignored = SphU.entry("AddUser");
System.out.println("新建一个用户");
return "新建一个用户";
} catch (BlockException e) {
System.out.println("系统繁忙,请稍后");
e.printStackTrace();
return "系统繁忙,请稍后";
}
}
/**
* 使用代码编写流控规则,项目中不推荐使用,这是硬编码方式
*
* 注解 @PostConstruct 的含义是:本类构造方法执行结束后执行
*/
@PostConstruct
public void initFlowRule() {
/* 1.创建存放限流规则的集合 */
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
/* 2.创建限流规则 */
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
/* 定义资源,表示 Sentinel 会对哪个资源生效 */
rule.setResource("AddUser");
/* 定义限流的类型(此处使用 QPS 作为限流类型) */
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
/* 定义 QPS 每秒通过的请求数 */
rule.setCount(2);
/* 3.将限流规则存放到集合中 */
rules.add(rule);
/* 4.加载限流规则 */
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
@GetMapping("/edit")
public String edit(){
return "编辑一个用户";
}
}
2、搭建 Sentinel 控制台
下载 Sentinel 控制台 jar 包:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases
启动 Sentinel 控制台,如下图所示
java -Dserver.port=9000 -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.6.jar

访问 Sentinel 控制台:http://127.0.0.1:9000/

账号/密码:sentinel/sentinel
3、SpringBoot 整合 Sentinel
3.1、Maven 依赖
<!-- Sentinel本地应用接入控制台,版本与控制台保持一致即可 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Sentinel本地应用接入控制台,版本与控制台保持一致即可 -->
3.2、在 idea 中设置本地应用的 JVM 启动参数
-Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=127.0.0.1:9000 Sentinel控制台的地址和端口号 -Dproject.name=sentinel 本地应用在控制台中的名称

3.3. 运行测试
第一次查看控制台,需要先访问一次被限流控制的接口,否则控制台中没有东西

快速在页面刷新,就会出现限流后的返回提示语

3.4. 采用控制台设置流控规则
3.4.1. 修改上述 UserController 类
删除使用代码编写的流控规则,项目中不推荐使用,这是硬编码方式
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/add")
public String create(){
try {
// 设置一个资源名称为 Hello
Entry ignored = SphU.entry("AddUser");
System.out.println("新建一个用户");
return "新建一个用户";
} catch (BlockException e) {
System.out.println("系统繁忙,请稍后");
e.printStackTrace();
return "系统繁忙,请稍后";
}
}
@GetMapping("/edit")
public String edit(){
return "编辑一个用户";
}
}
3.4.2. 启动上述项目,如下操作

3.4.3、测试
- 正常请求
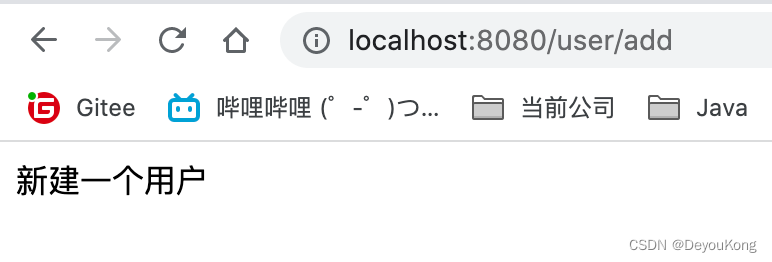
- 快速刷新页面

4、注解方式无侵入定义资源(推荐使用)
Sentinel 支持通过 @SentinelResource 注解来定义资源,并配置 blockHandler 函数来进行限流之后的处理
4.1、Maven 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-annotation-aspectj</artifactId> <version>1.8.0</version> </dependency>
4.2、AspectJ 的配置类
@Configuration
public class SentinelAspectConfiguration {
@Bean
public SentinelResourceAspect sentinelResourceAspect(){
return new SentinelResourceAspect();
}
}
4.3、Controller 层
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
// value:资源名称 blockHandler:设置限流或降级处理的类
@SentinelResource(value = "AddUser", blockHandler = "exceptionHandler")
@GetMapping("/add")
public String create(){
return "新增一个用户";
}
// 限流处理类
public String exceptionHandler(@NotNull BlockException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "系统繁忙,请稍后再试";
}
}
5、SpringBoot 整合 Sentinel 实现限流熔断的其他方式
实现方式有以下几种
- 抛出异常的方式
- 返回布尔值的方式
- 异步调用支持
- 注解方式(推荐,见目录4)
5.1、抛出异常的方式定义资源示例
使用这种方式当资源发生限流后会抛出 BlockException 异常。这个时候可以捕获异常,进行限流之后的逻辑处理,关键代码如下
@RequestMapping(path = {"/hello"}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello() {
try {
Entry ignored = SphU.entry("Hello");
System.out.println("Hello Sentinel");
return "Hello Sentinel";
} catch (BlockException e) {
System.out.println("系统繁忙,请稍后");
e.printStackTrace();
return "系统繁忙,请稍后";
}
}
5.2、返回布尔值的方式定义资源示例
使用的 API 为 SphO,限流后返回的值为 boolean 类型。注意:SphO.entry 必须和 SphO.exit 成对出现 否则会报错
@GetMapping("/boolean")
public boolean returnBoolean() {
// 使用限流规则
if (SphO.entry("Sentinel-boolean")){
try {
System.out.println("Hello Sentinel");
return true;
}finally {
// 限流的出口
SphO.exit();
}
} else {
// 限流后进行的操作
System.out.println("系统繁忙,请稍后再试");
return false;
}
}
5.3、异步调用支持示例
在启动类中添加 @EnableAsync,表示 SpringBoot 项目开启异步调用支持
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class SentinelQuickStartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SentinelQuickStartApplication.class, args);
}
}
5.3.1、创建 AsyncService 编写异步调用的方法
@Service
public class AsyncService {
// Async表示方法为异步调用
@Async
public void hello(){
System.out.println("异步调用开始======");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("异步调用结束=====");
}
}
5.3.2、Controller层
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/async")
public void async() {
// 1.进行限流控制
AsyncEntry asyncEntry = null;
try {
asyncEntry = SphU.asyncEntry("Sentinel_Async"); // 限流入口
asyncService.hello(); // 异步调用方法
System.out.println("异步测试");
} catch (BlockException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("系统繁忙请稍后再试");
} finally {
if (asyncEntry != null) {
asyncEntry.exit(); // 限流出口
}
}
}总结
到此这篇关于springboot整合sentinel的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot整合sentinel内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- Sentinel原理与SpringBoot整合实战案例讲解
- Springboot 中使用Sentinel的详细步骤
- springboot整合sentinel接口熔断的实现示例
- 在SpringBoot项目中使用Spring Cloud Sentinel实现流量控制
- springboot 整合sentinel的示例代码
- 详解Springboot集成sentinel实现接口限流入门
- SpringBoot2.0+阿里巴巴Sentinel动态限流实战(附源码)
- SpringBoot基于Sentinel在服务上实现接口限流
- 详解SpringBoot Redis自适应配置(Cluster Standalone Sentinel)
- SpringBoot整合Sentinel启动失败及运行时常见错误总结


